Session Information
Title: Rheumatoid Arthritis - Clinical Aspects (ACR): Comorbidities, Treatment Outcomes and Mortality
Session Type: Abstract Submissions (ACR)
Lymphoproliferative disorder (LPD) is a rare complication with rheumatoid arthritis (RA) patients treated with methotrexate (MTX). It is known that not little proportion of these LPD shows spontaneous regression by MTX withdrawal without chemotherapy. This study is to identify factors by which the spontaneous regression of MTX-LPD can be predicted.
All 32 RA patients regarded as being complicated with MTX-LPD
Five patients were given chemotherapy after the diagnosis of MTX-LPD, so we analyzed the remaining 27 patients in this study. Baseline characteristics of 27 patients were following: median age, 65 years old, female, 82%, duration of MTX administration, 7.5 years, RA duration, 11.9 years. In these patients, MTX was withdrawn without any additional treatment, and LPD was assessed during the follow up (median 5 weeks, range: 3-12 weeks). Seventeen patients were pathologically diagnosed as LPD and 10 were highly suspected of LPD with imaging tests. Spontaneous regression observed in 19 patients with 3 achieving complete remission (CR) and 16 partial remission (PR). Three patients were stable disease (SD) and 5 were progressive disease (PD).
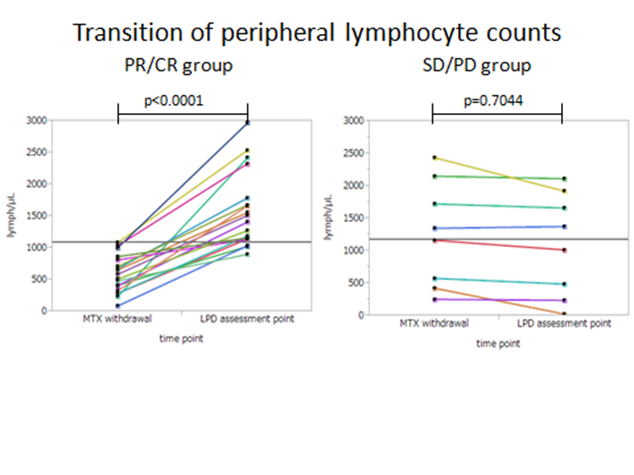
We focused on the time course changes in absolute number of lymphocytes at the MTX withdrawal and at the time of follow-up assessment. In CR/PR group, the number of lymphocytes were decreased at the MTX withdrawal (median 510/µL, range:87-1045), but restored at the time of follow-up assessment (median 1409/µL, 900-2969). In SD/PD group, the patients could be classified into 2 groups; 3 of low lymphocytes (median 426/µL, 255-578) and 5 of high lymphocytes (median 1725/µL, 1165-2438). However in both groups the lymphocyte counts did not change after follow up duration. Therefore, the ratio between the number of lymphocytes at the MTX withdrawal and at the time of follow-up assessment was significantly higher in PR/CR group than SD/PD group (3.73 vs 0.96, p=0.02). There was no significant difference of follow up duration between 2 groups (median 4 vs 5.5 weeks, p=0.46).
Same tendency were observed in histologically diagnosed 17 patients. The outcomes were 2 CR, 11 PR, and 4 PD, and lymphocytes ratios were 4.07 in CR/PR group and 0.65 in SD/PD group (p=0.04).
Of 17 histologically defined LPDs, 15 had information on Epstein Barr virus encoded small RNA (EBER). EBER positivity was relatively higher (9/11, 81%) in PR/CR group and lower (2/4,50%) in SD/PD group, but difference was not statistically significant (p=0.261).
Careful observation of the changes in the number of lymphocytes may predict the LPD spontaneous regression after the withdrawal of MTX.
Disclosure:
S. Saito,
None;
Y. Kaneko,
None;
K. Suzuki,
None;
M. Tokuhira,
None;
T. Takeuchi,
Abbott Japan Co., Ltd., Astellas Pharma, Bristol–Myers K.K., Chugai Pharmaceutical Co, Ltd., Daiichi Sankyo Co., Ltd., Eisai Co., Ltd., Janssen Pharmaceutical K.K., Mitsubishi Tanabe Pharma Co., Pfizer Japan Inc., Sanofi–Aventis K.K., Santen Pharmaceutica,
2,
Abbott Japan Co., Ltd., Bristol–Myers K.K., Chugai Pharmaceutical Co,. Ltd., Eisai Co., Ltd., Janssen Pharmaceutical K.K., Mitsubishi Tanabe Pharma Co., Pfizer Japan Inc., Takeda Pharmaceutical Co., Ltd., Astellas Pharma, Diaichi Sankyo Co.,Ltd.,
8,
Astra Zeneca K.K., Eli Lilly Japan K.K., Novartis Pharma K.K., Mitsubishi Tanabe Pharma Co., Asahi Kasei Medical K.K., Abbivie GK, Daiichi Sankyo Co.,Ltd.,
5.
« Back to 2014 ACR/ARHP Annual Meeting
ACR Meeting Abstracts - https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/spontaneous-regression-of-methotrexate-mtx-related-lymphoproliferative-disorder-correlates-with-lymphocyte-restoration-after-mtx-withdrawal/