Session Information
Date: Wednesday, November 15, 2023
Title: Abstracts: Vasculitis – Non-ANCA-Associated & Related Disorders III: Innovation
Session Type: Abstract Session
Session Time: 11:00AM-12:30PM
Background/Purpose: Giant cell arteritis (GCA) is a vasculitis in which Th17 cells have been identified in excess in lesions and in the blood of patients. While the efficacy of secukinumab has recently been reported in a phase II study, the role of interleukin-17 (IL-17) in the pathophysiology of GCA is not clearly understood. The aim of this study was to investigate the role of IL-17 in the pathogenesis of GCA.
Methods: Vascular myofibroblasts (MFs) were obtained from cultures of healthy arteries in MATRIGEL as previously described. After 3-6 doubling passages, MFs were treated with IL-17 (50 ng/mL), interferon-gamma (IFN-γ, 50 ng/mL), secukinumab (20 µg/mL) or the association of IL-17 and IFN- γ or IL-17 and secukinumab for 24 hours. mRNA expression was analyzed by RNA sequencing and RT-PCR. Proliferation was analyzed by impedancemetry and migration was assessed by scratch-wound healing assays. Fresh fragments of temporal artery biopsies (TAB) were prospectively collected, cut in 1-mm sections and cultured for 5 days in MATRIGEL®, as previously described, in the presence of IL-17, secukinumab or IgG control. Then, arterial sections were collected, homogenized and analyzed by RT-PCR.
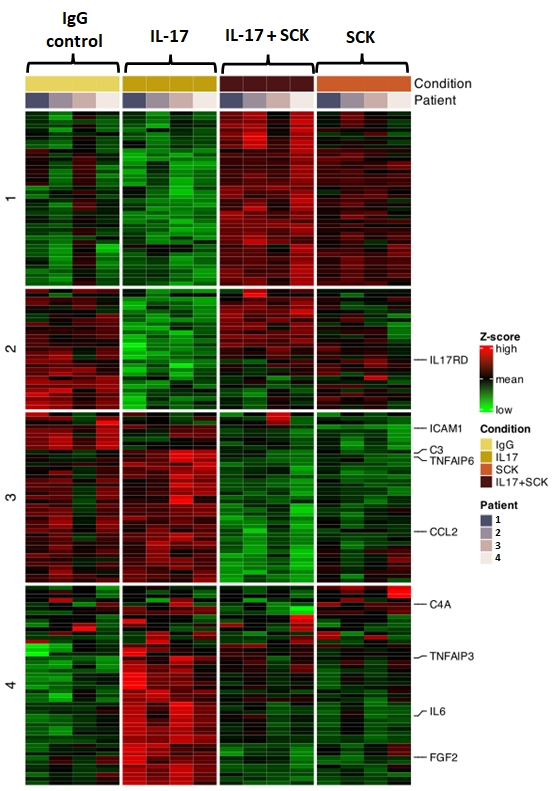
Results: The transcriptome of MFs was dramatically modified when IL-17 was added to the culture, with increased expression of genes involved in vascular inflammation (CCL2, IL6), NFkB pathway activation (TNFAIP6, TNFAIP3), leukocyte adhesion (ICAM1), complement activation (C3, C4A) and MF proliferation (FGF2) (Figure 1). These changes were reversed in the presence of secukinumab (Figure 1).
RT-PCR analysis of 8 MF lines showed that in the presence of IL-17, the mRNA expression of the genes encoding for IL1-β, IL-6, IL-12p35, VEGF-A, GM-CSF, CCL2 and CCL20 was increased (P < 0.01). There was no significant effect on the mRNA expression of IL-23p19, IL-12p40, collagen alpha chains 1 and 3, PDGFA, PDGFB, CXCL9 or CXCL10. The addition of IFN-γ to the culture increased the expression level of chains of the IL-17 receptor (IL17RA and IL17RC), creating a synergistic effect in the presence of IFN-γ and IL-17, thus resulting in a sharp rise in the expression of genes encoding for IL-1β, IL-6, IL-12p35, GM-CSF, VEGF-A, CCL2 and CCL20.
The study of MF migration and proliferation revealed that IL-17 had no direct effect on these MF functions.
Ex-vivo cultures of TAB revealed that treatment with IL-17 increased the expression of mRNA encoding for IL-6, VEGF-A, GM-CSF, CCL2 and CCL20 in negative TAB (n=8; P< 0.05) whereas treatment with secukinumab decreased the expression of mRNA encoding for IL-6 and CCL20 in positive TAB (n=12; P < 0.05).
Conclusion: IL-17 increases vascular inflammation and has a direct effect on MF synergistically with IFN-γ, which increases the production of pro-inflammatory cytokines (IL-1B, IL-6, GM-CSF), chemokines leading to the recruitment of T cells (CCL20) and monocytes (CCL2), and growth factors involved in neoangiogenesis (VEGF). In contrast, IL-17 does not appear to have a direct effect on MF proliferation and migration. These data explain why blocking the IL-17 signaling pathway could be useful in the treatment of GCA.
To cite this abstract in AMA style:
Greigert h, ramon a, Richard c, cladière c, CIUDAD M, creuzot-garcher c, martin l, AUDIA S, boidot r, Bonnotte B, Samson M. Study of the Role of interleukin-17 in Giant Cell Arteritis [abstract]. Arthritis Rheumatol. 2023; 75 (suppl 9). https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/study-of-the-role-of-interleukin-17-in-giant-cell-arteritis/. Accessed .« Back to ACR Convergence 2023
ACR Meeting Abstracts - https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/study-of-the-role-of-interleukin-17-in-giant-cell-arteritis/