Session Information
Session Type: Poster Session B
Session Time: 9:00AM-10:30AM
Background/Purpose: Beta-2-Glycoprotein I (B2GPI) is a serum protein of approximately 50kDa and is the main autoantigen of Antiphospholipid syndrome (APS). Antibodies to B2GPI (aB2GPI) are diagnostic of APS and are strongly associated with clinical events including thrombosis. B2GPI can adopt one of two structures, a circular closed structure or a linear open structure. It is proposed that these structures have different functions and thus alter disease pathogenesis. The structure of B2GPI in APS patients is poorly characterized. Here we present data comparing structure and antibody-binding properties of b2GPI from patients with APS and healthy controls (HC), delineating the structural differences in B2GPI within APS patients compared to healthy controls and how that affects binding of autoantibodies.
Methods: B2GPI was purified from APS and HC plasma by affinity chromatography and PEG precipitation avoiding acid steps. Samples were analysed by ion mobility-mass spectrometry on a Waters SELECT SERIES cIMS to assess structure, and increasing voltage was applied to investigate structural dynamics. Data were processed using MassLynx v4.2 (Waters). Antibody activity was tested by inhibition ELISA, briefly: serum from APS patients was incubated in the presence or absence of either HC or APS B2GPI and then used in a B2GPI ELISA to assess the fluid phase inhibition of anti-B2GPI antibodies.
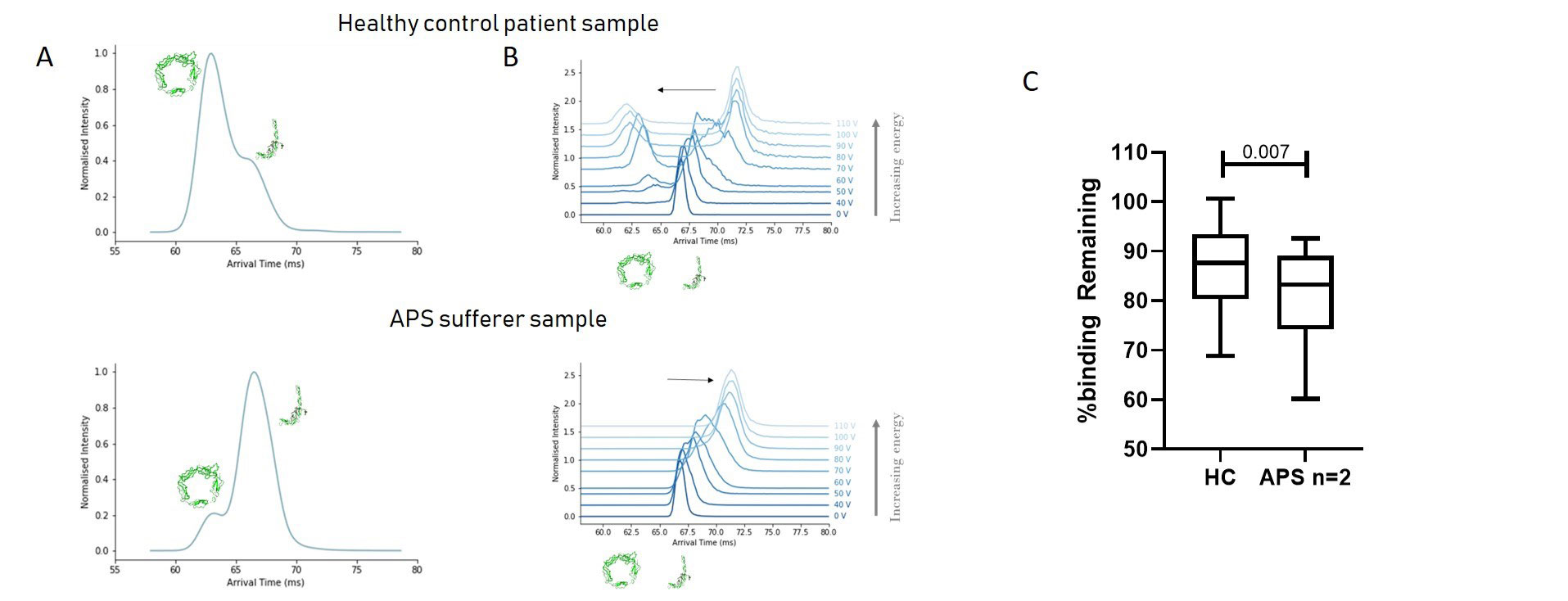
Results: Similar glycoisoforms of B2GPI were seen in HC and APS B2GPI. A different distribution of the two known structures was seen, with APS patients displaying more linear B2GPI compared to healthy controls at the same charge state. When voltage was applied to the linear form of B2GPI from HC, the protein was capable of adopting a more compact form again, however this was not possible for APS B2GPI. In an inhibition ELISA APS B2GPI from high aB2GPI positive patients (n=2) inhibited binding of anti-B2GPI antibodies to B2GPI significantly more than HC (19.1%vs13.5%, p=0.007).
Conclusion: Structural differences exist in APS patients compared to controls, with more linear B2GPI in patients and this may be explained by differences in the structural dynamics. Furthermore these structural differences are associated with better antibody binding which may suggest that this structural difference plays a role in autoantibody production in APS.
Panel A shows the distribution of B2GPI structures in healthy controls (top) and APS patients (bottom) at a single charge state. As can be seen the peaks are reversed with increased amounts of linear B2GPI shown in the APS samples (peak arrival ~67.5ms) and the inverse for the circular form (arrival time ~ 62.5ms). In panel B, when the linear form from healthy controls (Top) was then subjected to increased voltage, as can be seen the linear peak (~67.5ms) can form another peak equivalent to the circular form (~62.5ms) before progression to a superlinear form. In contrast, APS patients (Bottom) are not capable of this and progress to a superlinear form. Finally, Panel C shows blinding remaining in an anti-B2GPI ELISA using 10 APS patients serum challenged with either APS purified B2GPI (n=2) or HC B2GPI (Pooled). As can be seen APS B2GPI inhibits significantly better than healthy control equivalent.
To cite this abstract in AMA style:
Britt H, Bradford H, Spiteri V, Rahman A, Giles I, Delcea M, Dalby P, Thalassinos K, McDonnell T. Structural Differences Exist in Beta-2-Glycoprotein I from APS Patients Compared to Healthy Controls [abstract]. Arthritis Rheumatol. 2022; 74 (suppl 9). https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/structural-differences-exist-in-beta-2-glycoprotein-i-from-aps-patients-compared-to-healthy-controls/. Accessed .« Back to ACR Convergence 2022
ACR Meeting Abstracts - https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/structural-differences-exist-in-beta-2-glycoprotein-i-from-aps-patients-compared-to-healthy-controls/