Session Information
Session Type: Abstract Submissions (ACR)
Background/Purpose
ICG-enhanced fluorescence optical imaging (FOI) is a novel technology for the assessment of inflammation in arthritis [1,2]. Recent work suggested that a “green nail” sign in a FOI sequence could possibly be diagnostic for psoriatic arthritis (PsA) [3]. The objective of this study was to determine the sensitivity and specificity of this finding.
Methods
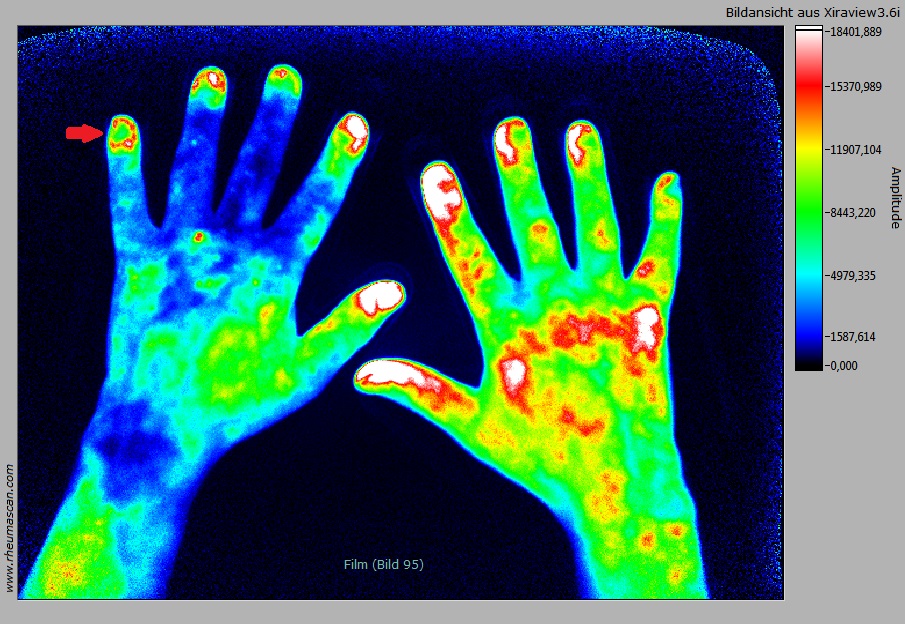
215 consecutive FOI sequences (n=54 PsA, n=29 RF+ RA, n=67 RF- RA, n=19 uA, n=16 SpA, n=30 other) were read for PVM, P1, P2 and P3 [1] separately. “Green nail” was defined as a caldera-like configuration with a larger rounded green area in the center of the nail and a smaller surrounding of circular or semicircular red or white FOI signals (fig).
Results
The green nail sign was observed in 18/54 subjects with PsA (33%), 2/29 RF+ RA (7%), 10/67 RF- RA (15%), 4/19 uA (21%) and 5/46 other diagnoses (11%) (sensitivity of 0.33, specificity of 0.87). In 9 subjects with green nails and diagnoses different from PsA clinical findings (e.g. nail changes, enthesitis, dactylitis) were suspicious to PsA. After exclusion of those cases specificity increased to 0.93. In PsA green nails were observed predominantly in FOI phase 1 or in early phase 2. The finding was observed more frequently in advanced (> 24 months, 13/36, 36%) than in early arthritis (5/18, 28%). The green nail sign has to be distinguished from a green dot phenomenon that was observed in some cases with RA (small green dot at the borderline between nail and nail fold) and from signs of impaired perfusion in connective tissue diseases and vasculitis that are typically located in the distal, acral regions of the fingers.
Conclusion
While the prevalence of the green nail sign in FOI sequences is relatively low the high specificity for psoriatic arthritis suggests that this finding could provide important additional information for differential diagnosis.
References
[1] Werner SG, Langer HE, Ohrndorf S et al, Inflammation assessment in patients with arthritis using a novel in vivo fluorescence optical imaging technology. Ann Rheum Dis 2011;71(4):504-510
[2] Werner SG, Langer HE, Schott P, et al: Indocyanine Green–Enhanced Fluorescence Optical Imaging in Patients With Early and Very Early Arthritis: A Comparative Study With Magnetic Resonance Imaging. Arthritis Rheum 2013; 65(12):3036–3044
[3] Wiemann O, Werner SG, Röver H, Lind-Albrecht G, Mettler S, Backhaus M, Langer HE: The extraarticular patterns of ICG-enhanced fluorescence optical imaging in Psoriatic Arthritis. Ann Rheum Dis 2014;73(Suppl2)
Fig.: Green nail sign (red arrow) in a FOI sequence of a 63-year old male patient with PsA. FOI sequences usually show intense red or white signal intensities in the nail area. In contrast the “green nail” displays a caldera-like green area with a relatively sharp demarcation from the surrounding red FOI signals.
Disclosure:
O. Wiemann,
None;
S. G. Werner,
None;
H. Röver,
None;
G. Lind-Albrecht,
None;
S. Mettler,
None;
M. Backhaus,
None;
H. E. Langer,
The research was supported in part by a grant of Pfizer,
2.
« Back to 2014 ACR/ARHP Annual Meeting
ACR Meeting Abstracts - https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/sensitivity-and-specificity-of-the-green-nail-sign-in-fluorescence-optical-imaging-in-psoriatic-arthritis/