Session Information
Session Type: Poster Session A
Session Time: 10:30AM-12:30PM
Background/Purpose: Treatment options for psoriasis or psoriatic arthritis (PsA) have expanded in the past decade. Secular trends in biologic disease modifying antirheumatic drug (bDMARD) prescribing for this population have not been described.
Methods: We used data from the US-based TriNetX electronic health records database. Patients were included if they had ICD-9-CM or ICD-10-CM codes for psoriasis or PsA and were new users of bDMARDs that had regulatory approval for psoriasis or PsA, which included tumor necrosis factor alpha inhibitors (TNFi), interleukin-17A inhibitors (IL17i), interleukin-23 inhibitors (IL-23i), or interleukin-12/23 inhibitors (IL-12/23i). Patients were categorized by the first bDMARD class they were prescribed. The proportion of new users by year was graphed.
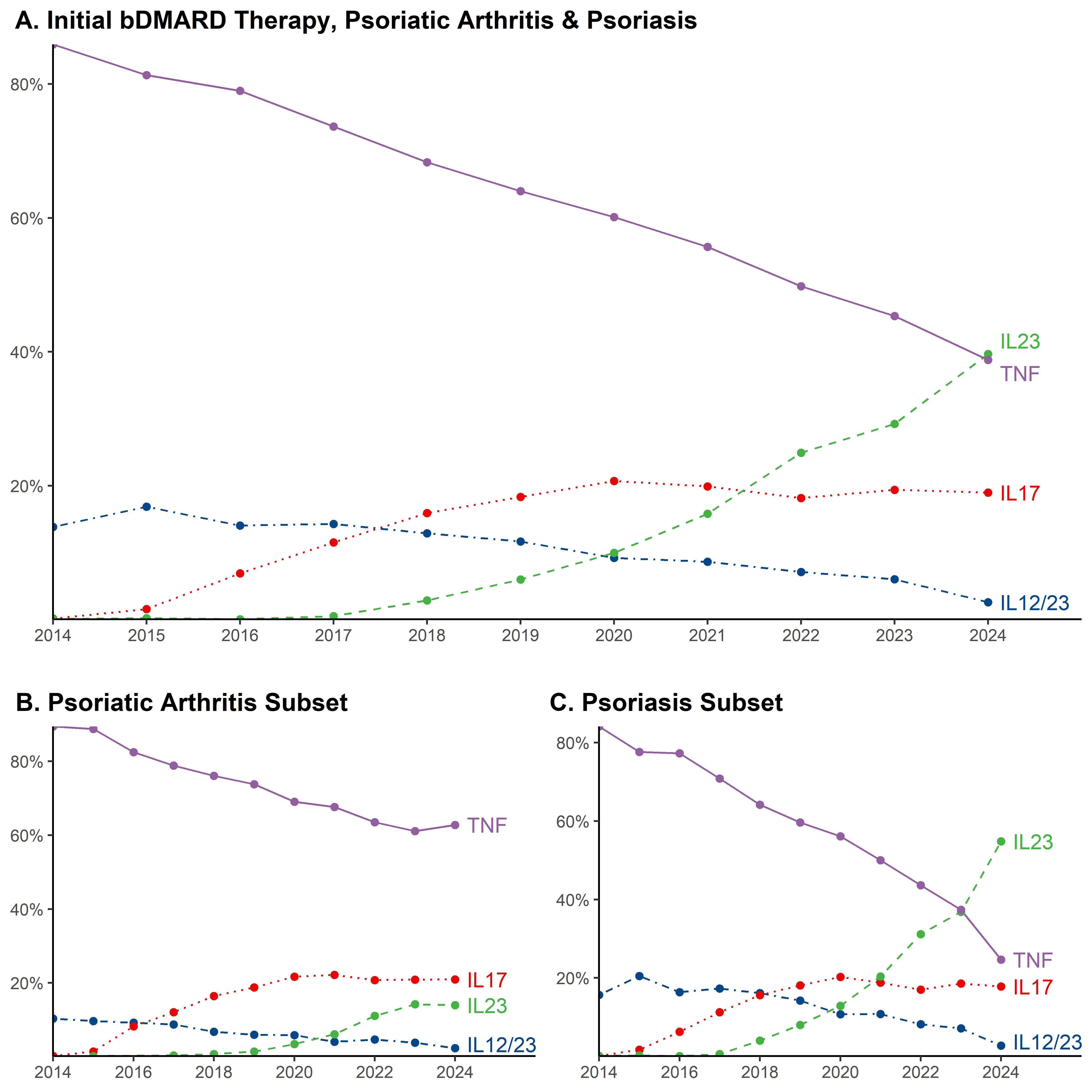
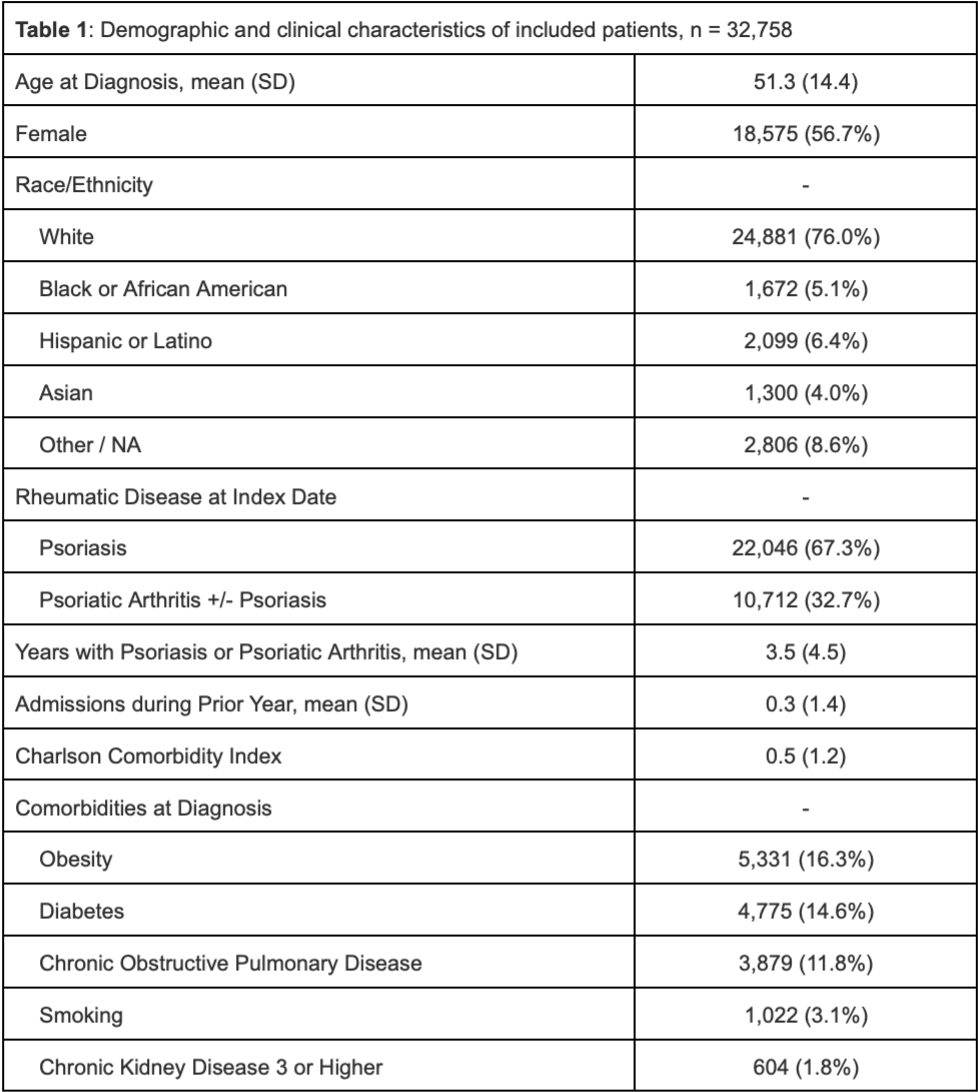
Results: We identified 32,758 patients (mean age at diagnosis 51.3 years, 56.7% female) who initiated biological therapies for psoriasis/PsA. Patients had psoriasis/PsA for a mean of 3.5 years (SD 4.5) prior to starting a biologic agent, the most common of which was a TNFi (62.9%) followed by IL-17i (15.4%), IL-23i (10.7%), and IL12/23i (10.7%). In the overall cohort, from 2014 to 2024 the proportion who initiated bDMARD therapy decreased for TNFi (85.0% to 38.8%) and IL-12/23i (13.8% to 2.6%) and increased for IL-17i (0.2% to 19%) and IL-23i (0.1% to 39.7%). Among patients with psoriasis, from 2014 to 2024 the proportion who initiated bDMARD therapy decreased for TNFi (84.1% to 24.7%) and IL-12/23i (15.7% to 2.7%) and increased for IL-17i (0.1% to 17.8%) and IL-23i (0.1% to 54.8%). Among patients with PsA, the proportion who initiated bDMARD therapy decreased for TNFi (89.4% to 62.8%) and IL-12/23i (10.4% to 2.3%) and increased for IL-17i (0.2% to 20.9%) and IL-23i (0.0% in 2014 to 14.0% in 2024).
Conclusion: TNF-i remain the most prescribed bDMARDs for PsA, despite the fact that the recent guidelines from European Alliance of Associations in Rheumatology (EULAR) and Group for Research and Assessment of Psoriasis and Psoriatic Arthritis (GRAPPA) do not advocate any particular class of bDMARDs over another as the preferred first line agent. However, IL-23i have become the most-prescribed initial bDMARD for psoriasis. The use of IL-17i has plateaued and IL12/23i are rarely prescribed as initial therapy. Preferences for IL-23i for psoriasis could be driven by several factors, including but not limited to superior skin efficacy, better side effect profile and dosing convenience.
Abbreviations: tumor necrosis factor alpha inhibitor (TNF); interleukin 12_23 inhibitor (IL12//23); interleukin 17 inhibitor (IL17); interleukin 23 inhibitor (IL23)
*Incomplete data for 2024
To cite this abstract in AMA style:
Mirza M, Liew J, Putman M, Singla S. Secular Trends in Biologic Prescribing for Psoriasis and Psoriatic Arthritis, 2014-2024 [abstract]. Arthritis Rheumatol. 2024; 76 (suppl 9). https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/secular-trends-in-biologic-prescribing-for-psoriasis-and-psoriatic-arthritis-2014-2024/. Accessed .« Back to ACR Convergence 2024
ACR Meeting Abstracts - https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/secular-trends-in-biologic-prescribing-for-psoriasis-and-psoriatic-arthritis-2014-2024/