Session Information
Date: Monday, November 14, 2016
Title: Rheumatoid Arthritis – Human Etiology and Pathogenesis - Poster II
Session Type: ACR Poster Session B
Session Time: 9:00AM-11:00AM
Background/Purpose: MicroRNAs (miRNAs) are ~22-nt RNAs that post-transcriptionally regulate gene expression and serve as biomarkers of many disease states. Most previous plasma miRNA studies in inflammatory autoimmune diseases have relied on PCR or microarray for candidate miRNAs based on limited information about miRNA function; however, unbiased small RNA sequencing (sRNAseq) could reveal new miRNA disease biomarkers. We hypothesized that plasma miRNAs are altered in inflammatory autoimmune diseases (RA and SLE) compared to control subjects and are differentially altered in RA and in SLE.
Methods: This cross-sectional study included patients with RA, SLE, and age, race and sex matched control subjects (N=12, each). Sequencing was done by Illumina HiSeq3000. High quality reads were mapped to the human genome using Bowtie1. MiRBase21.0 was used to quantify miRNAs. All samples had ≥1 million miRNA reads, and miRNAs having ≥10 reads per sample were analyzed. Reads per mapped read were compared between RA, SLE and control subjects. Significantly altered miRNAs with ≥1.5 fold difference were examined. Putative miRNA targets were generated using TargetScanHuman 7.1 and compared to disease-related pathway genes using the KEGG database.
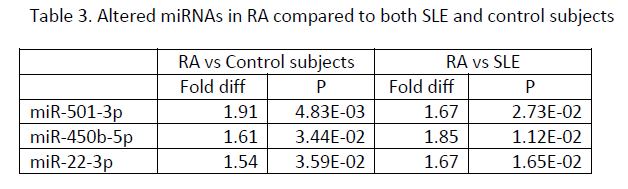
Results: Significantly elevated plasma miRNAs in patients with RA and SLE compared to control subjects (Table 1) were miR-24-3p and miR-345-5p, which are predicted to target mRNAs encoding interferon gamma or its receptor and HLA-DOA, HLA-DPB1, HLA-DRB1, and HLA-DRB5. Significantly altered plasma miRNAs in SLE compared to RA and control subjects (Table 2) included miR-194-5p, miR-424-3p, let-7d-5p, miR-652-3p, miR-548o-3p, miR-335-5p, let-7a-3p, miR-369-3p, miR-204-5p, and miR-98-3p, some of which are predicted to target histone and complement proteins, IL10, SSA, and NMDA receptors. Significantly increased plasma miRNAs in RA compared to SLE and control subjects (Table 3) included miR-501-3p, miR-450b-5p and miR-22-3p, some of which are predicted to target TGF beta or its receptor, TLR4, IL6 and IL17.
Conclusion: Several miRNAs in plasma measured by sRNAseq are differentially altered in patients with RA and SLE. Many of the altered miRNAs have predicted targets in disease-related pathways. Further validation is necessary to confirm these findings. 
To cite this abstract in AMA style:
Ormseth MJ, Solus JF, Guo Y, Sheng Q, Allen R, Vickers KC, Stein CM. Small Rnaseq Reveals Different Plasma miRNA Signature in Patients with RA and SLE: A Pilot Study [abstract]. Arthritis Rheumatol. 2016; 68 (suppl 10). https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/small-rnaseq-reveals-different-plasma-mirna-signature-in-patients-with-ra-and-sle-a-pilot-study/. Accessed .« Back to 2016 ACR/ARHP Annual Meeting
ACR Meeting Abstracts - https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/small-rnaseq-reveals-different-plasma-mirna-signature-in-patients-with-ra-and-sle-a-pilot-study/