Session Information
Session Type: ACR Late-breaking Abstract Session
Session Time: 4:30PM-6:00PM
Background/Purpose: Secukinumab, a fully human anti–interleukin-17A monoclonal antibody, reported improved signs and symptoms of ankylosing spondylitis (AS) in the MEASURE 1 trial.1 Here, we report efficacy, including imaging outcomes, and safety from the MEASURE 1 extension trial (NCT01863732) out to 4 years (208 weeks [wks]).
Methods: In the core study, 371 patients (pts) with active AS were randomized to secukinumab or placebo (PBO). Pts on secukinumab had a 10 mg/kg iv loading dose at baseline (BL), Wks 2 and 4, and then 150 mg sc (IV→150 mg) or 75 mg sc (IV→75 mg) every 4 wks from Wk 8 (same schedule for PBO). Based on ASAS20 response at Wk 16, PBO pts were re-randomized to secukinumab 150 or 75 mg sc at Wk 16 (non-responders) or Wk 24 (responders). Efficacy data at Wk 208 are reported for pts originally randomized to secukinumab 150 mg (approved dose with sc loading). Lateral radiographs of the cervical and lumbar spine at BL, Wk 104 and Wk 208 were read centrally by 2 independent readers, blinded to treatment arm and radiograph sequence, using the modified Stoke Ankylosing Spondylitis Spinal Score (mSASSS). For this analysis, radiographs performed at BL and Wk 104 were re-read for pts who completed 208 wks of treatment. Descriptive statistics on observed or imputed data are provided.
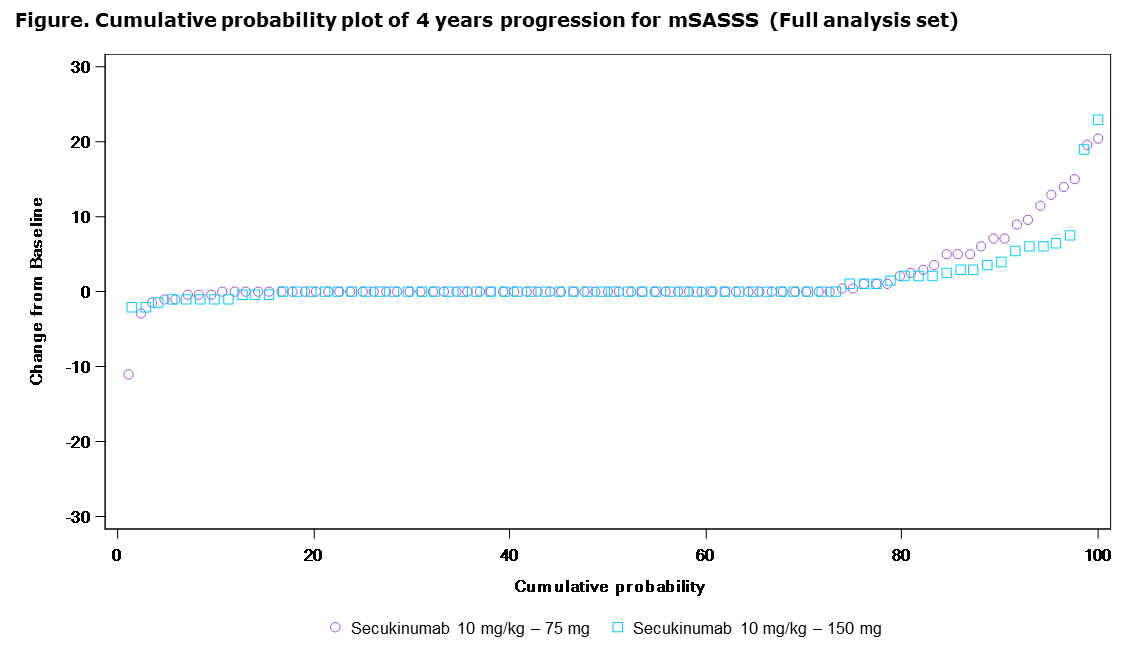
Results: Of the 274 patients in this extension study, 89.7% (78/87) originally assigned to secukinumab 150 mg completed 208 wks. Mean (±SD) change in mSASSS from BL to Wk 208 was lower with secukinumab 150 mg (1.2±3.91) vs 75 mg (1.7±4.70). No radiographic progression was seen in 73% (mSASSS change from BL ≤0) and 79% (mSASSS change from BL <2) of pts with secukinumab over 208 wks (Figure). Mean mSASSS changes at Wk 208 were numerically higher in males vs females, pts with elevated vs normal BL hsCRP, and pts with vs without BL syndesmophytes. Sustained efficacy in signs/symptoms was seen through Wk 208, evidenced by ASAS 20/40, BASDAI, BASFI, BASMI and ASDAS inactive disease (Table). Efficacy responses were numerically lower with secukinumab 75 mg vs 150 mg. Across the entire treatment period (secukinumab exposure [mean±SD]: 3.4±1.44 years), exposure-adjusted incidence rates for serious infections, Crohn’s disease, uveitis and malignant/unspecified tumors were 1.0, 0.6, 1.8 and 0.5 per 100 pt-years, respectively.
Conclusion: Secukinumab 150 mg demonstrates lower radiographic progression vs 75 mg at 4 years. These 4-year results confirm the sustained efficacy and known safety profile of secukinumab.1
References: 1. Braun J et al. Ann Rheum Dis 2016;0:1‒8
Table. Summary of efficacy data at Wk 208
|
Secukinumab IV→150mg (N=87) |
|
|
Radiographic outcomesa,b |
|
|
mSASSS at BL, mean±SD |
8.8±16.23 (n=71) |
|
Change in mSASSS from BL to Wk 208, mean±SD |
1.2±3.91 (n=71) |
|
Change in mSASSS from BL to Wk 104, mean±SD |
0.6±1.84 (n=57) |
|
Change in mSASSS from Wk 104 to Wk 208, mean±SD |
0.6±2.61 (n=58) |
|
Other efficacy outcomes |
|
|
ASAS20 / 40,c % |
76.4 / 58.0 |
|
BASDAI,d change from BL, LS mean±SE |
–3.3±0.23 |
|
ASDAS inactive disease,c % |
11.6 |
|
BASFI,b change from BL, mean±SD |
–2.9±2.39 (n=80) |
|
BASMI,b change from BL, mean±SD |
–0.52±1.12 (n=76) |
|
BL, baseline; LS, least squares; n, number of pts meeting criteria; N, total number of pts in the extension trial; SD, standard deviation; SE, standard error aRadiographs performed at BL and Wk 104 were re-read for pts who completed 208 wks of treatment; bObserved data; cEstimated using multiple imputation; dMMRM estimates |
|
Disclosure: J. Braun, Abbvie (Abbott), Amgen, BMS, Boehringer, Celgene, Celltrion, Centocor, Chugai, EBEWE Pharma, Medac, MSD (Schering-Plough), Mundipharma, Novartis, Pfizer (Wyeth), Roche, Sanofi-Aventis and UCB, 2,Abbvie (Abbott), Amgen, BMS, Boehringer, Celgene, Celltrion, Cetocor, Chugai, EBEWE Pharma, Medac, MSD (Schering-Plough), Mundipharma, Novartis, Pfizer (Wyeth), Roche, Sanofi-Aventis and UCB, 5,Abbvie (Abbott), Amgen, BMS, Boehringer, Celgene, Celltrion, Centocor, Chugai, EBEWE Pharma, Medac, MSD (Schering-Plough), Mundipharma, Novartis, Pfizer (Wyeth), Roche, Sanofi-Aventis and UCB, 8; X. Baraliakos, AbbVie, Merck, Pfizer, UCB, Novartis, and Chugai, 2,AbbVie, Merck, Pfizer, UCB, Novartis, and Chugai, 5,AbbVie, Merck, Pfizer, UCB, Novartis, and Chugai, 8; A. A. Deodhar, AbbVie, Amgen, Eli Lilly, GSK, Janssen, Novartis, Pfizer, UCB, 2,AbbVie, Amgen, Janssen, Novartis, Pfizer, UCB, 5; D. Poddubnyy, AbbVie, MSD, Novartis, 2,AbbVie, BMS, MSD, Novartis, Pfizer, UCB, 5,AbbVie, BMS, Janssen, MSD, Novartis, Pfizer, UCB, 8; P. Emery, AbbVie, BMS, Merck, Novartis, Pfizer, Roche, UCB, 5; E. M. Delicha, Norartis Pharma AG, 3; Z. Talloczy, Novartis Pharmaceutical Corporation, 1,Novartis Pharmaceutical Corporation, 3; B. Porter, Novartis Pharmaceutical Corporation, 1,Novartis Pharmaceutical Corporation, 3.
To cite this abstract in AMA style:
Braun J, Baraliakos X, Deodhar AA, Poddubnyy D, Emery P, Delicha EM, Talloczy Z, Porter B. Secukinumab Demonstrates Low Radiographic Progression and Sustained Efficacy through 4 Years in Patients with Active Ankylosing Spondylitis [abstract]. Arthritis Rheumatol. 2017; 69 (suppl 10). https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/secukinumab-demonstrates-low-radiographic-progression-and-sustained-efficacy-through-4-years-in-patients-with-active-ankylosing-spondylitis/. Accessed .« Back to 2017 ACR/ARHP Annual Meeting
ACR Meeting Abstracts - https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/secukinumab-demonstrates-low-radiographic-progression-and-sustained-efficacy-through-4-years-in-patients-with-active-ankylosing-spondylitis/