Session Information
Date: Tuesday, November 9, 2021
Title: Systemic Sclerosis & Related Disorders – Clinical Poster III (1836–1861)
Session Type: Poster Session D
Session Time: 8:30AM-10:30AM
Background/Purpose: Pulmonary arterial hypertension (PAH) and interstitial lung disease (ILD) are the leading causes of mortality in systemic sclerosis (SSc). Although the six-minute walk test (6MWT) is generally used for evaluating physical functioning in PAH and ILD, its relevance in clinical practice is still uncertain. The purpose of this study was to evaluate which variables of 6MWT are correlated with demographic, clinical and serological data.
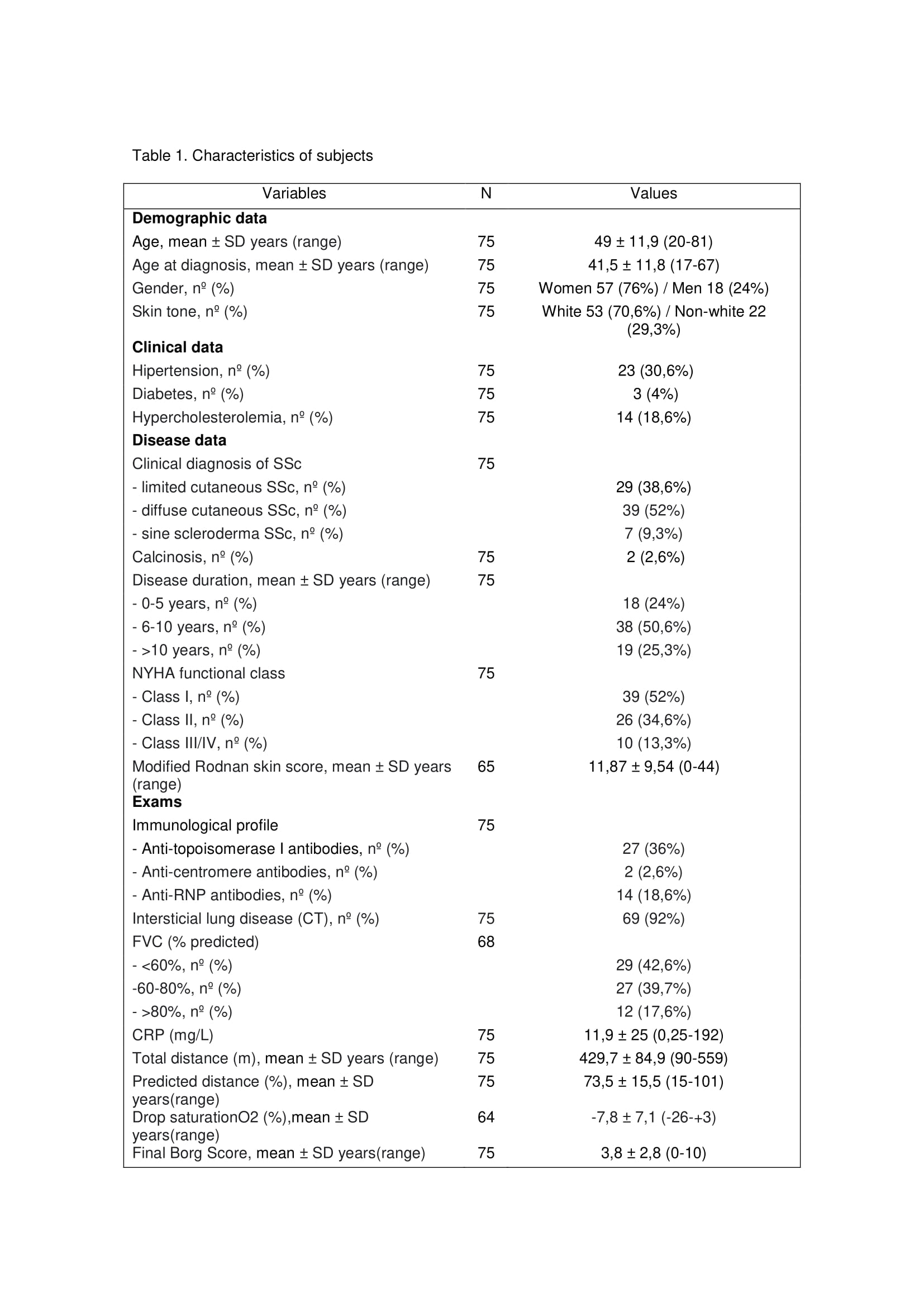
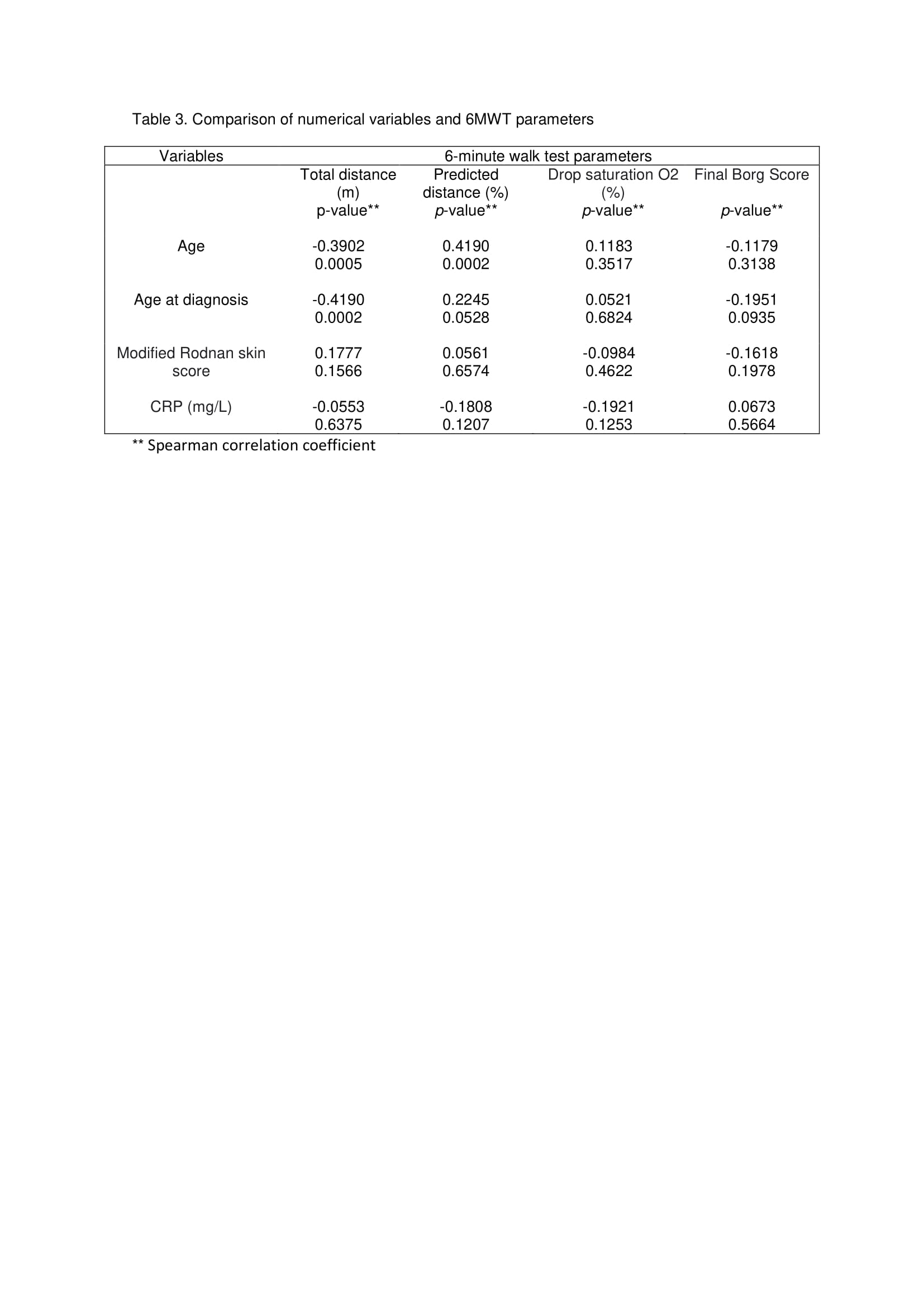
Methods: In this cross-sectional study, 75 SSc patients (all patients met the 2013 ACR-EULAR systemic sclerosis classification criteria) were evaluated regarding the following characteristics: demographic, clinical including diagnosis of SSc, disease duration, calcinosis, NYHA functional class, modified Rodnan skin score (MRSS), pulmonary function, ILD, c-reactive protein (CRP – mg/L) and immunological data (anti-topoisomerase-I, anticentromere and RNP antibodies) – table 1. Patients were submitted to 6MWT. A Kruskal-Wallis test followed by Dunn’s multiple nonparametric pairwise tests was used to compare the categorical items with 6MWT variables (table 2). The numerical items were compared applying Spearman correlation coefficient (table 3). All the data were analyzed using 5% level of significance (p< 0.05).
Results: Total distance was negatively associated with age and advanced age at diagnosis. Predicted distance was positively related to age, disease duration, greater forced vital capacity (FVC) and lesser NYHA functional class (I >II; II >III/IV) class. Borg scale was positively related to higher NYHA functional class (I< II, II< III/IV). Drop of saturation was positively associated with worse FVC and anti-topoisomerase-I positivity. There were no associations between 6MWT variables and race, clinical classification of SSc (limited, diffuse or sine scleroderma), presence of calcinosis, MRSS, anti-centromere, anti-RNP, presence of ILD and CRP values.
Conclusion: The performance on 6MWT was well correlated with pulmonary function, anti-topoisomerase-I positivity, NYHA functional class, disease duration and age. 6MWT is a straightforward and inexpensive test, useful in identifying SSc patients with adverse outcomes in clinical practice. Prospective studies are necessary to confirm our findings.
To cite this abstract in AMA style:
Soubihe V, Gaino J, Pugliesi A, Del Rio A, Sachetto Z, Dos Santos M, Palhares L. Six-minute Walk Test as a Prognostic Marker in Systemic Sclerosis [abstract]. Arthritis Rheumatol. 2021; 73 (suppl 9). https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/six-minute-walk-test-as-a-prognostic-marker-in-systemic-sclerosis/. Accessed .« Back to ACR Convergence 2021
ACR Meeting Abstracts - https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/six-minute-walk-test-as-a-prognostic-marker-in-systemic-sclerosis/