Session Information
Session Type: Poster Session A
Session Time: 9:00AM-11:00AM
Background/Purpose: There is still lack of data on the prognosis of patients with RA who have been infected with SARS-Cov-2 Omicron variant, a new strain with relatively low pathogenicity but high transmissibility. The aim of our study was to evaluate the factors influencing the infection of patients with RA and the COVID-19 outcomes.
Methods: Patients who were infected after December 5, 2022 were collected. The demographic characteristics, comorbidities, clinical profile, medication of RA, and treatment from 1107 patients with RA and 2800 controls were analyzed. The χ2 test, Fisher exact test for class variables, and Mann-Whitney U test were used for continuous variables. The independent correlation factors of hospitalization were estimated using multivariate-adjusted logistic regression.
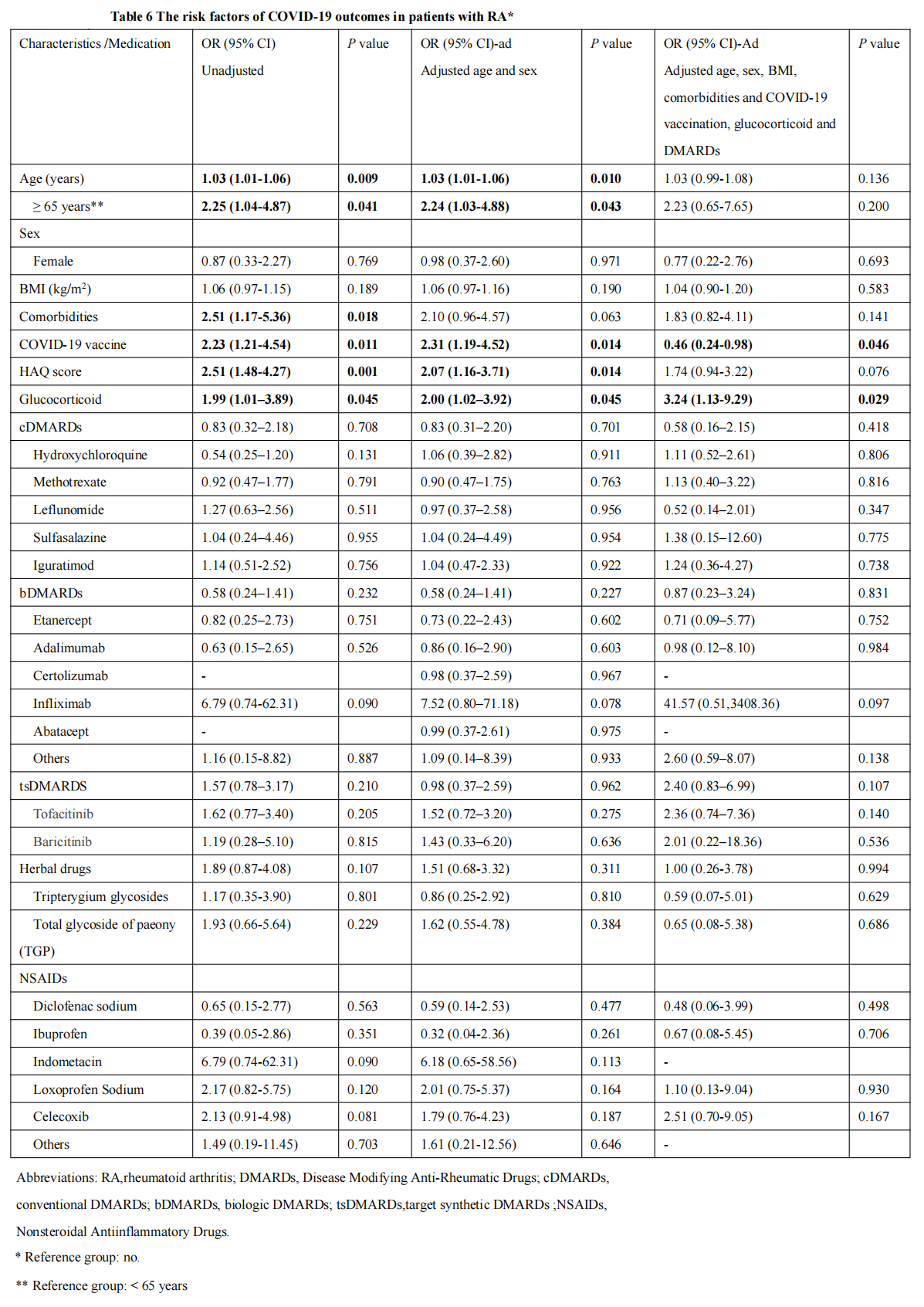
Results: Compared with the control group, patients with RA had significantly higher rates of COVID-19 symptoms. For all patients infected the COVID-19, RA (adjusted OR=2.69, 95%CI 1.37-5.29; p=0.004 ), older age (adjusted OR=1.03, 95%CI 1.01-1.05; p=0.012) and the use of glucocorticoid (adjusted OR=3.24, 95%CI 1.13-9.29; p=0.029) resulted in higher hospitalization rates. Scheduled vaccination (adjusted OR=0.46, CI 0.24-0.98; p=0.046) was a protective factor in patients with stable RA, who have a low hospitalization rate. Nevertheless, disease-modifying antirheumatic drugs (DMARDs) and non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs), which in some studies had to a certain extent on hospitalization rates in RA patients infected with COVID-19 to a certain extent, were not significantly associated with hospitalization in our study.
Conclusion: RA is a risk factor for increased hospitalization in patients with COVID-19, and glucocorticoids is a risk factor for hospitalization in RA patients.
To cite this abstract in AMA style:
Wang Y, zhang m, Zang S, luo l, Li C, He J, li z. Severity and Risk Factors of Hospitalization of Omicron in Patients with Rheumatoid Arthritis [abstract]. Arthritis Rheumatol. 2023; 75 (suppl 9). https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/severity-and-risk-factors-of-hospitalization-of-omicron-in-patients-with-rheumatoid-arthritis/. Accessed .« Back to ACR Convergence 2023
ACR Meeting Abstracts - https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/severity-and-risk-factors-of-hospitalization-of-omicron-in-patients-with-rheumatoid-arthritis/