Session Information
Session Type: Poster Session A
Session Time: 9:00AM-11:00AM
Background/Purpose: High-resolution vessel wall imaging (HR-VWI) is emerging as a tool of notable utility in the diagnosis of central nervous system vasculitis (CNS-V). However, little is known about monitoring the response to treatments in these patients. The aim of this study was to investigate the temporal vessel wall enhancement (VWE) pattern and its clinical practice through the management of patients with CNS-V
Methods: We extracted 9 patients with primary CNS-V who underwent serial high-resolution MRI vessel wall image (HR-VWI) from Cleveland Clinic prospective CNS vasculopathy registry. Visibility and VWE were analyzed in 17 intracranial artery segments (Bilateral ICA, M1, M2, A1, A2, P1, P2, VA, and BA). Intraluminal enhancement was classified into 3 categories (none, eccentric VWE, and concentric VWE).
Results: In unique 153 intracranial arterial segments, 39 arteries (25.5%) had concentric VWE on baseline HR-VWI. The frequencies of intracranial arteries with concentric VWE have decreased to 12.4% (19 of 153 arteries) at 1st follow-up image and 6.5% (10 of 153 arteries) at 2nd follow-up image, respectively (P< 0.001), [figure 1]. By contrast, the prevalence of intracranial arteries without VWE increased over time course (Baseline; 71.9% (110 of 153 arteries), 1st follow-up; 77.1% (118 of 153 arteries), and 2nd follow-up; 86.9% (133 of 153 arteries), P=0.004), [figure 2]. During the follow-up (mean follow-up 15.9 months), two patients had clinical flare-up at 1st follow-up image. New intraluminal enhancements were identified in 5 intracranial artery segments (Eccentric VWE: 0 to 2 arteries, Concentric VWE: 2 to 5 arteries). After intensive immunosuppressive treatment, VWE changes were improved at 2nd follow-up image (None: 27 to 31 arteries, Concentric VWE: 5 to 1 artery), [figure 3].
Conclusion: Decreasing contrast VWE at follow-up images were frequently observed in CNS-V patients after treatment. Patients with flare-up had temporal VWE worsening during the clinical course. Serial vessel wall enhancement pattern on HR-VWI may be useful for monitoring the response to treatment in patients with CNS-V. Larger studies are needed to validate our observation.
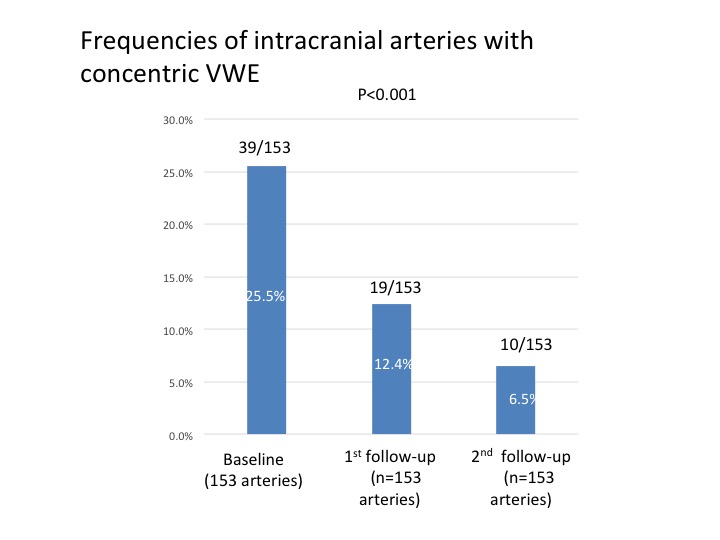 Frequencies of intracranial arteries with concentric vessel wall enhancement (VWE)
Frequencies of intracranial arteries with concentric vessel wall enhancement (VWE)
 Frequencies of intracranial arteries without any vessel wall enhancement (VWE)
Frequencies of intracranial arteries without any vessel wall enhancement (VWE)
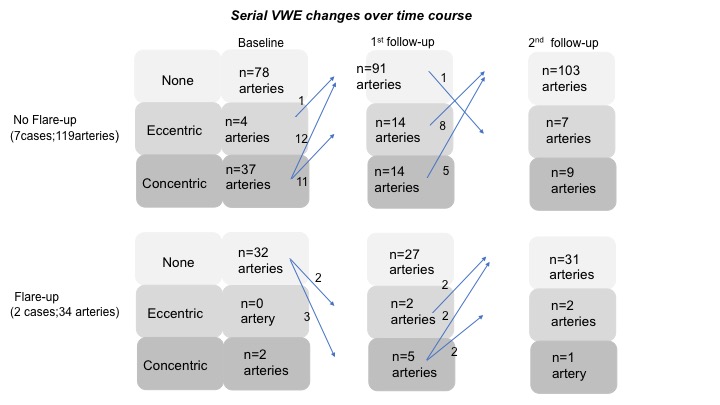 Serial vessel wall enhancement (VWE) changes over time
Serial vessel wall enhancement (VWE) changes over time
To cite this abstract in AMA style:
Shimoyama T, Uchino K, Calabrese L, Hajj-ali R. Serial Vessel Wall Enhancement Change on High-Resolution MRI Vessel Wall Imaging in Primary Central Nervous System Vasculitis [abstract]. Arthritis Rheumatol. 2020; 72 (suppl 10). https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/serial-vessel-wall-enhancement-change-on-high-resolution-mri-vessel-wall-imaging-in-primary-central-nervous-system-vasculitis/. Accessed .« Back to ACR Convergence 2020
ACR Meeting Abstracts - https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/serial-vessel-wall-enhancement-change-on-high-resolution-mri-vessel-wall-imaging-in-primary-central-nervous-system-vasculitis/
