Session Information
Date: Monday, November 14, 2022
Title: RA – Treatment Poster IV
Session Type: Poster Session D
Session Time: 1:00PM-3:00PM
Background/Purpose: Around 60% of rheumatoid arthritis (RA) patients treated with ≥1000 mg rituximab (RTX) has an insufficient deemed humoral response after two COVID-19 vaccinations. Recent research shows that a third COVID-19 vaccine may actually lead to a humoral response in 27% of patients with a previous non-response. After two-dose vaccination, both ultra-low dose (ULD) 200 mg RTX and a longer time between latest RTX and vaccination were positively associated with sufficient response. Yet, no data is available on the effect of those variables after a third vaccination in these ULD patients with an insufficient response after two vaccinations. Therefore, the aim of this study was to investigate the role of dosage and relative timing of RTX and vaccination on humoral response after a third COVID-19 vaccine in RA patients who had an insufficient humoral response after two COVID-19 vaccinations.
Methods: We included RA patients treated with ≥1 RTX dose in the year previous to the first vaccine from the COVAC-cohort (Netherlands Trial Register, NL9342), who had an insufficient humoral response after two COVID-19 vaccines. Humoral response was measured 2-6 weeks after the third vaccine. Patients were categorized based on their latest RTX dose before first COVID-19 vaccination. As there is still a lot of uncertainty about a serological correlate of protection, we dichotomized between ‘sufficient’ and ‘insufficient’ response based on the cut-off of the specific assay used. Univariable logistic regression was used to investigate the association between dosing and timing, and sufficient response.
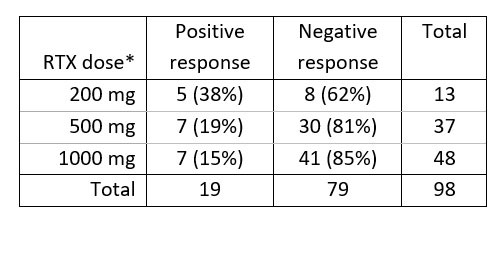
Results: Of the 196 patients in the cohort, 98 could be included in this follow-up study. Third vaccination response was higher for 200 mg RTX users (n=13, 38%; table 1) than 500 and 1000 mg (n=37, 19% and n=48, 15%). Non-significant trends were seen for higher response with lower dosing (200 versus 1000: OR 3.66, 95% CI 0.93-14.0, p=0.06) and later timing (per month since infusion: OR 1.16, 0.97-1.35, p=0.10).
Conclusion: Our study shows that a third COVID-19 vaccine can induce sufficient humoral response in a relevant proportion of (ultra-)low dose RTX treated RA patients who did not respond to the first two vaccinations, and that a RTX dose of 200 mg is associated with a numerical higher proportion of patients with sufficient humoral response. In patients with rheumatoid arthritis treated with rituximab, repeated vaccination as late as possible after the lowest RTX dose possible seems the best vaccination strategy.
To cite this abstract in AMA style:
van der Togt C, Ten Cate D, Rahamat-Langendoen J, van den Bemt B, den Broeder N, den Broeder A. Seroconversion After a Third COVID-19 Vaccination in Rheumatoid Arthritis Patients Treated with (ultra-)low Dose Rituximab with a Previous Insufficient Humoral Response Is Associated with Rituximab Dosage [abstract]. Arthritis Rheumatol. 2022; 74 (suppl 9). https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/seroconversion-after-a-third-covid-19-vaccination-in-rheumatoid-arthritis-patients-treated-with-ultra-low-dose-rituximab-with-a-previous-insufficient-humoral-response-is-associated-with-rituximab-do/. Accessed .« Back to ACR Convergence 2022
ACR Meeting Abstracts - https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/seroconversion-after-a-third-covid-19-vaccination-in-rheumatoid-arthritis-patients-treated-with-ultra-low-dose-rituximab-with-a-previous-insufficient-humoral-response-is-associated-with-rituximab-do/