Session Information
Session Type: Poster Session B
Session Time: 8:30AM-10:30AM
Background/Purpose: Health care utilization has an impact on disease progression and outcome in rheumatologic care. Disparities based on race, sex, education and income level affect care of our patients. Ocular inflammatory diseases increase disease burden in many rheumatologic conditions. We have compared Medicare and Intelligent Research in Sight (IRIS) data to identify similarities and differences in healthcare utilization for ocular inflammatory and infectious diseases. IRIS is a clinical registry, assembled by the American Academy of Ophthalmology. Registry uses Health Insurance Portability and Accountability Act (HIPAA) compliant methods to collect data directly from participating Ophthalmology practices’ individual electronic medical record (EMR) systems. In 2018, the registry collected data from more than 90% of ophthalmologists nationally
Methods: We have used Medicare and IRIS data available through National Vision and Eye Health Surveillance System (VEHSS). Medicare data are collected from research identifiable files obtained through the Center for Medicare and Medicaid Services (CMS) and include all fee for service beneficiaries.
VEHSS uses ICD-10 codes to identify ocular disorders and organizes them into two level categorization, which are category and subgroup. Each code is categorized in one subgroup and multiple subgroups are combined to form a category. The inflammatory and infectious eye disease category includes subgroups of ocular inflammatory conditions, lacrimal system and orbital inflammation, keratitis, conjunctivitis, eyelid inflammation and infection and endophthalmitis.
Utilization for the the Medicare and IRIS data was compared for the years 2016-2017. We have identified the impact of utilization for both the databases when stratified by sex and race alone and when stratified by race and sex together.
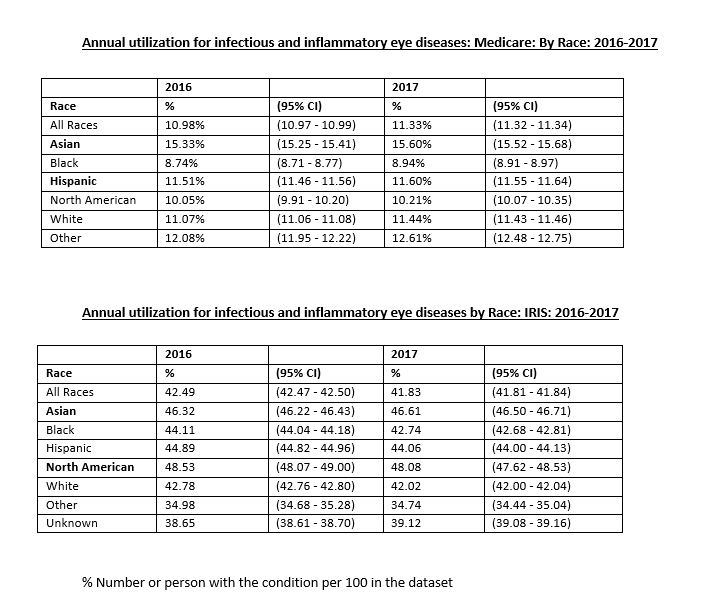
Results: Females have higher utilization across all races for the inflammatory and infectious eye diseases for both Medicare and IRIS data, for both 2016 and 2017. Asians have higher utilization for both males and females in both the databases. Whereas Hispanics have second highest utilization for Medicare data and North American Natives have second highest utilization for the IRIS data for both the years 2016-2017.
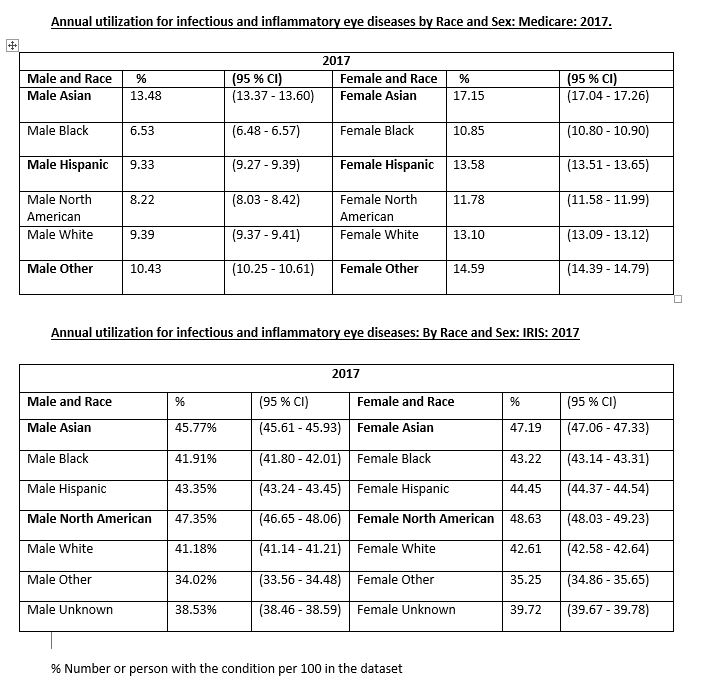
When the Medicare and IRIS databases are stratified by both race and sex, Asian females have the highest utilization, followed by Asian males for both the databases for both the years.
For the IRIS database, North American females have the second highest utilization followed by the North American males for both the years. For Medicare database, other females and other males have the second highest utilization followed by the Hispanic females and Hispanic males.
Conclusion: Comparing the Medicare and the IRIS data provides significant complimentary information on eye care utilization for inflammatory and infectious eye diseases. Females, Asians, Hispanics and Native Americans having higher utilization for both the years 2016-2017. This may be due to higher disease prevalence or higher service utilization. Further studies are needed to clarify this and to help in making informed policy decisions.
To cite this abstract in AMA style:
Chauhan K, Rosenbaum J. Sex and Race Based Utilization of Healthcare for Ocular Inflammation and Infection: Comparing the Results from the Medicare and the IRIS Data [abstract]. Arthritis Rheumatol. 2021; 73 (suppl 9). https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/sex-and-race-based-utilization-of-healthcare-for-ocular-inflammation-and-infection-comparing-the-results-from-the-medicare-and-the-iris-data/. Accessed .« Back to ACR Convergence 2021
ACR Meeting Abstracts - https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/sex-and-race-based-utilization-of-healthcare-for-ocular-inflammation-and-infection-comparing-the-results-from-the-medicare-and-the-iris-data/