Session Information
Date: Saturday, November 16, 2024
Title: SLE – Animal Models Poster
Session Type: Poster Session A
Session Time: 10:30AM-12:30PM
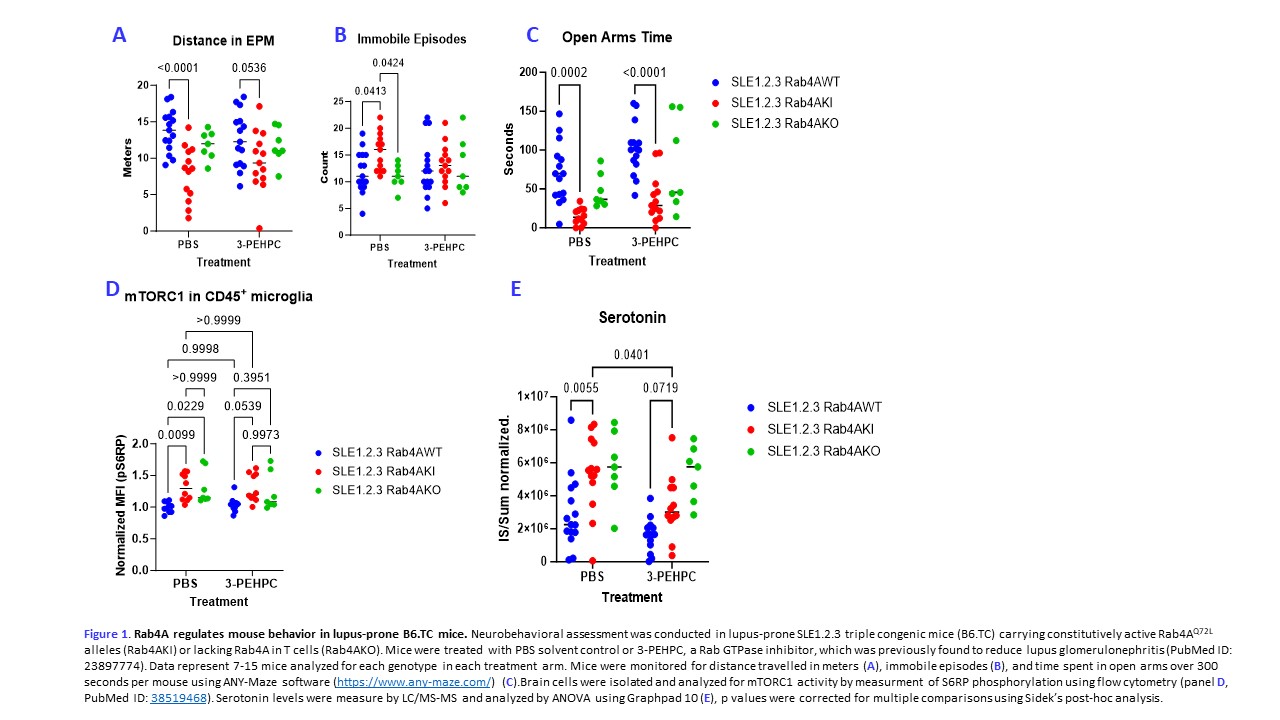
Background/Purpose: Rab4A is a small GTPase that is overexpressed in patients and mice with systemic lupus erythematosus (SLE, PubMed ID: 23897774; PubMed ID 31805010). Rab4A regulates endocytic recycling of receptors and organelles, thus promoting CD98-mediated uptake of aromatic amino acids and lysosomal localization and activation of the mechanistic target of rapamycin (mTOR; PubMed ID: 38519468). The present study was initiated to determine the effects of Rab4A on mTOR activation in CD45+ microglia, serum serotonin levels and mouse behavior in lupus-prone SLE1.2.3 triple congenic mice (B6.TC) carrying constitutively active Rab4AQ72L alleles (Rab4AKI) or lacking Rab4A in T cells (Rab4AKO). 3-PEHPC, a Rab GTPase inhibitor, which was previously found to reduce glomerulonephritis (PubMed ID: 23897774), was evaluated for its ability to control neurobehavioral disease in lupus-prone mice.
Methods: Female B6.TC mice carrying wild-type (WT), Rab4AKI, and Rab4AKO alleles were treated with 150ug/kg of 3-PEHPC or phosphate-buffered saline (PBS) solvent control. 7-15 age-matched mice per genotype and treatment groups, 70 total, were treated for 30 days. Elevated plus maze (EPM) was used to monitor activity and anxiety levels over 300 seconds per mouse using ANY-Maze software (https://www.any-maze.com/). Serum was analyzed by LC/MS-MS; brain cells were isolated and analyzed by flow cytometry (PubMed ID: 38519468).
Results: Rab4AKI mice exhibited decreased locomotion (FC=0.574, p=8.03E-5) and elevated anxiety levels, measured by immobile episodes in comparison to Rab4AWT mice (FC=1.45, p=0.022), respectively (Figures 1A-C). The phosphorylation of the mTORC1 substrate, S6RP, was increased significantly in Rab4AKI CD45+ microglia compared to Rab4AWT CD45+ microglia (FC= 1.31, p=0.01; Figure 1D). Rab4AKI mouse serum had significantly higher serotonin levels compared to Rab4AWT serum (FC=1.8, p=0.006; Figure 1C). When mice were given 3-PEHPC, the difference in pS6RP staining between Rab4AWT CD45+ microglia and Rab4AKI CD45+ microglia was no longer significant. 3-PEHPC also decreased anxiety and increased serum serotonin levels in Rab4AKI mice significantly as compared to Rab4AKI mice treated with PBS (FC=0.63, p= 0.040). Rab4AWT mice administered with 3-PEHPC also had lower anxiety levels compared to PBS-treated Rab4AWT mice measured by an increased time in the open arm of the EPM (Fold change = 1.60, p-value = 0.025).
Conclusion: This study suggests that Rab4A regulates mTORC1 activation in CD45+ microglia cells and serotonin serum levels, which likely control neurobehavioral dysfunction in lupus-prone B6.TC mice.
To cite this abstract in AMA style:
Winans T, Wang X, Lewis J, Nolan J, Morel L, Perl A. Small GTPase Rab4A Regulates Mouse Behavior Through Altered Serum Serotonin Levels and Microglial mTORC1 Activation in Lupus-prone B6.TC Mice [abstract]. Arthritis Rheumatol. 2024; 76 (suppl 9). https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/small-gtpase-rab4a-regulates-mouse-behavior-through-altered-serum-serotonin-levels-and-microglial-mtorc1-activation-in-lupus-prone-b6-tc-mice/. Accessed .« Back to ACR Convergence 2024
ACR Meeting Abstracts - https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/small-gtpase-rab4a-regulates-mouse-behavior-through-altered-serum-serotonin-levels-and-microglial-mtorc1-activation-in-lupus-prone-b6-tc-mice/