Session Information
Session Type: ACR Concurrent Abstract Session
Session Time: 11:00AM-12:30PM
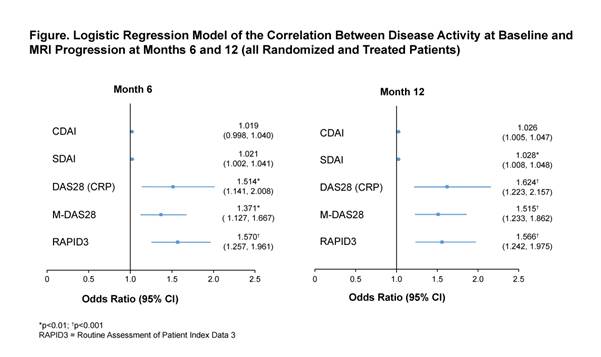
Conclusion: In this post hoc analysis of MTX-naïve, ACPA-positive patients with early RA, DAS28 (CRP), M-DAS28 and RAPID3 were significant predictors of structural damage progression at Months 6 and 12, as measured using MRI, with RAPID3 showing the highest predictive value for MRI progression.
| |
||
| |
|
|
| |
|
|
| |
|
|
| |
|
|
| |
|
|
| |
|
|
| |
||
To cite this abstract in AMA style:
Keystone EC, Ahmad H, Yazici Y, Liu X, Bergman M. Structural Damage in Patients with Very Early RA Is Predicted with Clinical Measures of Baseline Disease Activity: DAS28 (CRP), SDAI, M-DAS28 and RAPID3 but Not CDAI [abstract]. Arthritis Rheumatol. 2017; 69 (suppl 10). https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/structural-damage-in-patients-with-very-early-ra-is-predicted-with-clinical-measures-of-baseline-disease-activity-das28-crp-sdai-m-das28-and-rapid3-but-not-cdai/. Accessed .« Back to 2017 ACR/ARHP Annual Meeting
ACR Meeting Abstracts - https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/structural-damage-in-patients-with-very-early-ra-is-predicted-with-clinical-measures-of-baseline-disease-activity-das28-crp-sdai-m-das28-and-rapid3-but-not-cdai/
