Session Information
Session Type: Abstract Session
Session Time: 2:00PM-3:30PM
Background/Purpose: Systemic lupus erythematosus (SLE) is a common multisystem autoimmune disease with chronic inflammation. Many efficacy evaluation indicators of randomized clinical trials (RCTs) for SLE have been proposed but the comparability remains unknown. We aim to explore the preference and comparability of indicators reporting response rate and provide basis for primary outcome selection when evaluating the efficacy of SLE pharmaceutical treatment.
Methods: We systematically searched 3 databases and 3 registries to identify pharmacological intervention-controlled SLE RCTs. Relative discriminations between indicators were assessed by the Bayesian hierarchical linear mixed model.
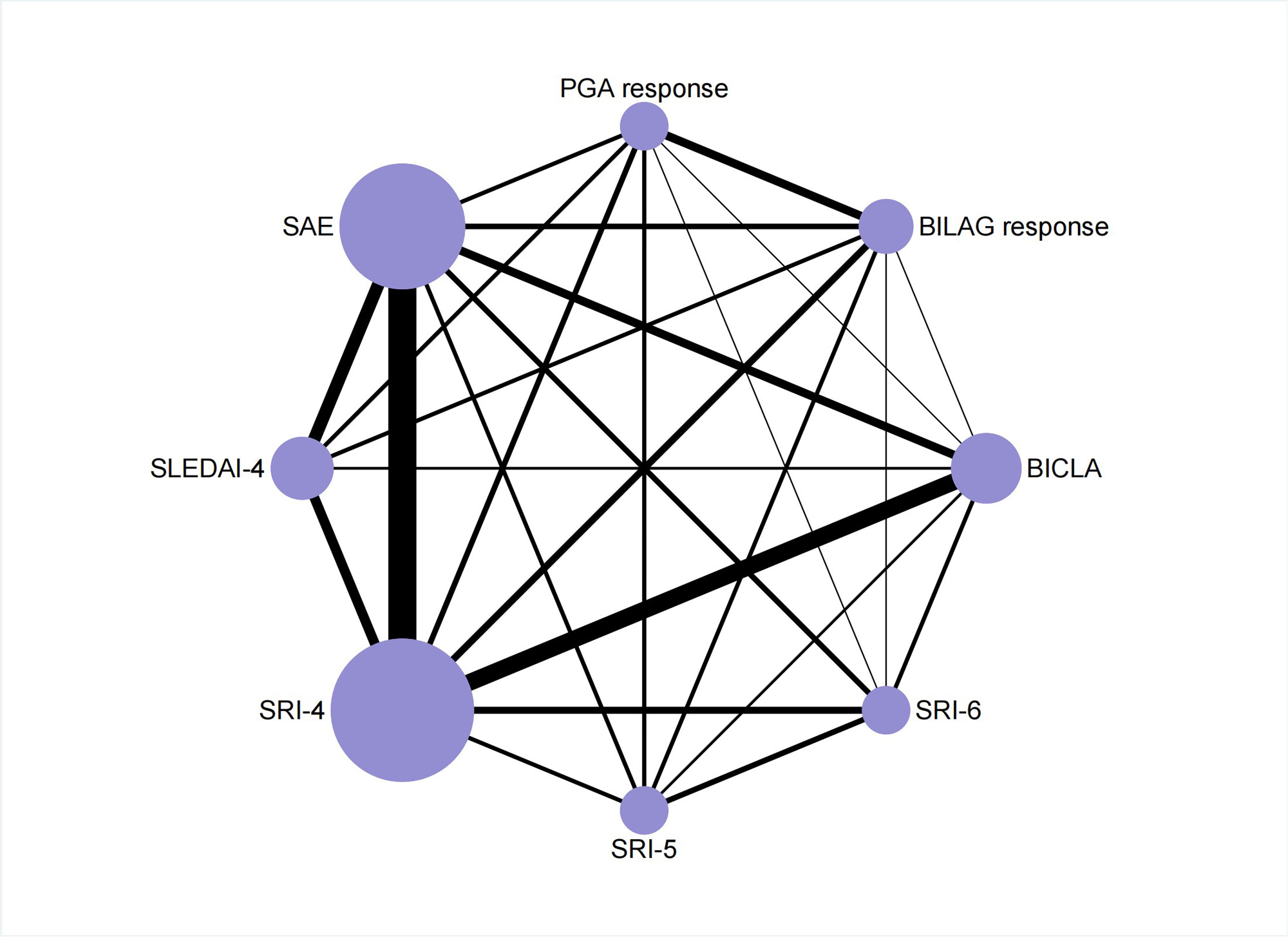
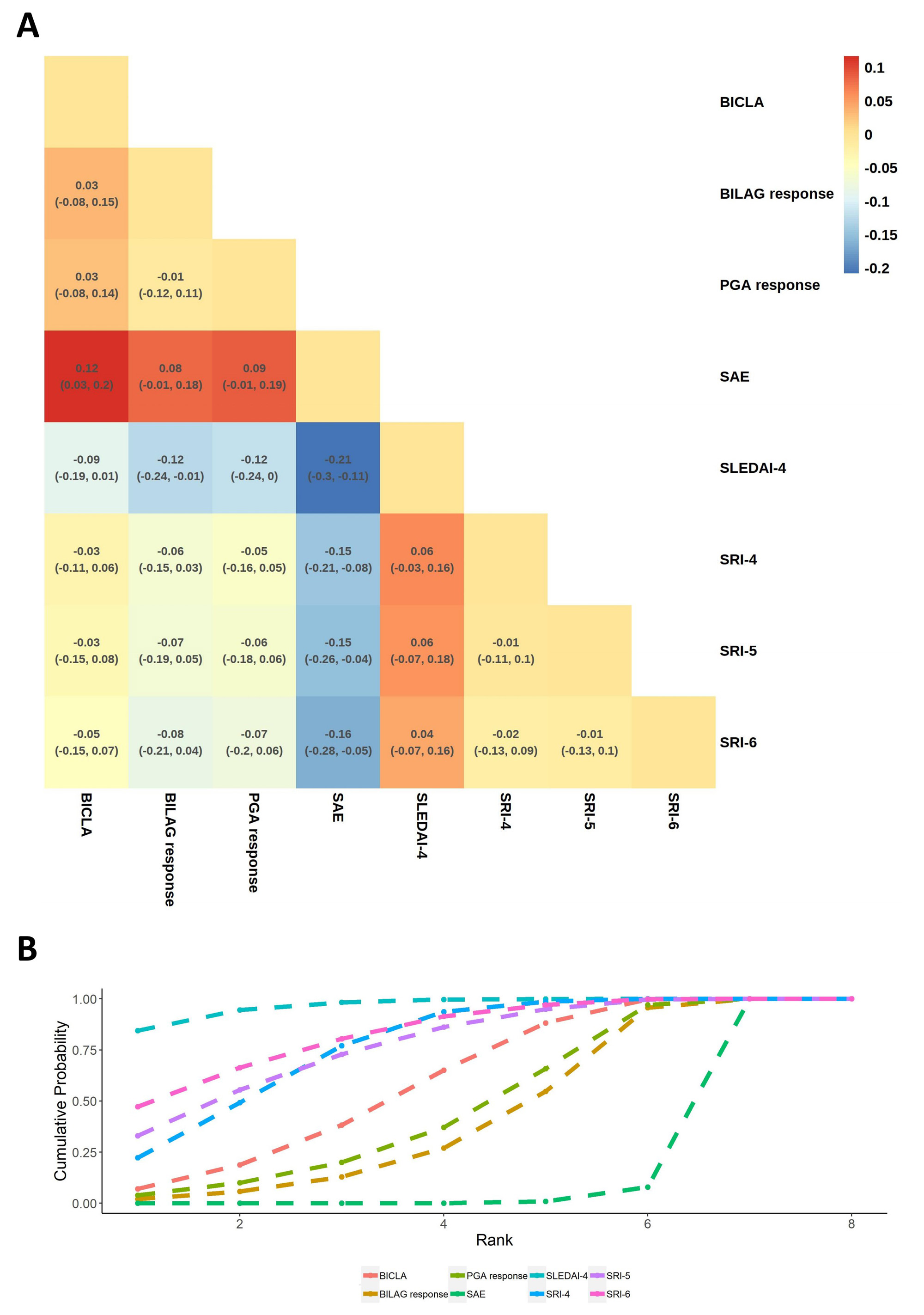
Results: 33 RCTs met our inclusion criteria and we compared 8 of the most commonly used indicators reporting response rate (Figure 1). Systemic Lupus Erythematosus Disease Activity Index (SLEDAI)-4and Systemic Lupus Erythematosus Responder Index(SRI)-4 were considered the best recommended indicators reporting response rate to discriminate the pharmacological efficacy. Indicator preference was altered by disease severity, classification of drugs and outcome of trials, but SLEDAI-4 had robust efficacy in discriminating ability for most interventions. Of note, British Isles Lupus Assessment Group (BILAG) Index-based Combined Lupus Assessment (BICLA) showed efficacy in trials covering all-severity patients, as well as non-biologics RCTs. BILAG response and Physician’s Global Assessment (PGA) response were more cautious in evaluating disease changes. Serious adverse events (SAE) was often applied to evaluate the safety and tolerability of treatments rather than efficacy (Figure 2).
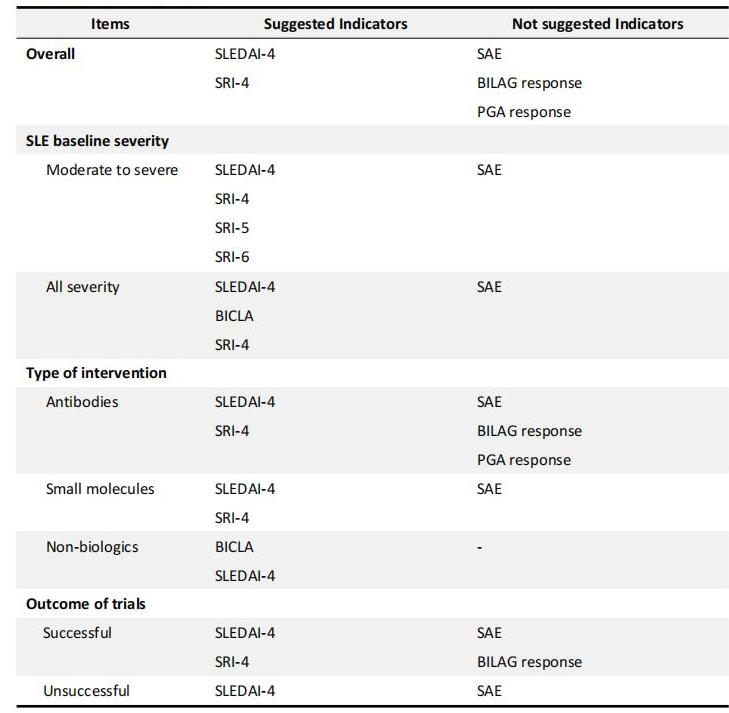
Conclusion: The impressionable efficacy discrimination ability of indicators highlights the importance of flexibility and comprehensiveness when choosing primary outcome(s) (Table 1). As for trials that are only evaluated by SLEDAI-4, attention should be paid to outcome interpretation to avoid the exaggeration of treatment efficacy.
The size of the nodes (purple circles) corresponds to the number of trials. Comparisons are linked with a line, the thickness of which corresponds to the number of trials that assessed the comparison.
(A) Bayesian hierarchical linear mixed model estimated effectiveness with 95% uncertainty intervals on indicators reporting response rate in pharmacological intervention-controlled RCTs for SLE.
(B) The rank of indicators reporting response rate. The sooner an indicator reaches 1, the stronger ability to discriminate treatment efficacy.
To cite this abstract in AMA style:
Tian J, Kang S, Zhang D, Lu Q. Selection of Indicators Reporting Response Rate in Pharmaceutical Trials for Systemic Lupus Erythematosus: Preference and Relative Sensitivity [abstract]. Arthritis Rheumatol. 2023; 75 (suppl 9). https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/selection-of-indicators-reporting-response-rate-in-pharmaceutical-trials-for-systemic-lupus-erythematosus-preference-and-relative-sensitivity/. Accessed .« Back to ACR Convergence 2023
ACR Meeting Abstracts - https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/selection-of-indicators-reporting-response-rate-in-pharmaceutical-trials-for-systemic-lupus-erythematosus-preference-and-relative-sensitivity/