Session Information
Date: Saturday, November 16, 2024
Title: Vasculitis – Non-ANCA-Associated & Related Disorders Poster I
Session Type: Poster Session A
Session Time: 10:30AM-12:30PM
Background/Purpose: A significant unmet need in Polymyalgia Rheumatica (PMR) is the lack of a disease specific serum biomarker for diagnosis, and monitoring of disease activity. The aim of this study was to evaluate readily available laboratory tests as markers of disease activity in isolated PMR.
Methods: Full blood count, liver function tests, c-reactive protein (CRP), erythrocyte sedimentation rate (ESR), serum fibrinogen, haptoglobins and immunoglobulins were tested on steroid naïve patients recruited from a multicentre fast track PMR clinic, at baseline, subsequent remission, and in the event of disease relapse. Those with signs, symptoms, or imaging confirmation of GCA were excluded.
Normally distributed continuous variables are expressed as means with standard deviations (SD). Continuous variables are compared using the independent t-test. Categorical variables are summarised by frequency and percentage (%) and compared using the chi-square test or Fishers exact test. The association between continuous variables and categorical variables is assessed using the Kruskal-Wallis test. The statistical analysis was performed using SPSS Version 29. P values < 0.05 are considered statistically significant.
Results: 55 patients (52.7% (n=29) female) were included, with a total of 36 relapses.
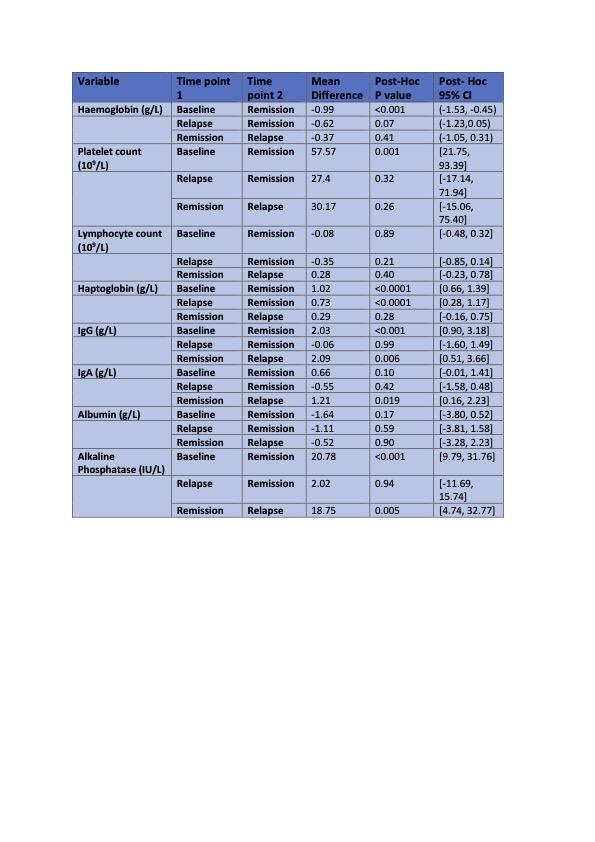
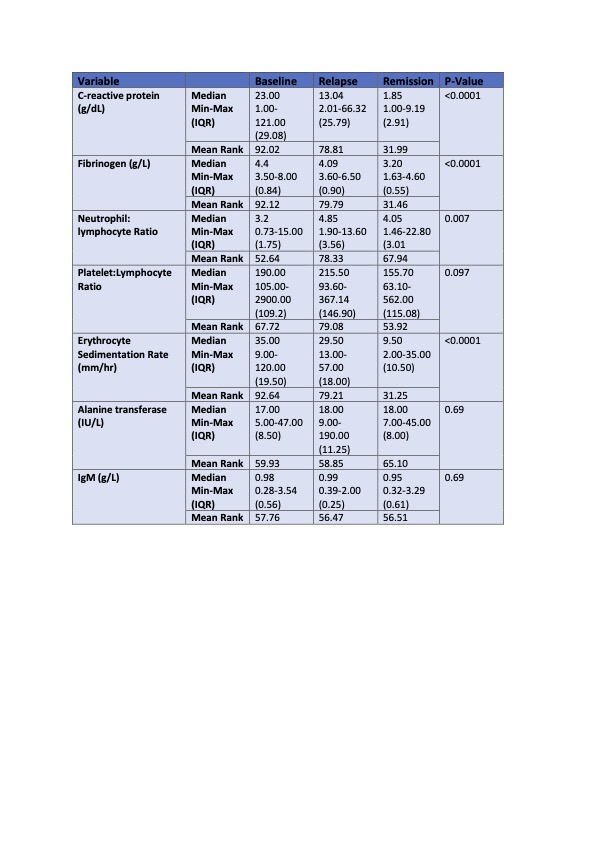
Comparing baseline with remission bloods, there was a statistically significant increased mean difference in platelet count (p=0.001), fibrinogen (p< 0.0001), ESR (p< 0.001), haptoglobin (p< 0.0001), alkaline phosphatase (p< 0.001), CRP (< 0.0001) and IgG (< 0.001). There was also a significant decreased Hb between baseline (p < 0.001) and relapse (0.07) versus remission. When comparing relapse to remission bloods, there was a statistically significant increased mean difference in fibrinogen (p< 0.0001), ESR (p< 0.0001), haptoglobin (p< 0.0001) and CRP (p< 0.0001) during relapse. A ROC analysis was performed with fibrinogen (1.000), ESR (0.986), Haptoglobin (0.976), CRP (0.986) and alkaline phosphatase (0.854) demonstrating high sensitivity and specificity for the detection of increased disease activity at baseline versus remission (p=0.000).
Conclusion: We have demonstrated the clinical utility of using serum fibrinogen, haptoglobin and other readily available serum markers in the diagnosis, and detection of relapse in an Irish isolated PMR cohort. Further studies, incorporating such markers into a diagnostic algorithm are warranted to enhance diagnostic accuracy and detection of relapse in isolated PMR.
To cite this abstract in AMA style:
Harkins P, Cowley S, McKittrick s, Harrington R, Kane D, Conway R. Serum Markers of Disease Activity in Polymyalgia Rheumatica [abstract]. Arthritis Rheumatol. 2024; 76 (suppl 9). https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/serum-markers-of-disease-activity-in-polymyalgia-rheumatica/. Accessed .« Back to ACR Convergence 2024
ACR Meeting Abstracts - https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/serum-markers-of-disease-activity-in-polymyalgia-rheumatica/