Session Information
Session Type: Abstract Submissions (ACR)
Background/Purpose . The recent discovered cytokine interleukin-33 (IL33) could be involved in B-cell activation as well as in RA pathophysiology. After a whole-blood transcriptomic analysis showing that baseline IL-33 mRNA upregulation was associated with clinical response to rituximab (RTX) (1), we investigated whether the serum level of IL-33 was associated with RA features and whether it may predict response to RTX.
Methods . We used ELISA to quantify serum IL-33 level and assessed B-cell–activation biomarkers (rheumatoid factor [RF], anti-CCP antibodies, free light chains, IgG, IgA, IgM, and BAFF levels), serum CXCL12, CXCL13 and CCL19 levels (all log transformed for analysis) in 205 RA patients before receiving a 1st course of RTX (1g on days 1 and 15) in the SMART trial and 63 controls (CT). Uni and multivariate analyses were performed to identify factors associated with a EULAR response 24 weeks after RTX.
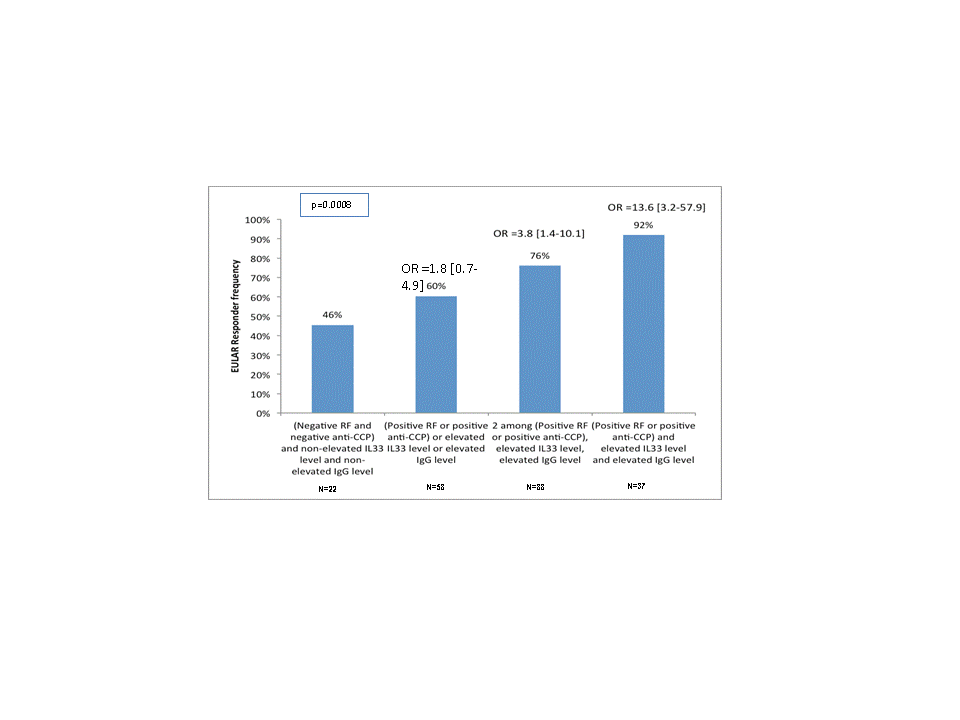
Results . Serum IL-33 level was higher in patients with RA than in CT (median [interquartile range]: 258 [75;1345] vs 35 [22;664] pg/mL; p≤0.001) as well as in anti-CCP positive compared with anti-CCP negative patients (359 [87-1619] vs 102 [39-368] pg/mL, p=0.001). A similar result was observed for RF status (p=0.001). Serum IL-33 level was uncorrelated neither with DAS28 nor with CRP level. Unexpectedly, serum IL-33 level was highly correlated with CCL19 (r=0.7 ; p<0.0001) and CXCL13 levels (r=0.15 p=0.003). There were 146 (71%) responders (i.e. 44 good and 102 moderate). Using ROC curve analyze, 249 pg/mL was the optimal serum IL-33 level cut-off to discriminate responders from non-responders. Multivariate analysis indicated that IL33 level was independently associated with subsequent response to RTX (odds ratio [95% confidence interval]: 2.25 [1.14;4.43]; p=0.02), as well as the presence of anti-CCP antibodies or RF (OR: 2.76 [1.24;6.15]; p=0.01), with a similar trend for IgG level (OR: 2.00 [0.97;4.11]; p=0.059). These 3 parameters acted synergistically on the RTX response prediction since their simultaneous presence, observed in 20% of RA patients in SMART, frankly increased the likelihood of response (OR: 13.6 [3.2;57.9]) (Figure).
Conclusion . Serum IL-33 level, intrinsically increased in RA, represents a simple marker predicting accurately clinical response to RTX, independently of and synergistically with auto-antibodies and serum IgG level.
Disclosure:
J. Sellam,
Roche France,
2;
H. Chavez,
None;
S. Rouanet,
Reche France,
3;
N. Vernet,
Roche France,
3;
B. Ly,
None;
S. Marion-Thore,
None;
B. Combe,
Roche France,
2;
J. Sibilia,
Roche France,
2;
J. Tebib,
Reche France,
2;
G. Chiocchia,
Roche France,
2;
M. Dougados,
Roche France,
2;
Y. Taoufik,
Riche France,
2;
X. Mariette,
Roche France,
2.
« Back to 2014 ACR/ARHP Annual Meeting
ACR Meeting Abstracts - https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/serum-il-33-level-is-increased-in-rheumatoid-arthritis-and-predicts-response-to-rituximab-in-combination-with-high-serum-igg-level-and-autoantibody-positivity-an-open-label-prospective-multicentre/