Session Information
Session Type: Poster Session A
Session Time: 10:30AM-12:30PM
Background/Purpose: Radiomics involves the high-throughput extraction of quantitative data from medical imaging. This study aimed to develop a radiomic analysis pipeline applied to hand radiographs and evaluate its ability to classify joints according to the Kellgren-Lawrence (KL) score, a grading system for hand osteoarthritis severity. The goal was to assess whether radiomic features could enable automated and standardized KL classification, complementing expert visual assessment.
Methods: The study was based on 436 hand radiographs from the DIGICOD cohort, a prospective study of patients with hand osteoarthritis according to American College of Rheumatology criteria. After excluding 30 radiographs not found in PACS and 25 with artifacts or surgical hardware, 381 radiographs were analyzed, representing 10,531 joints (trapeziometacarpal [TMC], metacarpophalangeal [MCP], proximal interphalangeal [PIP], and distal interphalangeal [DIP] joints). KL grading was performed by an experienced radiologist at baseline.Radiomic analysis involved several steps: (1) joint segmentation using an algorithm developed for the study. Manual segmentations from 20 patients served as ground truth to train a U-Net model with iterative training and correction; (2) extraction of 179 radiomic features (4 shape, 45 intensity histogram, and 130 texture features); (3) exclusion of texture features with relative variation < 0.05 after pixel shuffling (deemed non-informative); (4) dimensionality reduction by removing highly correlated features (Spearman > 0.9), resulting in 86 features. A random forest model with stratified cross-validation selected the 20 most relevant features for predicting KL scores. Classification performance was evaluated by comparing predicted vs. expert-assigned KL scores, using area under the curve (AUC), accuracy, and balanced accuracy. Accuracy reflects the proportion of correctly classified joints, while balanced accuracy adjusts for class imbalance.
Results: The radiomic model achieved good classification performance for KL grading. Differentiation between affected joints (KL 2–4) and normal or borderline joints (KL 0–1) yielded an AUC of 0.81 and accuracy of 0.74. Discrimination between non/mildly affected (KL 0–2) and severely affected joints (KL 3–4) achieved an AUC of 0.83 and accuracy of 0.68. Considering all KL classes, the overall AUC was 0.76, with balanced accuracy of 0.37. Joint-type specific analysis (affected vs. normal/borderline) showed lower performance, with AUCs of 0.67, 0.71, and 0.49 and balanced accuracies of 0.34, 0.35, and 0.39 for MCP, PIP, and DIP joints, respectively. A downsampling strategy was applied to mitigate class imbalance, slightly improving overall classification, especially for the most frequent classes.
Conclusion: This study is the first to evaluate radiomic analysis in hand osteoarthritis. Radiomics enabled, to some extent, automated reproduction of KL classification. However, performance varied depending on joint type and severity. While this approach shows promise as a complementary tool for assessing hand osteoarthritis, external validation on an independent cohort is required before clinical application.
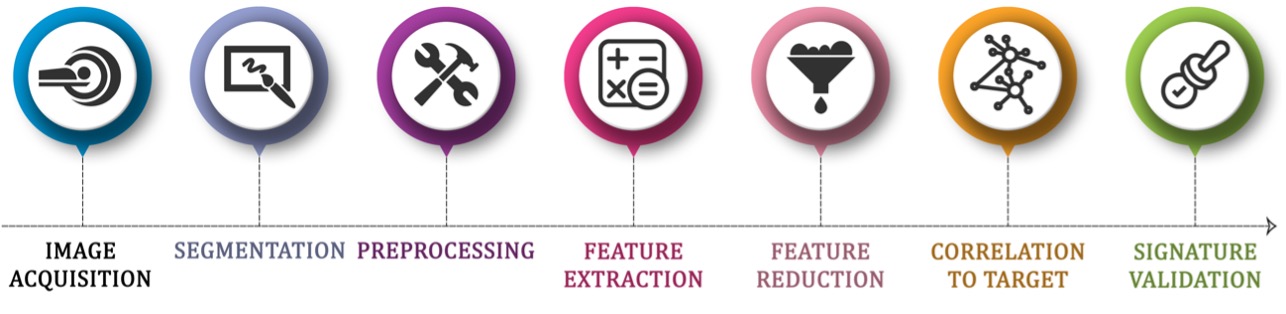 Overview of the radiomic pipeline used in this study, from image acquisition and joint segmentation to feature extraction and classification modeling. The pipeline was designed to automate Kellgren-Lawrence scoring from standard hand radiographs in patients with hand osteoarthritis (DIGICOD cohort).
Overview of the radiomic pipeline used in this study, from image acquisition and joint segmentation to feature extraction and classification modeling. The pipeline was designed to automate Kellgren-Lawrence scoring from standard hand radiographs in patients with hand osteoarthritis (DIGICOD cohort).
.jpg) Comparison Between Manual and Automated Segmentation of Hand Joints.
Comparison Between Manual and Automated Segmentation of Hand Joints.
Comparison between manual segmentation by the radiologist (in orange) and automated segmentation using a U-Net-based model (in light blue). Concordant areas between both segmentations are shown in dark blue, indicating high overlap and supporting reliable feature extraction for radiomic modeling.
.jpg) Confusion Matrix for Binary Classification of Joint Osteoarthritis Severity.
Confusion Matrix for Binary Classification of Joint Osteoarthritis Severity.
Confusion matrix illustrating the performance of the radiomic model in predicting affected (KL 2–4) versus non-affected (KL 0–1) joints.
To cite this abstract in AMA style:
Perronne L, JEREMIE S, Decoux A, Duron L, de Margerie C, Dougados M, Saarakala S, Maheu E, Crema M, Miquel A, BERENBAUM F, Arnoux A, Laredo J, Fournier L. Structural Severity Assessment of Hand Osteoarthritis Using Radiomic Analysis: Correlation with the Kellgren-Lawrence Score – Results from the DIGICOD Cohort [abstract]. Arthritis Rheumatol. 2025; 77 (suppl 9). https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/structural-severity-assessment-of-hand-osteoarthritis-using-radiomic-analysis-correlation-with-the-kellgren-lawrence-score-results-from-the-digicod-cohort/. Accessed .« Back to ACR Convergence 2025
ACR Meeting Abstracts - https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/structural-severity-assessment-of-hand-osteoarthritis-using-radiomic-analysis-correlation-with-the-kellgren-lawrence-score-results-from-the-digicod-cohort/
