Session Information
Date: Saturday, November 16, 2024
Title: Imaging of Rheumatic Diseases Poster I: Inflammatory Arthritis
Session Type: Poster Session A
Session Time: 10:30AM-12:30PM
Background/Purpose: The aim of this study is to evaluate the prevalence and severity of spinal structural lesions on radiograph versus opportunistic thoraco-abdomino-pelvic CT (TAP CT) in ankylosing spondylitis (AS).
Methods: This
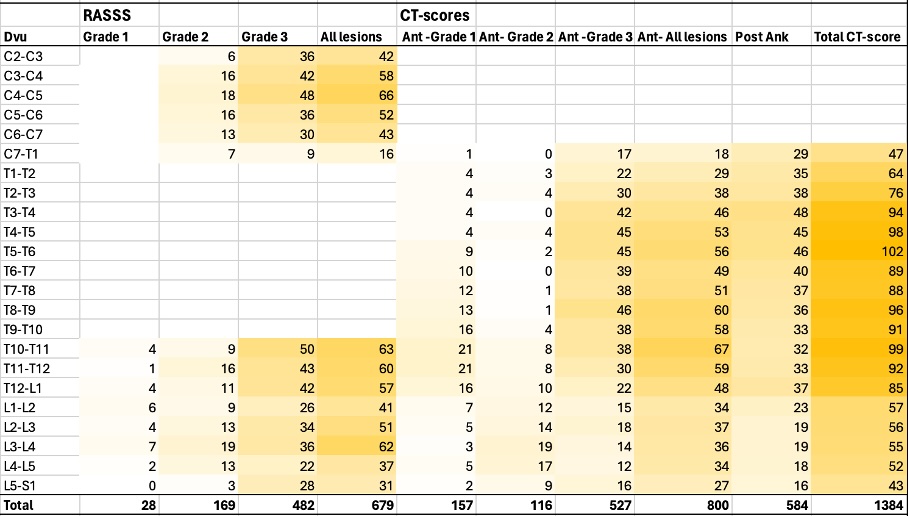
monocentric restrospective study included AS patients responding to modified New York criteria for radiographic sacroiliitis. Patients were required to have undergone spine x-ray and a TAP CT within a delay of 12 months. On TAP CT, the 36 anterior vertebra corner from C7 to S1 were graded for erosion/squaring (grade 1), syndesmophytes (grade 2) and bone bridge (grade 3). The anterior CT score ranged from 0 to 108 (sum of the grades). The posterior segment evaluated facet ankylosis as present (grade 3) or absent (grade 0). The posterior CT score ranged from 0 to 108 (sum of the grades). The total CT-score (ant+post) ranged from 0 to 216.
Spine radiographic structural assessment was established by one experienced reader on sagittal x-rays according to the RASSS (from 0-84).
Results: 142 patients were included: median age 54 y [47-62], 70.4% male, 66.6% smokers, 77.6% HLA-B27 status, median duration disease 14 y [6-26], 43.5% treated by bDMARDS. Among them, 90 (62.7%) and 102 (71.8%) patients presented spine structural damage according to the RASSS and the total CT-score respectively (p=0.0001). For the total CT-score, 94 patients presented at least one lesion at the anterior vertebra corner and 68 with facet joint ankylosis. The sensitivity, the specificity and the accuracy of the CT score were 60.0%, 72.5% and 69% respectively with RASSS as referent score. The mean RASSS and total CT-scores were 13.1 (± 20.0) and the 37.2 ((± 47.2) respectively. The correlation between RASSS and total CT score was excellent (value= 0.83; p< 0.0001). For RASSS, linear regression analysis showed associations with age (value =0.23; p=0.01), disease duration (value 0.27; p< 0.002), male gender (value =8.4 p=0.01) and CRP >5 mg/l (value = 0.17; p=0.03). The total-CT score showed association with age (value=0.17; p=0.034), male gender (value=0.16; p=0.03) disease duration (value=0.31; p=0.0001), and CRP >5 mg/l (value=0.25; p=0.001) in multivariate analysis. Reading was performed with excellent intra reader reliabilities for both radiographic and CT assessment (ICCs >0.90).
Conclusion: In AS patients, screening spine structural lesion on opportunistic TAP CT is an efficient, reproductible and complementary approach to x-ray imaging. In our study, CT screening allowed anterior and posterior dorsolombar spine assessment, which can be challenging to achieve with x-rays, with a greater number of spine lesions to be detected.
To cite this abstract in AMA style:
Morizot C, Favre-Felix I, Mennini A, Bauer E, Chary-Valckenaere I, Loeuille D. Spine Structural Lesions in Ankylosing Spondylitis: Comparison Between Radiographic (RASSS) and Opportunistic Thoraco-abdomino-pelvic CT Assessment [abstract]. Arthritis Rheumatol. 2024; 76 (suppl 9). https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/spine-structural-lesions-in-ankylosing-spondylitis-comparison-between-radiographic-rasss-and-opportunistic-thoraco-abdomino-pelvic-ct-assessment/. Accessed .« Back to ACR Convergence 2024
ACR Meeting Abstracts - https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/spine-structural-lesions-in-ankylosing-spondylitis-comparison-between-radiographic-rasss-and-opportunistic-thoraco-abdomino-pelvic-ct-assessment/