Session Information
Date: Monday, November 9, 2020
Title: Vasculitis – Non-ANCA-Associated & Related Disorders Poster II
Session Type: Poster Session D
Session Time: 9:00AM-11:00AM
Background/Purpose: Systemic vasculitides are complex and heterogeneous diseases with overlapping features that frequently pose a diagnostic challenge to clinicians. The temporal artery biopsy (TAB) is the gold standard for the diagnosis of giant cell arteritis (GCA) with cranial involvement. Occasionally, the TAB shows small vessel vasculitis (SVV) surrounding a normal temporal artery as the only pathological finding. Ultimate diagnosis and, consequently, optimal treatment remain uncertain in these patients.
The aim of this project is to characterize biomarkers with diagnostic potential in TAB disclosing SVV surrounding a spared temporal artery.
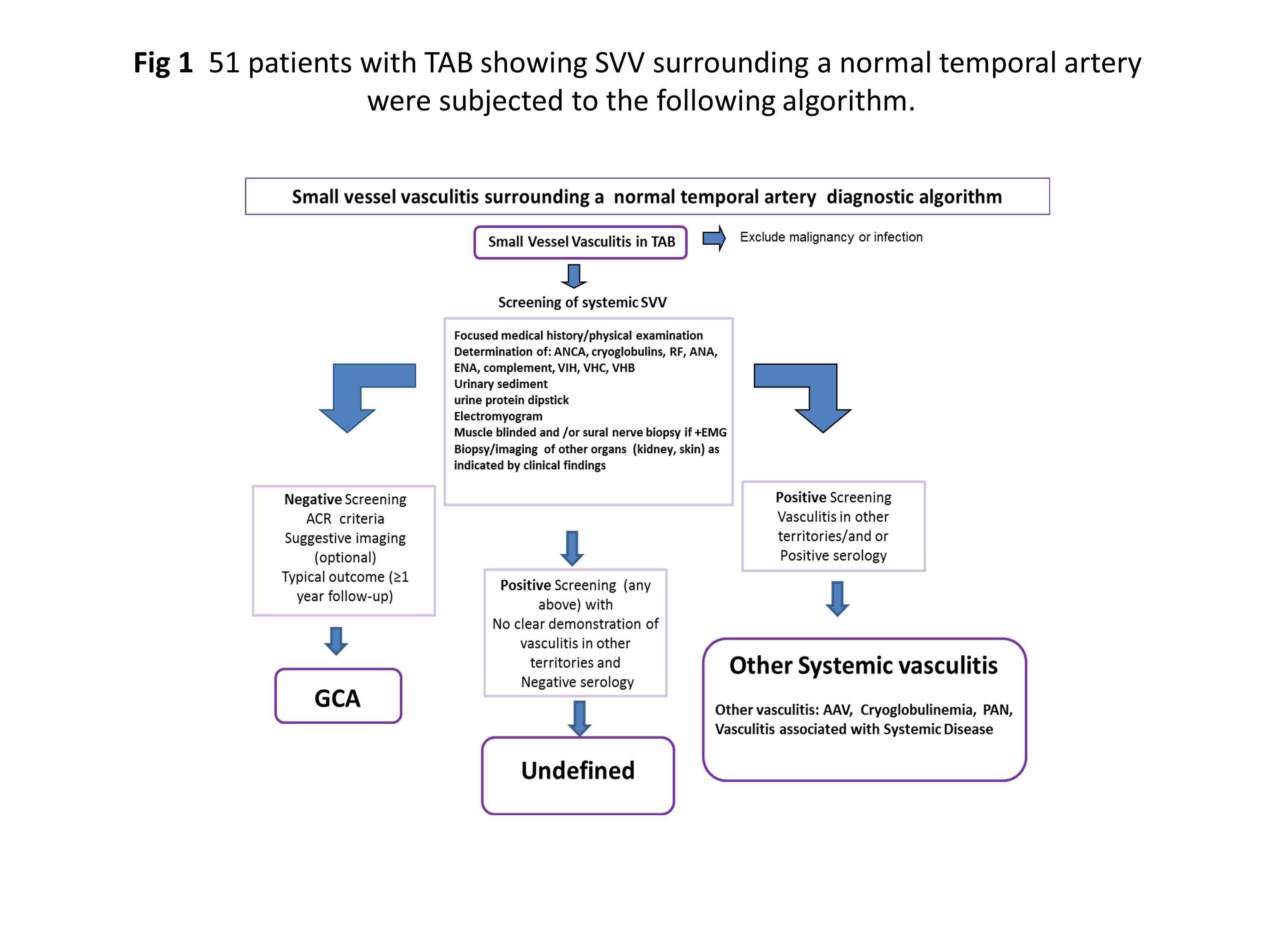
Methods: 51 Patients with TAB showing SVV surrounding a normal temporal artery were subjected to a pre-established diagnostic algorithm combining clinical, imaging and serological data (Fig 1). The algorithm led to the following classification: 19 GCA; 20 systemic vasculitis (ANCA-associated vasculitis (AAV) and other vasculitis); and 12 could not be classified. TAB samples from 15 SVV patients (8 classified as GCA[SVV-GCA] and 7 systemic vasculitis [SVV-SV]: 4 AAV and 3 other vasculitis) and 16 controls with negative temporal artery biopsies, were used for RNA isolation and microarray hybridization (Human Clariom S, Affymetrix). Genes differentially expressed were identified by a multivariate permutation t test using the BRB ArrayTools 4.6 software package (Biometric Research Branch, NCI). We set parameters in the univariate 2-sample t test permutation with a random variance model. Permutation P values for significant genes (P < 0.001) were computed based on 10,000 random permutations that result in an estimated false discovery rate below 1%.
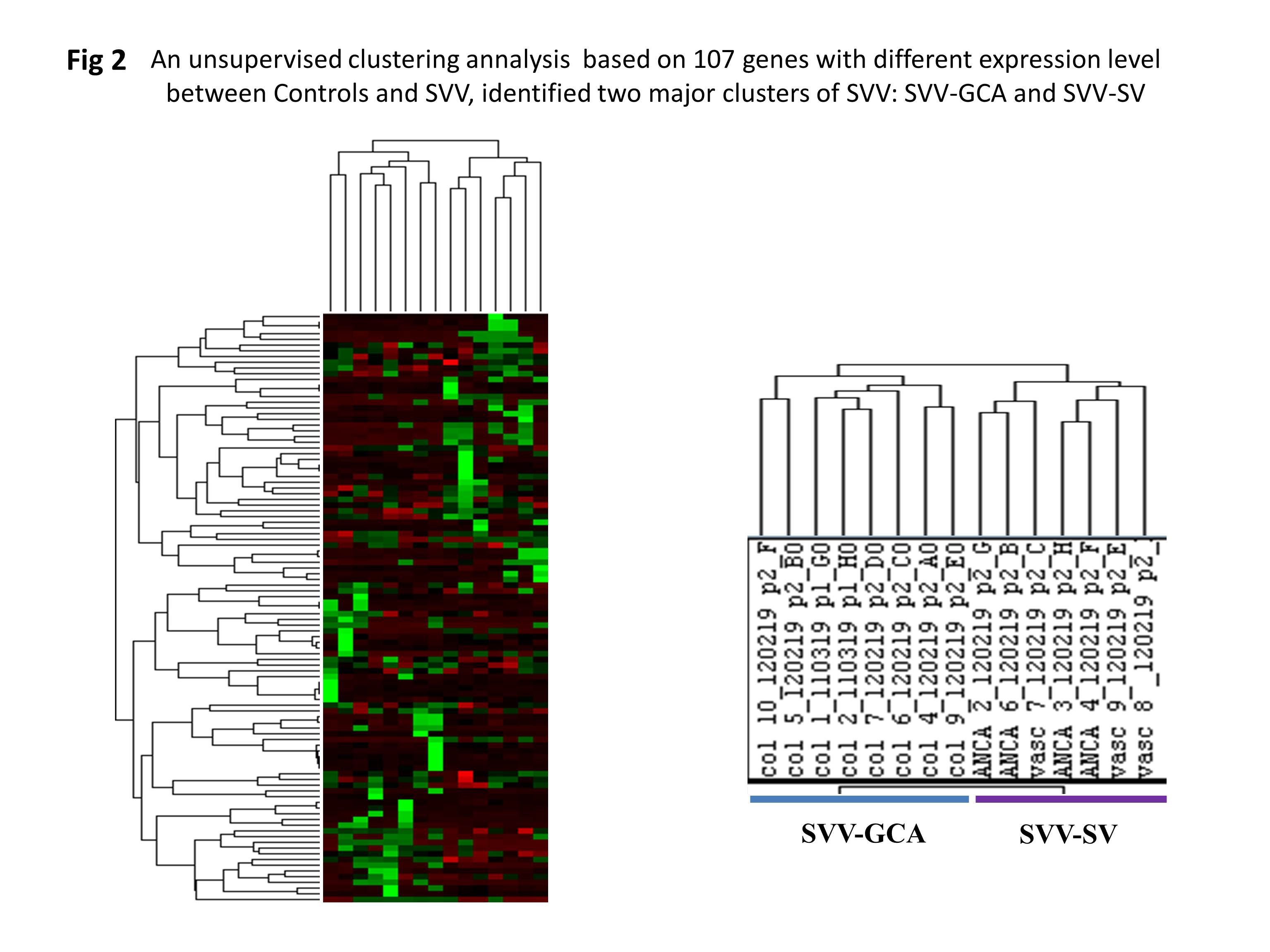
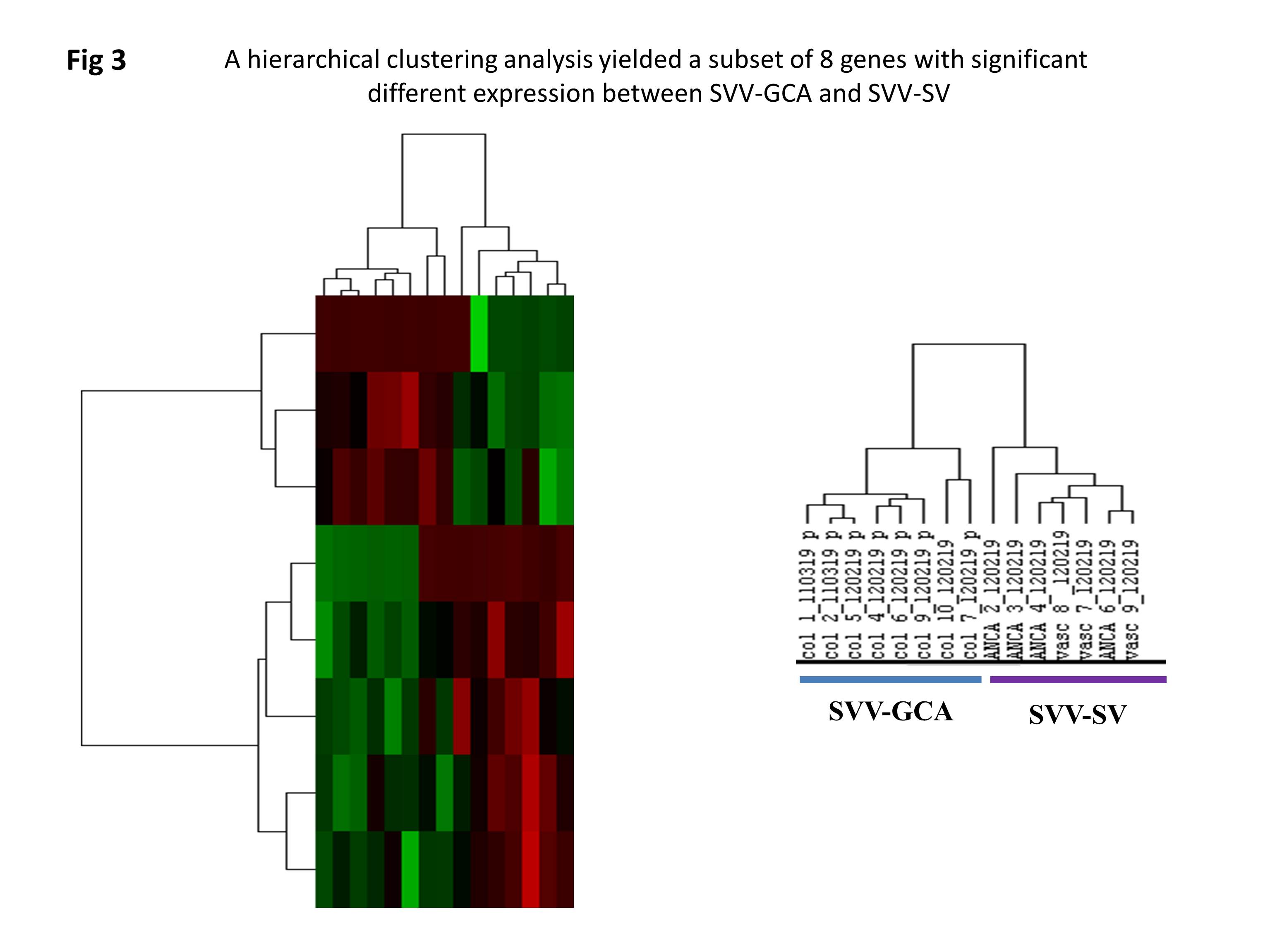
Results: We compared gene expression in normal temporal arteries and the different subgroups of SVV. The expression level of 42 genes was found to be significantly different between normal arteries and SVV-GCA, whereas the expression level of 65 genes was significantly different between normal arteries and SVV-SV. Interestingly, an unsupervised hierarchical clustering based on this subset of 107 genes was able to cluster subgroups of SVV: SVV-GCA and SVV-SV (Fig 2). In addition, a hierarchical clustering analysis yielded a subset of 8 genes with significant different expression between SVV-GCA and SVV-SV (Fig 3). Sub-analysis between SVV-GCA and SVV-AAV and SVV-GCA and SVV-other vasculitis, showed significant differences in expression level of 17 and 23 genes respectively.
Conclusion: SVV surrounding a spared TA is a relevant but equivocal finding. After a detailed diagnostic work-up most patients can be diagnosed with GCA or other systemic vasculitis although diagnosis remains uncertain in some cases. Cluster analysis of the gene expression profile differentiates diagnostic subgroups of SVV. Further studies are needed to validate differentially expressed genes.
“Supported by PI15/00092, Plan Estatal de Investigación Científica y Técnica de Innovación 2013-2016 y cofinanciado por el ISCIII-Subdirección General de Evaluación y el Fondo Europeo de Desarrollo Regional (FEDER)”
To cite this abstract in AMA style:
Espígol-Frigolé G, Alba-Rovira R, Naranjo-Suárez S, Terenas M, Prieto-González S, Corbera-Bellalta M, Marco-Hernández J, Alba M, Kamberovic F, Ríos-Garcés R, Hernández-Rodríguez J, Cid M. Small Vessel Vasculitis Surrounding a Preserved Temporal Artery: Search for Tissue Biomarkers with Potential Diagnostic Value [abstract]. Arthritis Rheumatol. 2020; 72 (suppl 10). https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/small-vessel-vasculitis-surrounding-a-preserved-temporal-artery-search-for-tissue-biomarkers-with-potential-diagnostic-value/. Accessed .« Back to ACR Convergence 2020
ACR Meeting Abstracts - https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/small-vessel-vasculitis-surrounding-a-preserved-temporal-artery-search-for-tissue-biomarkers-with-potential-diagnostic-value/