Session Information
Session Type: Poster Session A
Session Time: 10:30AM-12:30PM
Background/Purpose: Recent single cell analyses have unveiled novel dendritic cell (DC) subpopulations that could potentially be linked to rheumatoid arthritis (RA). This study aimed to elucidate DC dynamics in RA through single cell RNA-sequencing (scRNA-seq) analysis.
Methods: Peripheral blood from 20 RA patients and 4 healthy controls (HC) was sorted for CD45+ CD3/16/19/88/89– HLA-DR+ live cells to construct a scRNA-seq/CITE-seq library of DCs. We assessed the correlation between DC subpopulation proportions and gene expressions with clinical features (Figure 1A). Additionally, we reanalyzed public AMP RA phase 2 synovium scRNA-seq data from RA and osteoarthritis (OA) patients .
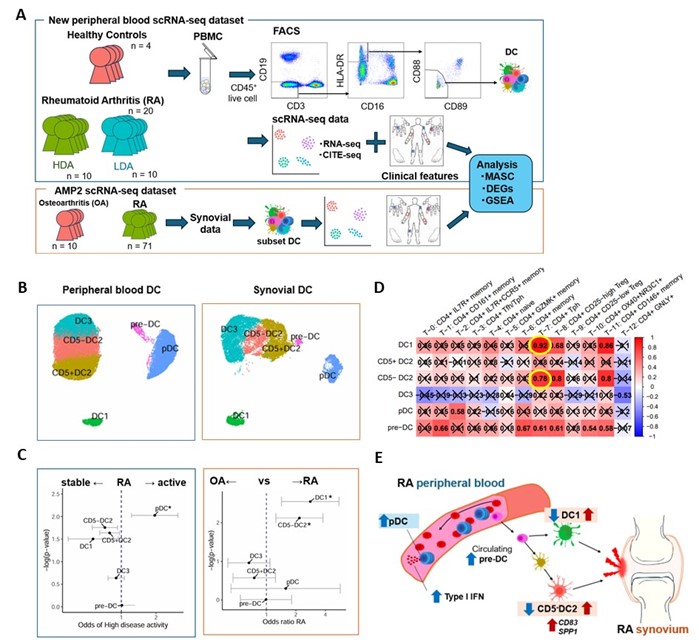
Results: In our peripheral blood and synovium scRNA-seq analysis, DCs were classified into plasmacytoid DC (pDC) and four myeloid DC clusters: classical DC1 (DC1), classical DC2 with different CD5 expressions (CD5+ DC2, CD5– DC2), DC3, and precursors of classical DCs (pre-DC) (Figure 1B). In the peripheral blood mixed-effects association testing for single cells, RA patients showed a decrease in DC1 and CD5– DC2 and an increase in pre-DC and pDC compared to HC. Among RA patients, those with high disease activity demonstrated significantly decreased DC1 and DC2 and increased pDC. Conversely, RA synovium displayed a notable increase in cDC1 and CD5– DC2 compared to OA (Figure 1C). Differentially expressed gene (DEG) analysis in RA patients revealed a large number of DEGs in cDC2 clusters in both peripheral blood and RA synovium. CD5– cDC2 exhibited heightened CD83 activation marker expression in both datasets, with elevated SPP1 expression in RA synovium. Gene Set Enrichment Analysis indicated that active RA upregulated type I and II interferon signaling in cDC clusters in both peripheral blood and synovium. Regarding DC cluster interactions with other immune cell clusters, CD5– cDC2 and DC1 abundance significantly correlated positively with peripheral helper T cell (Tph) in RA synovium who had had an inadequate response to TNF inhibitors (Figure 1D). These DC clusters showed enhanced interactions of CCL16-CXCR6, SPP1 signaling, and antigen presentation with Tph in patients with an inadequate response.
Conclusion: The decrease in cDC1 and CD5– cDC2 in RA peripheral blood may correspond to the increase in these mature DCs in the RA synovium (Figure 1E). Targeted scRNA-seq analysis of rare DCs can contribute to understanding RA pathology and offer novel candidate therapeutic targets.
(A) Study overview. (B) UMAP of DC clusters in peripheral blood and synovial scRNA-seq data. (C) MASC analysis of DC clusters in peripheral blood (left) and synovial (right) datasets. * < Bonferroni-adjusted p value < 0.05. (D) A heatmap of the correlation coefficients of the proportions of synovial DC clusters and CD4+ T cell clusters in RA patients with an inadequate response to TNF-inhibitors (n = 16). Cross marks indicate Pearson correlation p value > 0.05. (E) Schematic summary of this study. Blue arrows represent changes in peripheral blood, and red arrows indicate changes in the synovium of the DC clusters.
HDA, high disease activity; LDA, low disease activity; PBMC, peripheral blood mononuclear cells; FACS, fluorescence-activated cell sorting; DC, dendritic cell; MASC, mixed-effects association testing for single cells; DEG, differentially expressed gene; GSEA, gene set enrichment analysis.
To cite this abstract in AMA style:
Suwa Y, Yamada S, Ushijima T, Takahashi H, Okamura T, Nagafuchi Y, Fujio K. Single Cell RNA-sequencing Analysis Revealed Peripheral Blood and Synovial Alterations of Dendritic Cells in Rheumatoid Arthritis [abstract]. Arthritis Rheumatol. 2024; 76 (suppl 9). https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/single-cell-rna-sequencing-analysis-revealed-peripheral-blood-and-synovial-alterations-of-dendritic-cells-in-rheumatoid-arthritis/. Accessed .« Back to ACR Convergence 2024
ACR Meeting Abstracts - https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/single-cell-rna-sequencing-analysis-revealed-peripheral-blood-and-synovial-alterations-of-dendritic-cells-in-rheumatoid-arthritis/