Session Information
Session Type: Poster Session A
Session Time: 10:30AM-12:30PM
Background/Purpose: Vaccine acceptance is important to achieve high vaccination coverage and possibly herd immunity. Related to the evolution of the SARS-CoV-2 pandemic with its socio-political implications and efforts to mitigate it, public acceptance of the vaccine may have changed over time and have influenced vaccine uptake.The aim of this study was to examine the extent to which the initial acceptance or hesitancy to vaccinate against SARS-CoV-2 have changed over time, whether this has influenced vaccine uptake, and to identify predictive factors for vaccine hesitancy. In addition, we compared vaccine uptake of IRD patients with data from the general population in Germany.
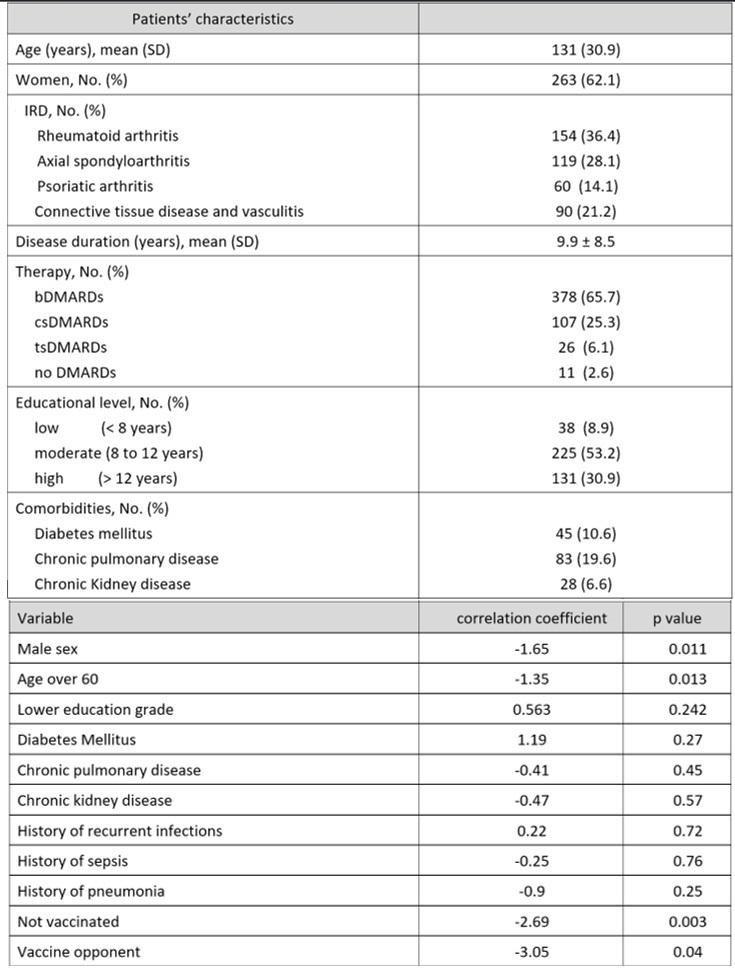
Methods: Sociodemographic and disease-specific data and comorbidities of patients with IRD presenting to our tertiary center between February-April 2021 were assessed and patients were asked to complete a structured questionnaire on SARS-CoV-2 vaccination including a question on their acceptance of vaccination against SARS-CoV- 2 on a numerical rating scale (NRS) from 0 to 10. We defined patients as being hesitant if their score was < 5. Information on SARS-CoV-2 vaccination was collected from their medical records between January and December 2021. Information on the general population in Germany was collected from COVIMO (COVID-19 Vaccination Rate Monitoring in Germany) reports. Binomial logistic regression was used to identify predictors of hesitancy and chi-square tests to assess differences between groups.
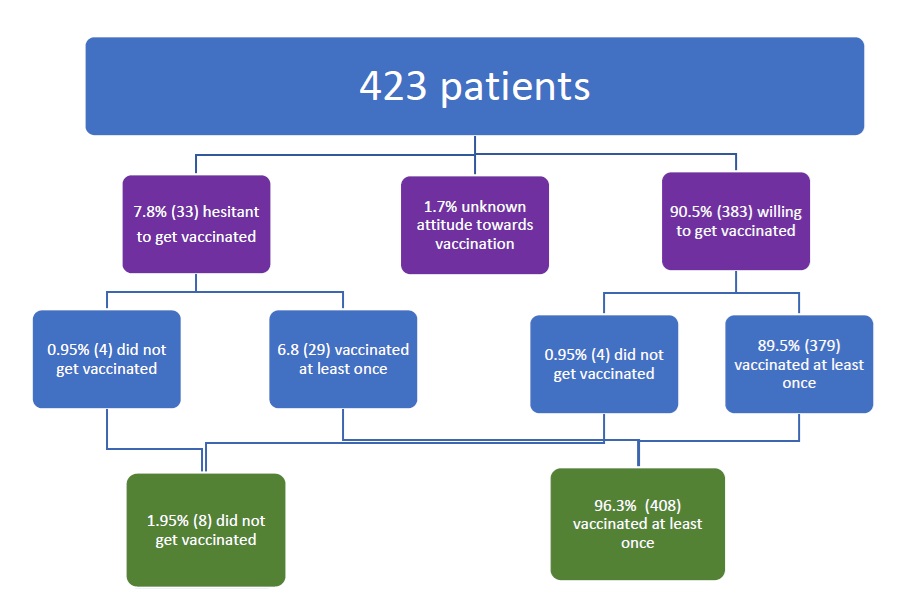
Results: Complete vaccination data of 423 out of 514 patients initially enrolled in the study (82.2%) were available. The majority of patients (n=383) agreed to receive SARS-CoV-2 vaccination (90.5%), while only 33 had been hesitant (7.8%). A total of 379 initially acceptive patients were at least once vaccinated (98.9%). On the other hand, 29 of the initially hesitant patients (87.8%) received at least one vaccination (Fig.1).
Regarding the temporal distribution of vaccine uptake there was no significant difference between patients who had initially been hesitant and those who had initially accepted and then ultimately underwent vaccination. Both groups had an approximately 50% uptake until July 2021: 48.2% vs 66.2% (p=0.18). A logistic regression model to identify predictors of vaccination hesitancy showed that out of all variables analysed, only female sex, age below 60 years and being a vaccine opponent significantly predicted hesitancy (p=0.005). According to COVIMO reports between February-April 2021, 79.5% of the general adult population in Germany agreed to be vaccinated, while 20.5% were hesitant. Furthermore, the vaccination rate of patients receiving 2 vaccinations in December 2021 (Table1) was higher in IRD patients (88.8%) than in the general German population (85.4%).
Conclusion: In this study, we observed a high vaccination uptake rate in IRD patients – even a higher than expected from the reported vaccination acceptance rate and potentially a bit higher than in the general population. Indeed, most IRD patients had received the basic vaccination on time. The vaccination campaigns and educational activities performed may have been successful. In this regard, more attention should be paid to young patients and females.
To cite this abstract in AMA style:
roman i, Baraliakos X, Kiltz U, Braun J, Andreica I. SARS-CoV-2 Vaccine Acceptance, Hesitancy and Uptake in a Cohort of Patients with Inflammatory Rheumatic Diseases (IRD) [abstract]. Arthritis Rheumatol. 2024; 76 (suppl 9). https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/sars-cov-2-vaccine-acceptance-hesitancy-and-uptake-in-a-cohort-of-patients-with-inflammatory-rheumatic-diseases-ird/. Accessed .« Back to ACR Convergence 2024
ACR Meeting Abstracts - https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/sars-cov-2-vaccine-acceptance-hesitancy-and-uptake-in-a-cohort-of-patients-with-inflammatory-rheumatic-diseases-ird/