Session Information
Session Type: Abstract Submissions (ACR)
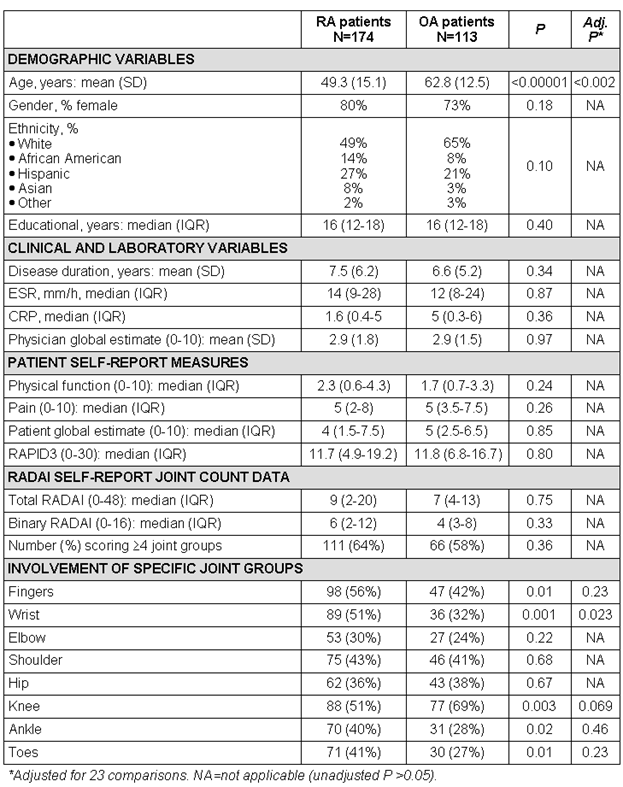
Background/Purpose: Rheumatoid arthritis (RA) and osteoarthritis (OA) are distinct diagnoses, based on widely differing pathogenetic mechanisms and treatments. However, OA patients may experience functional disability, pain and global distress at levels similar to RA patients. Furthermore, although differences may have been more pronounced in the past, at this time many OA patients have polyarthritis and levels of erythrocyte sedimentation rate (ESR) and C-reactive protein (CRP) similar to RA patients. A systematic comparison of patients with RA vs OA, including patient self-report scores, involvement of specific joints, laboratory tests, and physician global assessment, appeared of value.
Methods: All patients seen at an academic rheumatology center complete a multidimensional health assessment questionnaire (MDHAQ) at each visit to assess physical function, pain, patient global estimate (all 0-10), routine assessment of patient index data (RAPID3) – a composite of these 3 measures (0-30), and a rheumatoid arthritis disease activity index (RADAI) self-report of painful joints. RADAI is scored 0-3 for 16 joint groups (8 right, 8 left): fingers, wrist, elbow, shoulder, hip, knee, ankle, toes (total 0-48). A binary scoring of 0 or 1 (to mimic a physician joint count) was also computed. All patients are assigned a physician global estimate. ESR and CRP are assessed in many patients. Measures were compared in 174 RA vs 113 OA consecutive patients: normally distributed variables by means and t tests, non-normally distributed variables by medians and Mann-Whitney tests, and categorical variables by chi-square tests; p values were adjusted for 23 comparisons.
Results: Mean age was 49.3 in RA patients vs 62.8 years in OA patients (p <0.0002, adjusted for 23 comparisons). Median values for physical function, pain, patient global estimate, RAPID3, ESR, CRP, and mean physician global estimate did not differ in RA vs OA. Median total RADAI and binary scores were slightly higher in RA than OA (not statistically significant). More than 4 involved joint groups were self-reported by 64% of RA and 58% of OA patients. Involvement of wrists was higher in RA vs OA (51% vs 32%, adjusted p=0.023); no other differences in specific joint group involvement were statistically significant, adjusted for 23 comparisons.
Conclusion: OA and RA result in similar patient self-report MDHAQ scores. Further, physician global estimate, ESR, CRP and polyarticular involvement are similar in OA and RA at this time. RA and OA may have been more distinct in the past, when RA patients were younger, had much more severe clinical status, and less effective treatments. The data emphasize the need for careful evaluation by a knowledgeable physician to distinguish OA from RA, and may improve understanding of the concerns of OA patients, most of whom have polyarticular disease, functional disability and pain scores similar to patients with RA.
Disclosure:
I. Castrejón,
None;
Y. Yazici,
None;
T. Pincus,
None.
« Back to 2012 ACR/ARHP Annual Meeting
ACR Meeting Abstracts - https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/similarities-of-patient-self-report-scores-from-a-multidimensional-health-assessment-questionnaire-mdhaq-laboratory-tests-physician-global-assessment-and-polyarticular-involvement-in-patient/