Session Information
Date: Tuesday, November 14, 2023
Title: (2370–2386) Vasculitis – ANCA-Associated Poster III: Biomarkers & Renal Outcomes
Session Type: Poster Session C
Session Time: 9:00AM-11:00AM
Background/Purpose: Signal regulatory protein alpha (SIRPα) is primarily found on myeloid cells, including macrophages and neutrophils. Upon binding to CD47, SIRPa signaling regulates various cellular functions, including phagocytosis, antigen presentation, cell proliferation, cellular fusion, and cell migration. Therefore, SIRPamay be involved in the pathogenesis of autoimmune diseases including systemic vasculitis. This study aimed to assess SIRPa expression in tissue samples from patients with vasculitis.
Methods: Immunohistochemical staining for SIRPα was performed on kidney, lung, and temporal artery (TA) biopsy samples from patients with granulomatosis with polyangiitis (GPA), microscopic polyangiitis (MPA), giant cell arteritis (GCA), and patients without vasculitis. Cells were grouped into 4 categories: i) monocytes/macrophages/dendritic cells; ii) neutrophils; iii) eosinophils; and iv) lymphocytes. Categories iii and iv were not analyzed because of positive isotype control staining and absence of SIRPα+ cells, respectively. A semiquantitative estimation of SIRPα+ cells in categories i and ii were reported using the H-score system based on a visual estimate of the percentage of SIRPα+ cells and the staining intensities classified from 0 to 3 (H-score = 0 x [% with 0 intensity] + 1 x [% with 1 intensity] + 2 x [% with 2 intensity] + 3 x [% with 3 intensity]). Density of inflammatory infiltrate for individual cell categories were visually estimated and reported using an ordinal scale. Statistical analysis was done using GraphPad Prism 9.5.
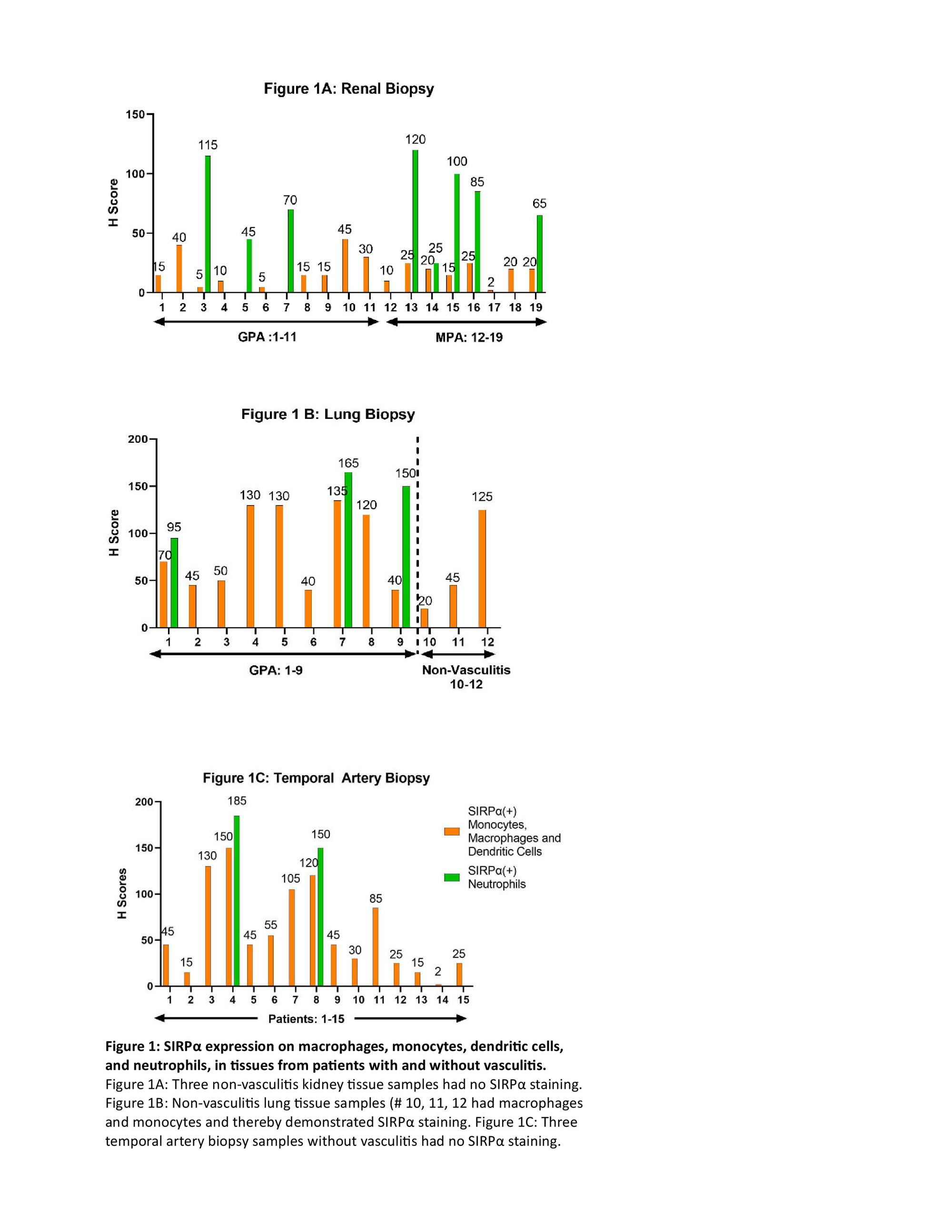
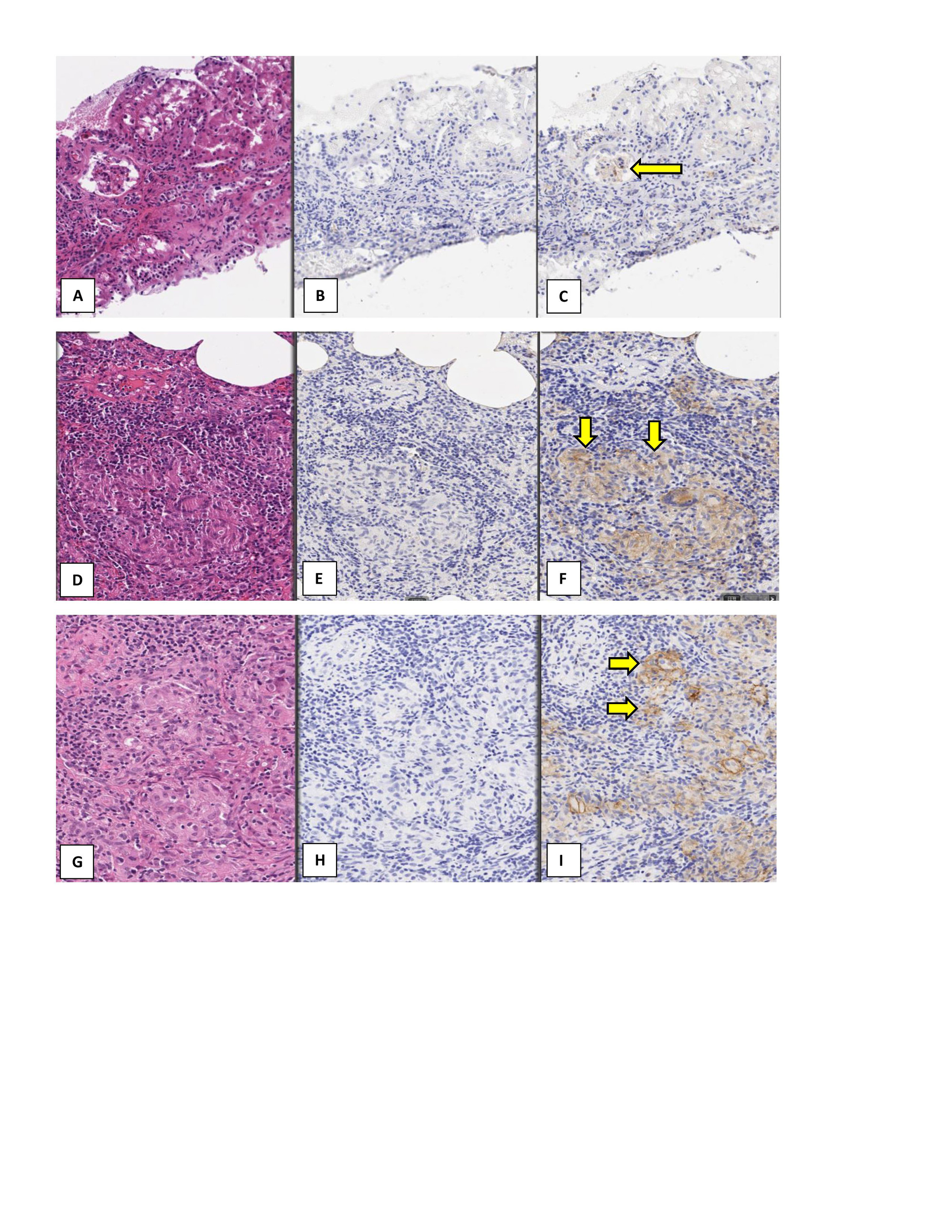
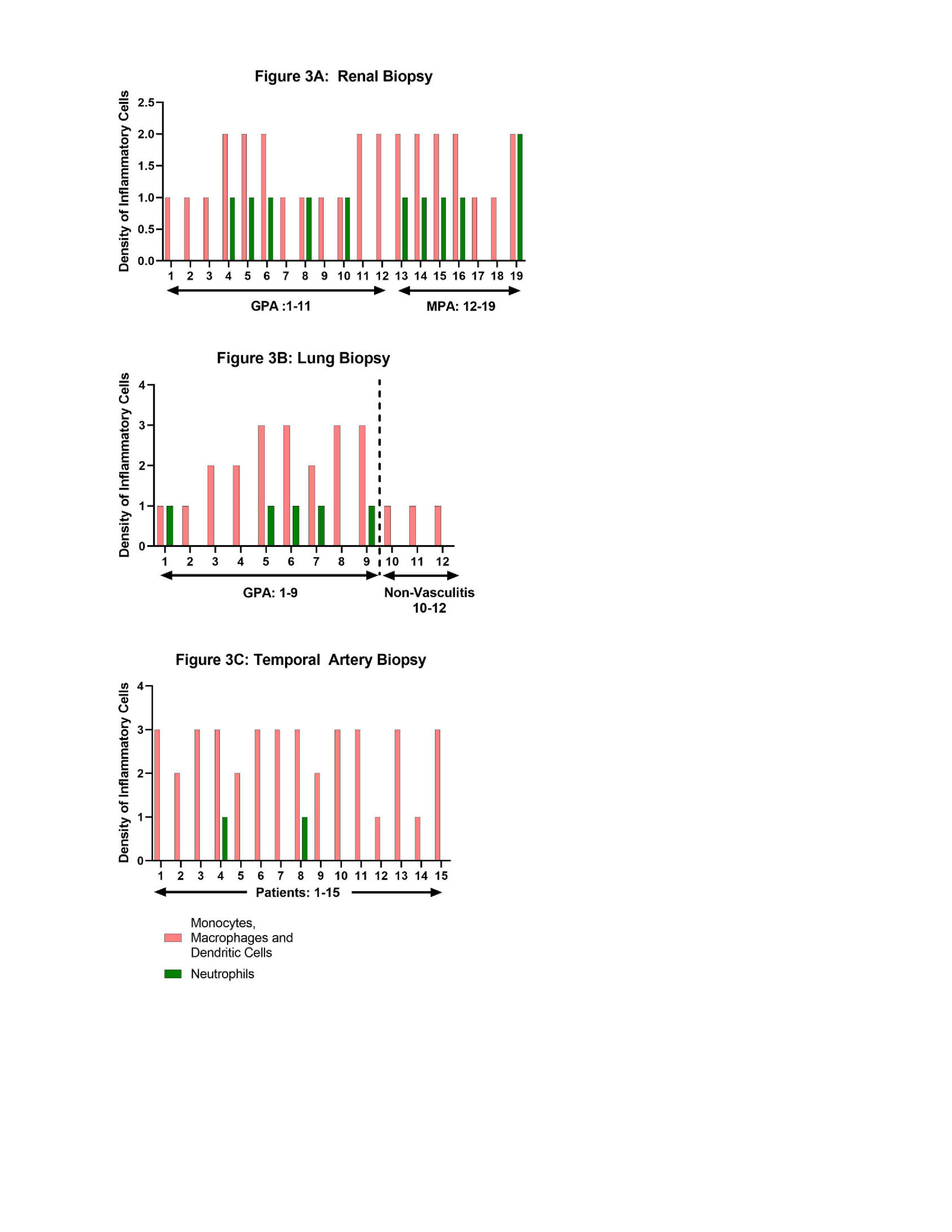
Results: Samples from 43 patients (20 with GPA, 8 with MPA, and 15 with GCA) were included in the study. Tissue samples included kidney from 11 patients with GPA and 8 patients with MPA; lung from 9 patients with GPA; and TA from 15 patients with GCA. All renal biopsies demonstrated glomerulonephritis with crescents. Inflammation was found in all the lung tissue samples and 6/9 (67%) demonstrated granuloma formation. All 15 TA samples showed inflammation in the arterial wall consistent with the diagnosis of GCA and 9 (60%) demonstrated granuloma formation/multinucleated giant cell infiltration and disruption of the internal elastic lamina. Figure 1 summarizes the data on SIRPa expression by tissue type. All tissue samples from patients with active vasculitis showed SIRPα staining. Due to absence of infiltrating immune cells, the kidney and TA samples from patients without vasculitis did not show any SIRPα staining. However, due to the presence of tissue-resident macrophages and monocytes, lung tissue from patients without vasculitis showed SIRPα staining. Figure 2 provides examples of SIRPα staining in tissue samples from patients with vasculitis. Figure 3 shows the overall density of inflammatory infiltrate of cell categories i and ii in the tissues.
Conclusion: This study demonstrates high-level expression of SIRPα in macrophages and monocytes in affected tissues in systemic vasculitis. Some tissues also had SIRPα+ neutrophils. These findings pave the way for further studies exploring the role of the SIRPα/CD47 pathway in the pathogenesis of systemic vasculitis and the potential for blockade of SIRPα and/or the depletion of SIRPa+ cells as treatment of systemic vasculitis.
Figure 1A: Three non-vasculitis kidney tissue samples had no SIRPα staining. Figure 1B: Non-vasculitis lung tissue samples (# 10, 11, 12 had macrophages and monocytes and thereby demonstrated SIRPα staining. Figure 1C: Three temporal artery biopsy samples without vasculitis had no SIRPα staining.
and neutrophils, in tissues from patients with and without vasculitis. An ordinal scale ranging from 0 to 3+ (0 = none, 1+ = rare/mild, 2+ = moderate, 3+ = severe/dense inflammatory infiltrate) was used to represent the density of each cell type infiltrate. Figure 3A: Three non-vasculitis kidney tissue samples had no inflammatory infiltrate. Figure 1B: Non-vasculitis lung tissue samples (# 10, 11, 12) had infiltration of macrophages and monocytes. Figure 1C: Three temporal artery biopsy samples without vasculitis had no inflammatory infiltrate.
To cite this abstract in AMA style:
Banerjee S, Rose E, Panicker S, Khalidi N, Koening C, Langford C, Monach P, Pagnoux C, McAlear C, Merkel P. SIRPα Expression in Systemic Vasculitis [abstract]. Arthritis Rheumatol. 2023; 75 (suppl 9). https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/sirp%ce%b1-expression-in-systemic-vasculitis/. Accessed .« Back to ACR Convergence 2023
ACR Meeting Abstracts - https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/sirp%ce%b1-expression-in-systemic-vasculitis/