Session Information
Date: Monday, November 14, 2016
Title: Rheumatoid Arthritis – Small Molecules, Biologics and Gene Therapy - Poster II
Session Type: ACR Poster Session B
Session Time: 9:00AM-11:00AM
Background/Purpose: Improvement in physical function and morning stiffness are key goals of rheumatoid arthritis (RA) treatment. Sirukumab, a selective human anti–IL6 monoclonal antibody, has recently been evaluated in the SIRROUND-T global, Phase 3 study for the treatment of RA in patients (pts) with active disease who were intolerant or refractory to therapies targeting tumor necrosis factor (TNF). This study evaluated the impact of sirukumab on physical function and morning stiffness in pts with active RA despite anti-TNF therapy.
Methods : Eligible pts with active RA who were intolerant or refractory to anti-TNF therapy were randomized (1:1:1) to sirukumab SC 50 mg q4w, sirukumab SC 100 mg q2w, or placebo SC q2w. A significant proportion of pts were also exposed to other non-anti-TNF therapies. At Wk 18, pts in the placebo group were re-randomized to 1 of the 2 sirukumab doses if they had insufficient (<20%) improvement in tender/swollen joints, and at Wk 24, all pts remaining in the placebo group crossed over to 1 of the 2 sirukumab doses. To assess physical function, pts completed the Health Assessment Questionnaire-Disability Index (HAQ-DI) at baseline (BL) and from Wk 2 to 52. A clinically meaningful improvement in HAQ-DI from BL was defined as a change (reduction) of 0.22 in HAQ-DI, and a normal HAQ-DI score was defined as ≤0.5. The average duration of daily morning stiffness during the previous week in minutes (0–1440 minutes) was evaluated at the same visits as HAQ-DI.
Results: Mean improvement from BL in HAQ-DI score was significantly greater for both sirukumab 50 mg q4w and sirukumab 100 mg q2w compared with placebo at Wk 24 (both P <0.001; Table). Improvements from BL were maintained for both sirukumab doses through Wk 52. Improvements from BL in the HAQ-DI score were clinically meaningful (change of −0.22) for a significantly greater proportion of pts with both doses of sirukumab compared with placebo at Wk 24 (both P <0.001); differences between sirukumab and placebo in the proportion of pts achieving a clinically meaningful improvement in HAQ-DI scores were observed as early as Wk 4. A significantly greater proportion of pts receiving sirukumab 100 mg q2w (numerically greater with 50 mg q4w) achieved a HAQ-DI score of ≤0.5 at Wk 24 compared with placebo (P = 0.029). Additionally, there was a significantly greater reduction from BL in the duration of morning stiffness with sirukumab 50 mg q4w (P = 0.011) and a numerically greater reduction from BL with sirukumab 100 mg q2w compared with placebo at Wk 24; for both sirukumab dose groups, these reductions were observed as early as Wk 2 and maintained through Wk 52.
Conclusion: Sirukumab treatment was associated with early, sustained, and clinically meaningful improvements in both physical function and morning stiffness in pts with active RA who were intolerant or refractory to anti-TNF therapy. 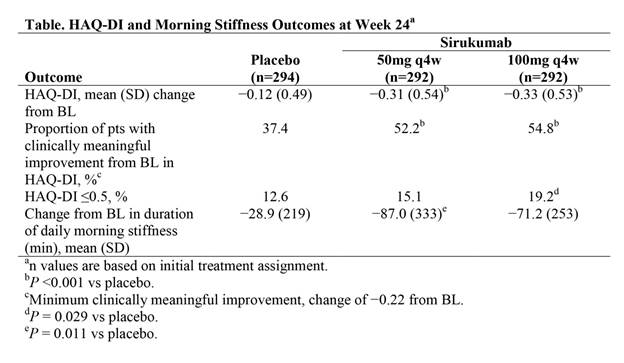
To cite this abstract in AMA style:
Tanaka Y, Bingham C III, Aletaha D, Agarwal P, Popik S, Kurrasch R, Peterson S, Ganguly R, Han C, McQuarrie K. Sirukumab, an Anti–IL-6 Cytokine Monoclonal Antibody, Significantly Improves Physical Function and Reduces Morning Stiffness in Patients with Active Rheumatoid Arthritis Despite Anti-TNF Therapy: Results from a Global, Randomized, Placebo-Controlled, Phase 3 Trial [abstract]. Arthritis Rheumatol. 2016; 68 (suppl 10). https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/sirukumab-an-anti-il-6-cytokine-monoclonal-antibody-significantly-improves-physical-function-and-reduces-morning-stiffness-in-patients-with-active-rheumatoid-arthritis-despite-anti-tnf-thera/. Accessed .« Back to 2016 ACR/ARHP Annual Meeting
ACR Meeting Abstracts - https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/sirukumab-an-anti-il-6-cytokine-monoclonal-antibody-significantly-improves-physical-function-and-reduces-morning-stiffness-in-patients-with-active-rheumatoid-arthritis-despite-anti-tnf-thera/
