Session Information
Session Type: Poster Session A
Session Time: 1:00PM-3:00PM
Background/Purpose: Arthrocentesis of the painful but non-effusive knee is usually not undertaken due to a high arthrocentesis failure rate. We hypothesized that compression-assisted arthrocentesis of the symptomatic non-effusive knee would permit synovial fluid analysis and provide useful diagnostic information.
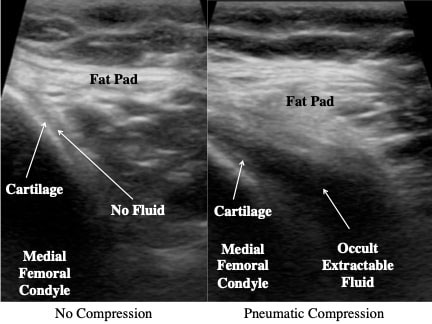
Methods: The absence of a knee effusion was determined by physical examination and ultrasound visualization. Conventional arthrocentesis first with and then without pneumatic compression was performed in 114 consecutive painful, non-effusive knees and synovial fluid was collected and analyzed for total nucleated cell (TNC) counts, TNC differential, crystals, Gram stain, and bacterial cultures.
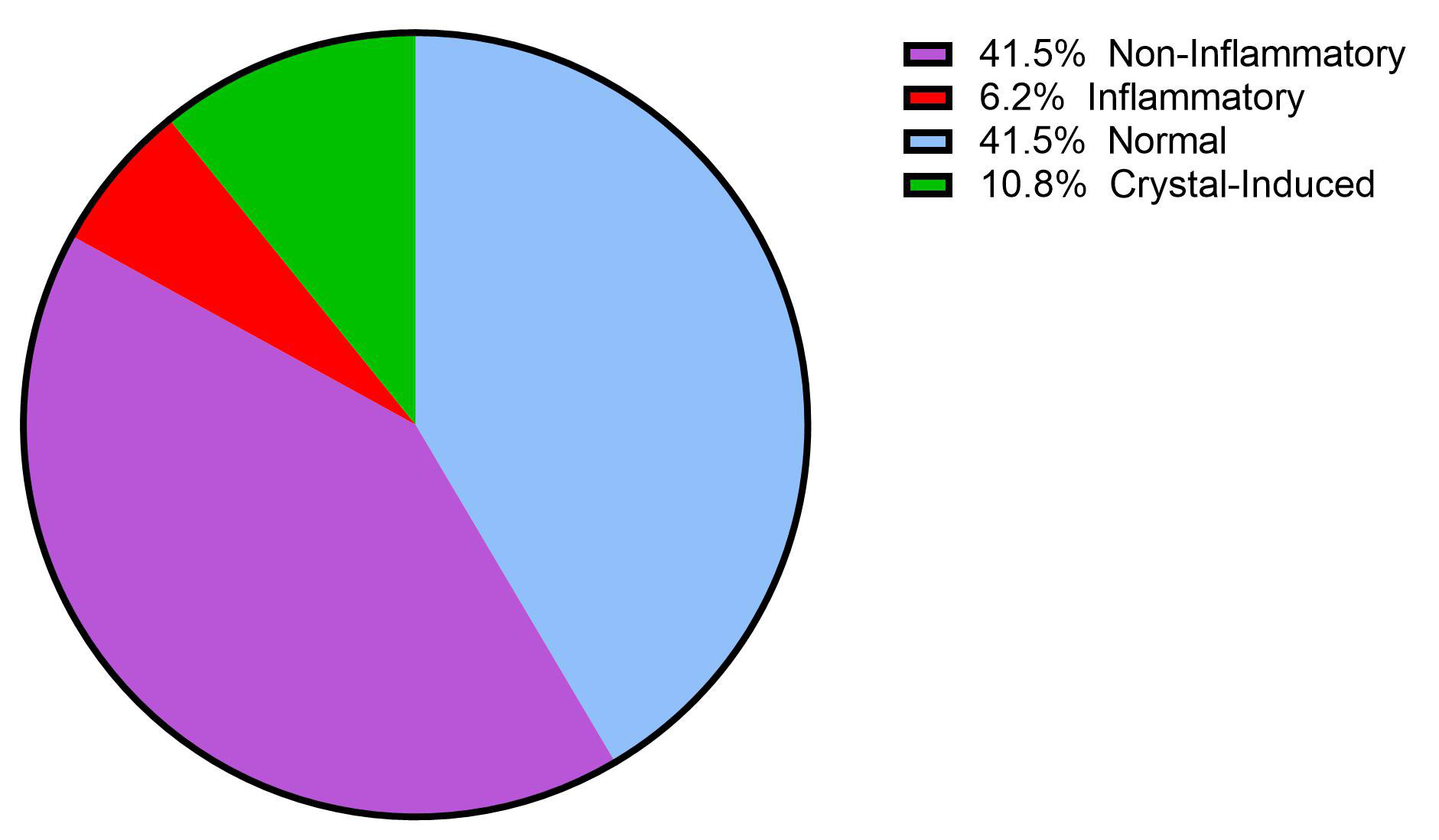
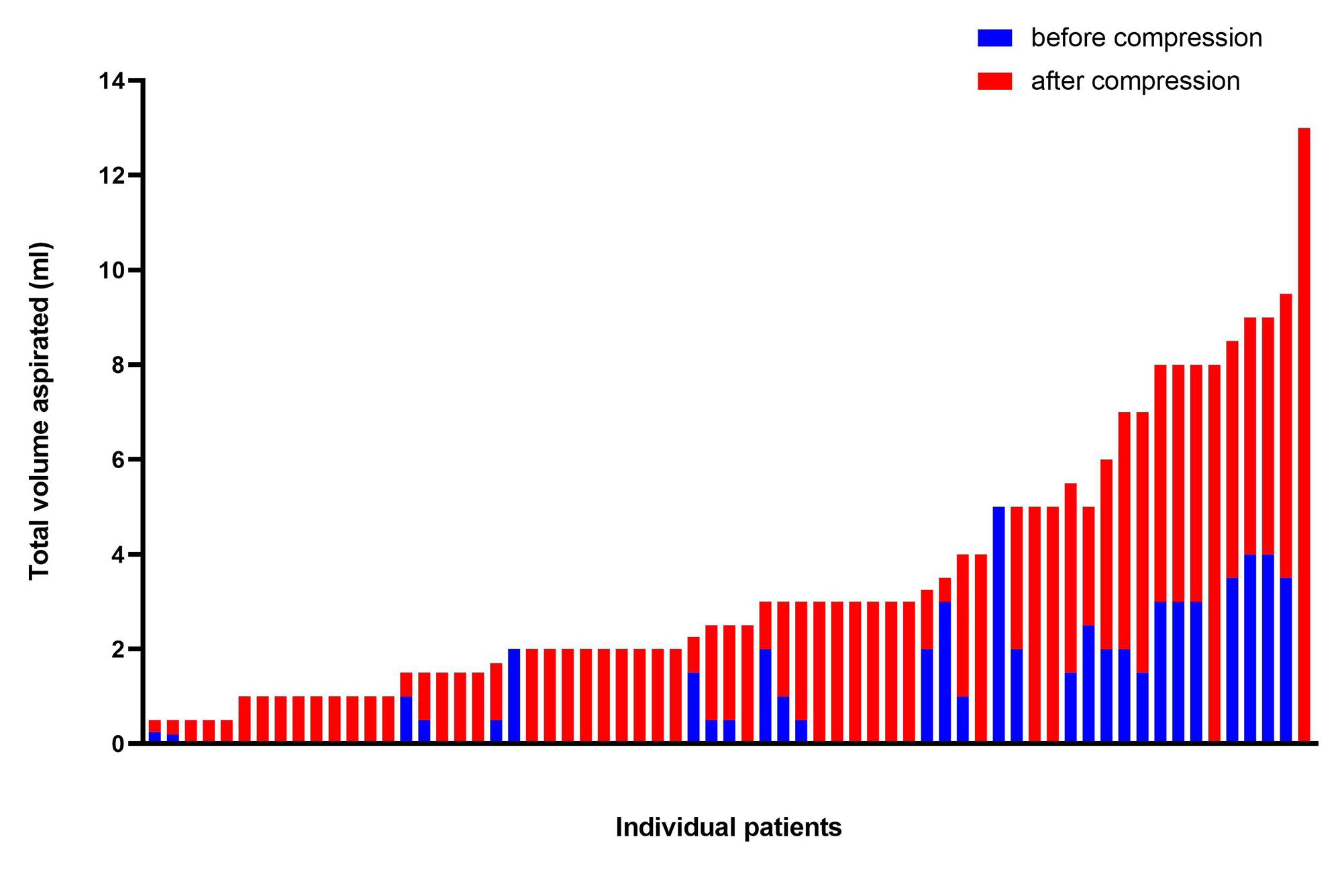
Results: Arthrocentesis success (≥ 0.5 ml) in the symptomatic non-effusive knee was 23.7% (27/114) without compression and 57.0% (65/114) with compression. OR: 0.22 (OR: 0.23 (0.13, 0.41); p=0.0001). The volume of aspirated synovial fluid increased from 0.43±0.95 ml to 1.8±2.5; p< 0.0001) when compression was used. Fluid from the non-effusive knee demonstrated: I) Normal fluid (TNC< 200) in 41.5% (27/65) (mean TNC 56.3±37.8), II) Non-inflammatory fluid (TNC 200-2000) in 41.5% (27/65) (mean TNC 556±3304), III) Inflammatory (TNC >2000) in 6.2% (4/65) (mean TNC 30,108±26,102); and V) Crystal-induced in 10.8% (7/65) (mean TNC 7115±1625). Amongst the crystal-induced fluid, two had sodium urate crystals both with normal or non-inflammatory fluid and five had calcium pyrophosphate dihydrate (CPPD) only one of which was inflammatory.
Conclusion: Compression-assisted arthrocentesis of the symptomatic non-effusive knee is successful in most cases and detects non-effusive inter-critical gout, other crystal-induced diseases, and inflammatory arthritis. Diagnostic arthrocentesis of the symptomatic non-effusive knee should be particularly considered in cases where there has been no prior synovial fluid analysis.
To cite this abstract in AMA style:
Patel R, Ariza-hutchinson A, Iqbal A, McElwee M, Emil N, Nunez S, muruganandam m, O'Sullivan f, Fields R, Waters Y, Sibbitt W. Should Arthrocentesis Be Attempted in the Symptomatic but Non-Effusive Knee? [abstract]. Arthritis Rheumatol. 2022; 74 (suppl 9). https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/should-arthrocentesis-be-attempted-in-the-symptomatic-but-non-effusive-knee/. Accessed .« Back to ACR Convergence 2022
ACR Meeting Abstracts - https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/should-arthrocentesis-be-attempted-in-the-symptomatic-but-non-effusive-knee/