Session Information
Session Type: Poster Session B
Session Time: 10:30AM-12:30PM
Background/Purpose: IgG4-related disease (IgG4-RD) is a rare, systemic, immunomediated fibroinflammatory process with uncertain etiology and pathophysiology that can affect multiple organs, presenting common clinical, radiological, and serological characteristics. Although the disease is associated with IgG4, serum levels are not elevated in all patients; it has also been described in other respiratory system diseases (bronchiectasis, asthma, sarcoidosis), pancreatic diseases (chronic pancreatitis), liver diseases (cirrhosis), or in relation to other autoimmune diseases such as systemic lupus erythematosus (SLE), rheumatoid arthritis (RA), or inflammatory myopathies. Our objetive is to determine the prevalence and clinical significance of IgG4 positivity in the blood of patients with an initial suspicion of systemic autoimmune disease.
Methods: A single-center cross-sectional study was conducted, in which all results from the electronic medical records of patients with elevated IgG4 ( >135 mg/dL) from a single center and requested by various hospital departments from January 2010 to Juny 2023 were analyzed. Demographic data were collected, as well as final diagnoses, including those with IgG4-RD.
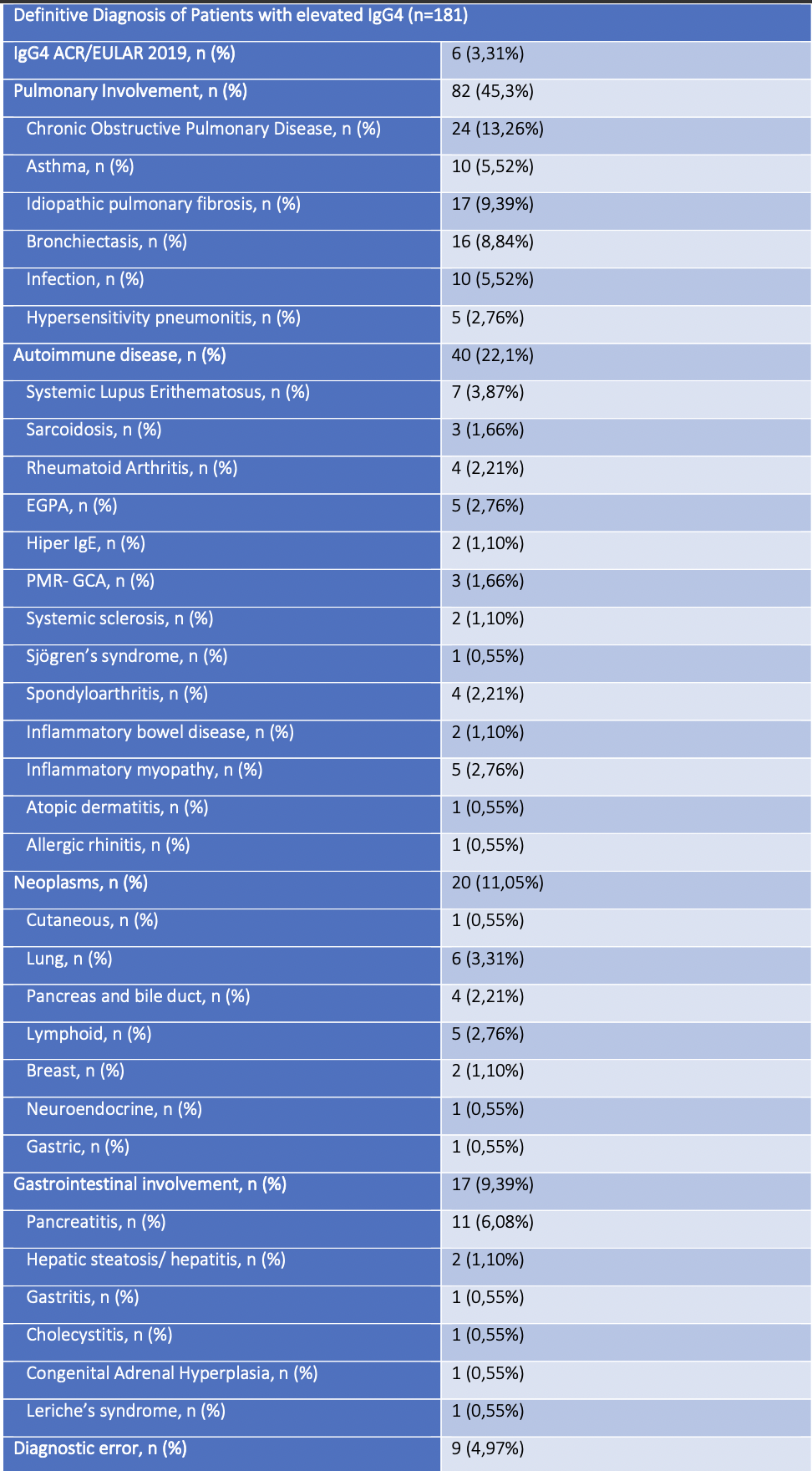
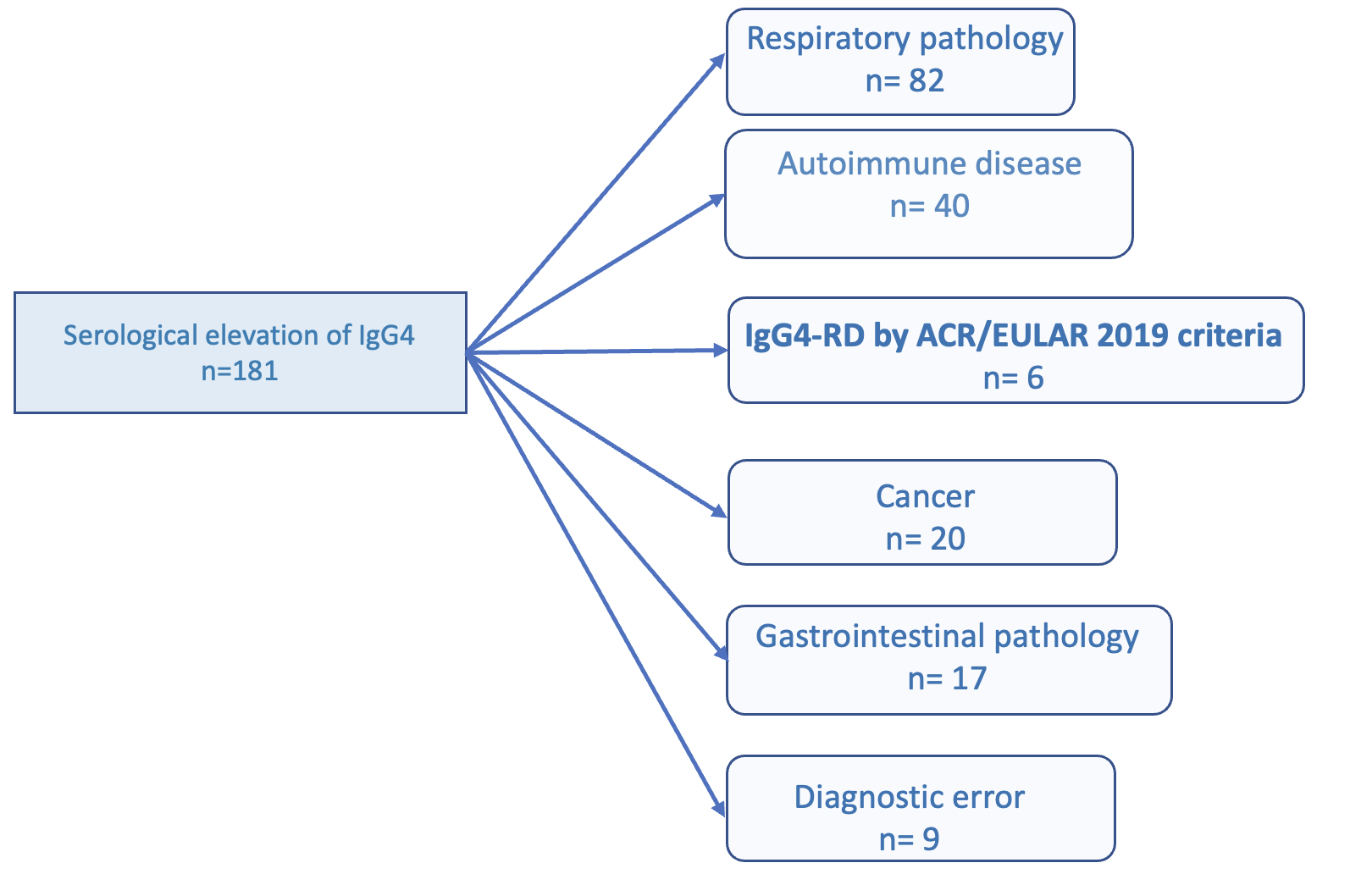
Results: A total of 181 patients with serological elevation of IgG4 were reviewed (Table 1). Of the patients analyzed, only 6 met the diagnostic criteria for IgG4-RD according to the ACR/EULAR 2019 criteria. Among the remaining patients, the majority (45.3%) presented with respiratory pathology, mostly comprising patients with COPD (13.26%), or asthma (5.52%). An elevation of IgG4 was also observed in other systemic autoimmune diseases (22.1%), being more frequent in patients diagnosed with SLE (3.87%), RA (2.21%), or EGPA (2.76%); or patients diagnosed with some malignancy (11.05%), most frequently in pulmonary (3.31%) or pancreatic and biliary tract cancers (2.2%). Finally, elevation of this immunoglobulin was also observed in patients with digestive pathology (9.34%), especially in patients with pancreatitis (6.04%).
Conclusion: Our study indicates that elevated IgG4 levels are not exclusive to IgG4-RD, appearing also in various respiratory (COPD), autoimmune (SLE, RA), and neoplastic conditions. These data suggest that high IgG4 levels may indicate a more generalized immune response and may not be useful as a screening tool for IgG4-RD.
To cite this abstract in AMA style:
Martínez Calabuig P, Salvador Maicas L, Sanmartín Martínez M, Lorente Betanzos I, Fragío Gil J, González Mazario R, Rueda A, Lerma Garrido j, Molina Almela C, Campos Fernández C. Serological Elevation of IgG4: Clinical Correlation and Differential Diagnosis [abstract]. Arthritis Rheumatol. 2024; 76 (suppl 9). https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/serological-elevation-of-igg4-clinical-correlation-and-differential-diagnosis/. Accessed .« Back to ACR Convergence 2024
ACR Meeting Abstracts - https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/serological-elevation-of-igg4-clinical-correlation-and-differential-diagnosis/