Session Information
Date: Sunday, November 5, 2017
Title: Rheumatoid Arthritis – Clinical Aspects Poster I: Treatment Patterns and Response
Session Type: ACR Poster Session A
Session Time: 9:00AM-11:00AM
Background/Purpose: Physicians equipped with low cost, patient-administered, “from home” genomic tests for monitoring disease activity and therapy response could revolutionize treatment for rheumatoid arthritis (RA) by enabling treat-to-target strategies, minimizing the use of ineffective therapies, and detecting changes in disease activity before a flare occurs. However, development of a “from home” strategy for patient care requires rigorous testing in the intended use cohort. In addition, the costs associated with recruiting and analyzing a patient cohort of sufficient size are formidable and further compounded by the possible confounding effects of concomitant RA therapies. Here, we investigated the feasibility of recruiting a patient cohort entirely through social media at minimal cost and cohort metrics were compared with clinical data of patients enrolled in a traditional, clinically managed study.
Methods: A cohort of self-reported RA participants were recruited under an IRB-approved, HIPAA compliant, Direct-to-Patient observational study entitled Baseline Rheumatoid Arthritis Verification and Outcomes (BRAVO; www.bravostudy.com). Participants were asked to complete 3 rounds of disease monitoring over a one month period, which included a short disease history questionnaire with RAPID3 ePRO and a self-collected 100 µL fingerstick blood sample returned through the US mail. Total RNA (50 ng) was isolated from the self-collected blood samples and sequenced using a custom 1200-gene pan-immunity Ampliseq panel on the Ion S5. Patient cohort metrics were compared with clinical data from the multi-center, longitudinal observational, 14-year, 1,400+ patient Brigham Women’s Rheumatoid Arthritis Sequential Study (BRASS; www.brassstudy.org).
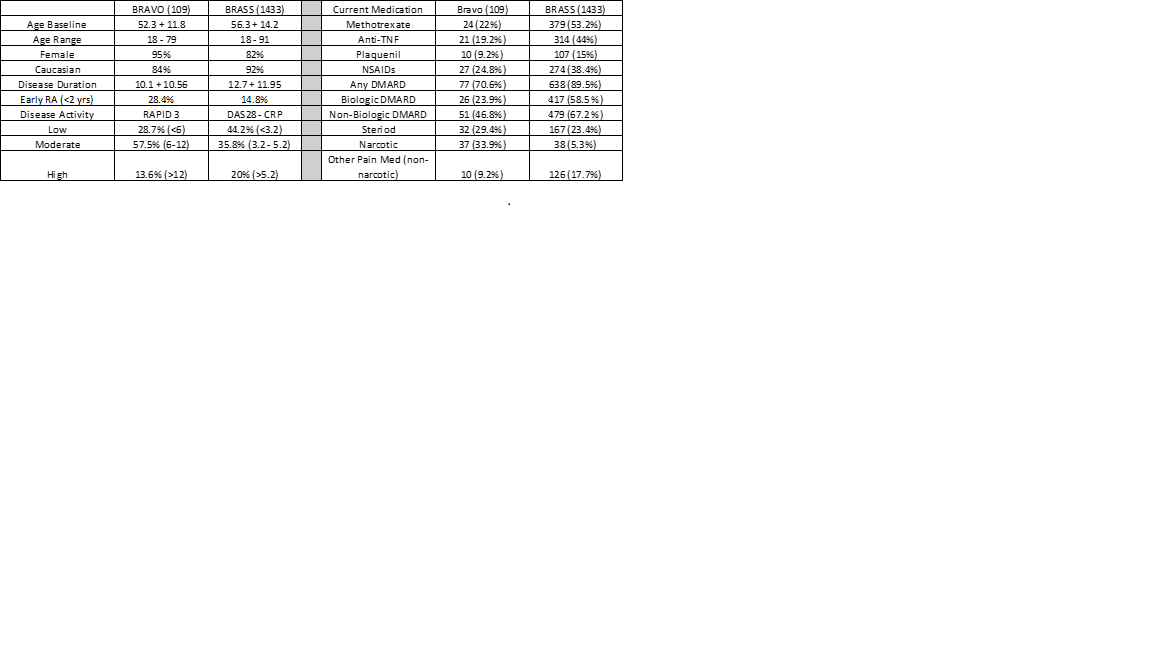
Results: BRAVO participants (n = 109) were recruited over a 12-week period through social media platforms. Most participants (80%) enrolled and completed the questionnaires using a mobile device, and 84% of patient samples yield at least 100ng of isolated RNA with an average RIN of 7.1. Comparison of cohort attributes at baseline between BRAVO and BRASS individuals (Table) exhibited significant similarities between mean age, disease duration, and range of medications. However, the BRAVO cohort tended to have higher disease activity, lower use of biologic and non-biologic DMARDS, higher use of narcotic/opioid pain meds and increased ethnicity.
Conclusion: Social media and molecular analysis of patient-collected fingerstick samples are viable and cost-effective methods to examine efficacy of direct-to-patient testing for RA affected individuals. Cohorts however differed significantly on the basis of critical clinical parameters indicating that a direct-to-patient approach has the power to add depth to the complex RA patient population that can be effectively monitored.
To cite this abstract in AMA style:
Warren K, Derbeneva O, Flores F, Frits M, Healy J, Iannaccone C, Khalid O, Morampudi K, Shadick N, Weinblatt M, Wijesuriya H, Terbrueggen R. Social Media Based, Direct-to-Patient Study Designed for Development of “from Home” Testing for Rheumatoid Arthritis Patients Is Feasible and Engaged Individuals with Distinct Clinical Characteristics [abstract]. Arthritis Rheumatol. 2017; 69 (suppl 10). https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/social-media-based-direct-to-patient-study-designed-for-development-of-from-home-testing-for-rheumatoid-arthritis-patients-is-feasible-and-engaged-individuals-with-distinct-clinical/. Accessed .« Back to 2017 ACR/ARHP Annual Meeting
ACR Meeting Abstracts - https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/social-media-based-direct-to-patient-study-designed-for-development-of-from-home-testing-for-rheumatoid-arthritis-patients-is-feasible-and-engaged-individuals-with-distinct-clinical/