Session Information
Date: Saturday, November 6, 2021
Title: Epidemiology & Public Health Poster I: COVID-19 & Vaccination (0084–0117)
Session Type: Poster Session A
Session Time: 8:30AM-10:30AM
Background/Purpose: The relative risk of COVID-19 among patients with rheumatic and musculoskeletal disease (RMD) and the comparative severity of COVID-19 infection in RMD remain uncertain. This systematic review seeks to quantify the risk for SARS-CoV-2 infection and to describe the clinical course and outcomes of COVID-19 in people with RMD.
Methods: A systematic literature search was conducted across 14 databases from inception to February 13th 2021. We included observational studies and experimental trials in RMD patients reporting the following outcomes: 1) comparative rates of SARS-CoV-2 infection, 2) hospitalization, 3) oxygen supplementation/ICU admission/mechanical ventilation, and 4) mortality. Studies were screened, data extracted, and quality assessment performed by two independent reviewers with a third reviewer to resolve conflicts. The methodological quality of all included studies was evaluated using the Newcastle-Ottawa scale or JBI Critical Appraisal Tools.
Results: Of 5799 abstracts screened, 528 articles underwent full text review, and 100 studies met criteria for inclusion. Most studies (54%) had low risk of bias. br>
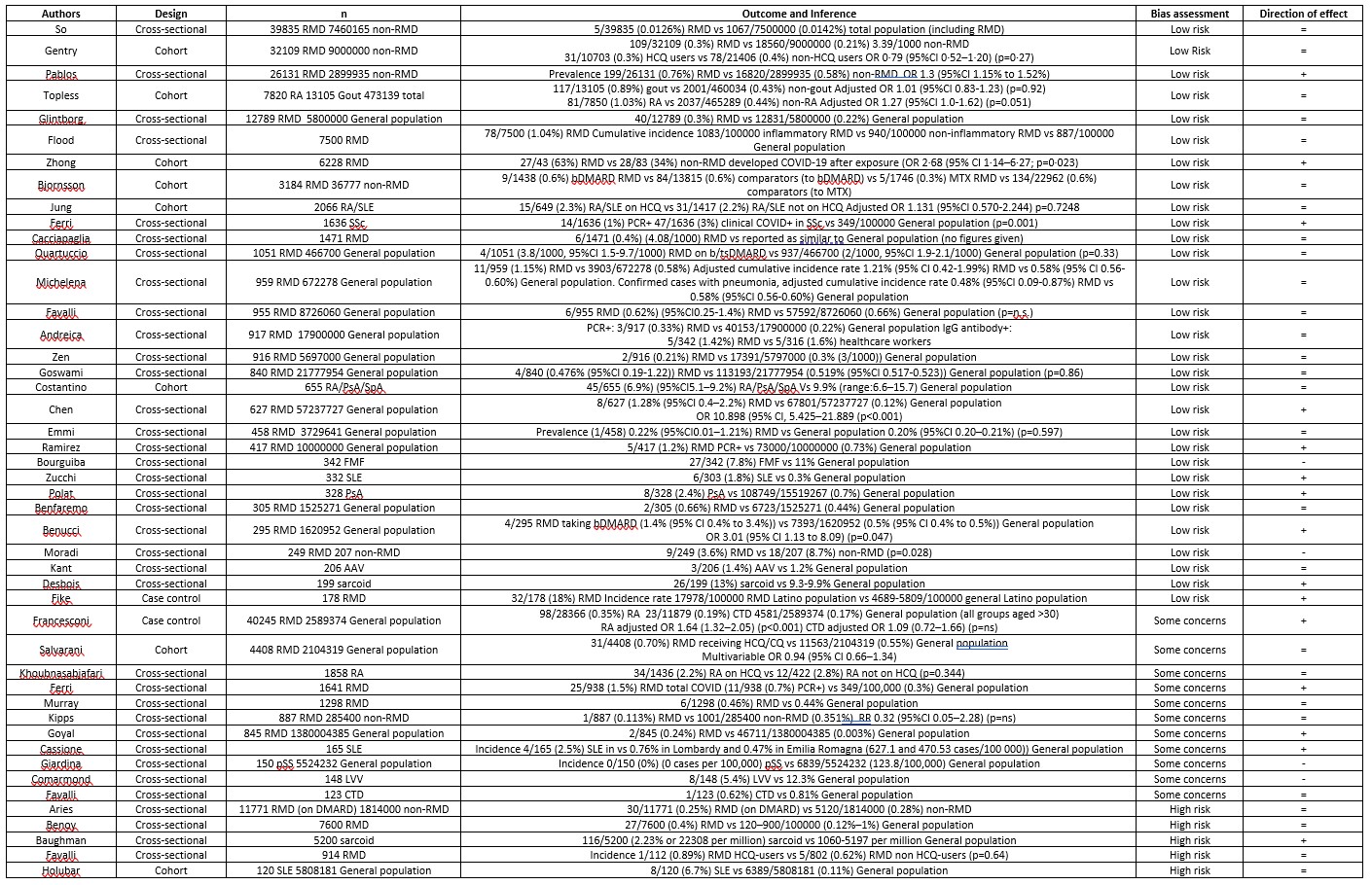
47 studies reported comparative rates of SARS-CoV-2 infection in people with RMD, 15 showed increased rates, 28 no difference, and 4 decreased rates (Table 1). Adjusted comparative risk measures were reported in 8 studies; 4 reported increased risk, 4 showed no difference in risk.
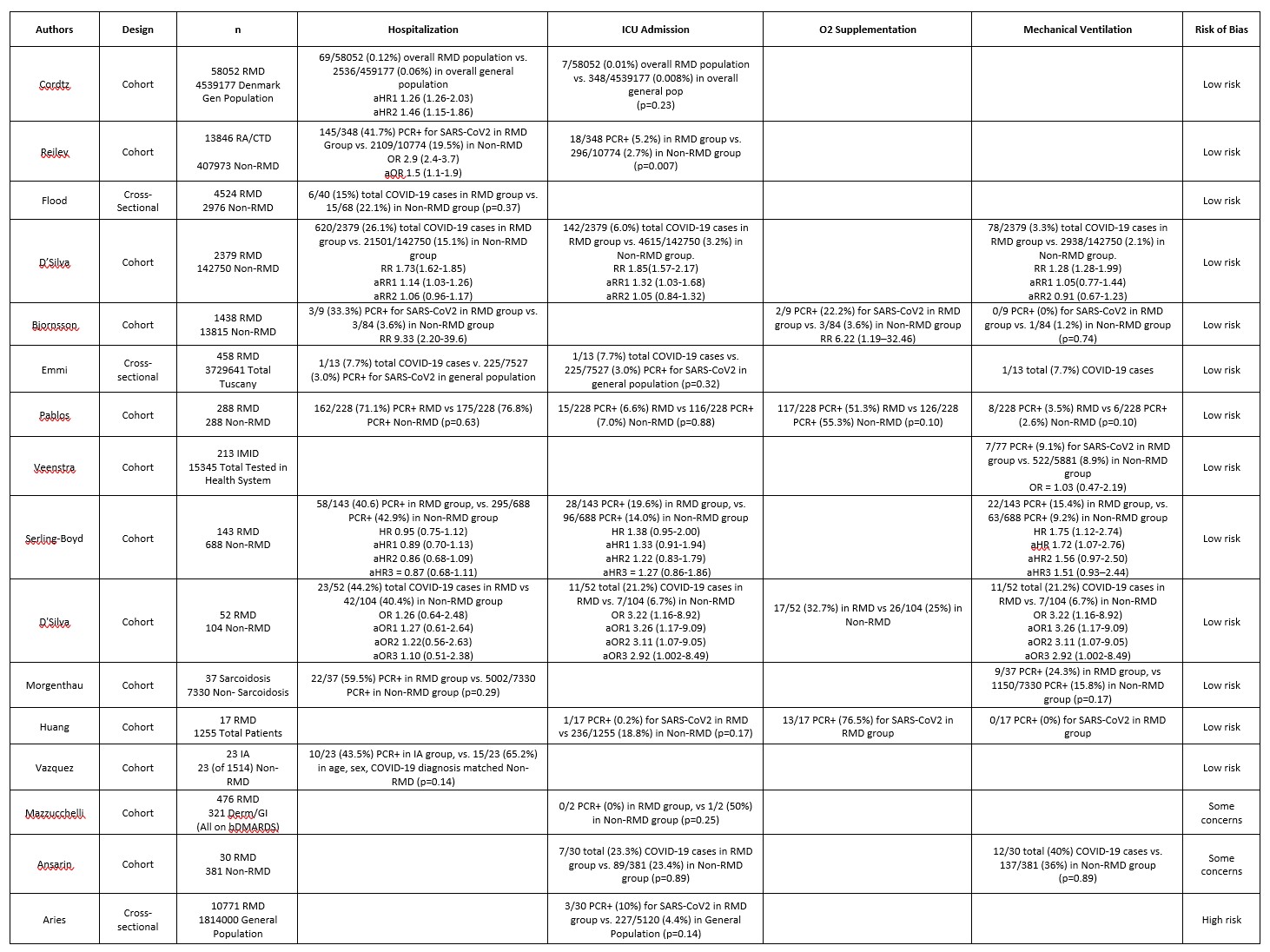
70 studies reported hospitalization rates among RMD patients. Of the 11 studies providing comparative data (Table 2) 3 showed increased risk among patients with RMD, and 7 showed no significant effect. No studies found decreased risk for hospitalization. In 5 studies reporting adjusted analyses, 2 reported increased risk, whereas 3 found no significant differences.
In terms of oxygen supplementation (n=28 studies), 3 studies reported comparative findings: 1 showed increased risk among patients with RMD, while 2 found no significant difference. Regarding ICU admission (n=52 studies), 11 comparative studies were identified, 2 showed increased risk among RMD patients and the remainder showed no differences. For mechanical ventilation (n=42 studies), among 8 comparative studies, 7 showed no effect of RMD status and 1 showed a positive correlation. Only 2 studies reported adjusted risk estimates for ICU admission/mechanical ventilation, with 1 reporting a positive correlation, and the other, no effect.
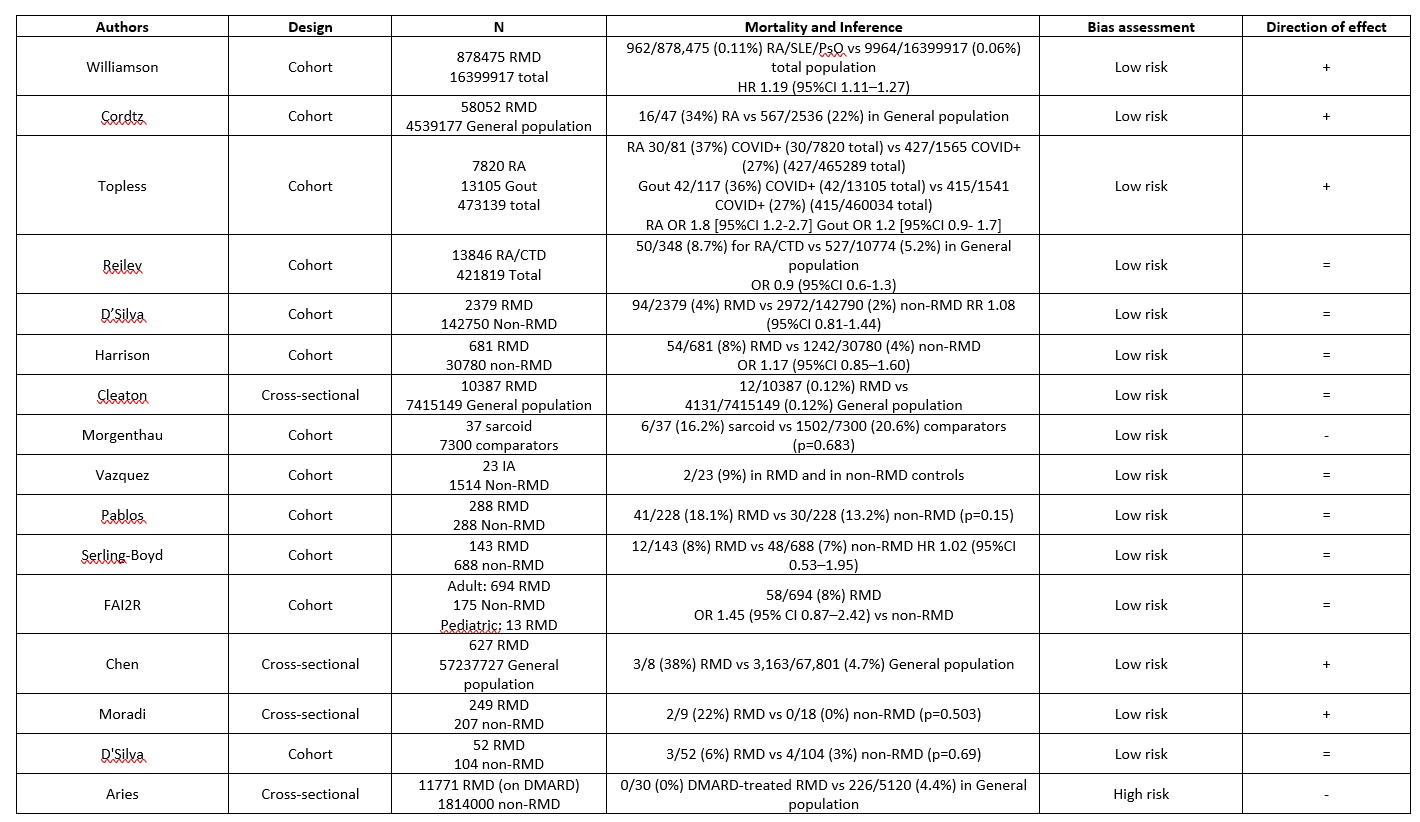
71 studies reported mortality;16 reported comparative mortality rates (Table 3). Of these, 5 reported increased risk, 9 no difference, and 2 decreased risk in the RMD group; notably the 3 largest studies showed increased risk. 7 studies reported adjusted risk estimates. Compared to the general population, 2 studies reported increased mortality and 1 found no difference. Compared to non-RMD comparators 4 studies reported no difference in mortality.
Conclusion: This is the largest systematic review to date on COVID-19 in RMD. Although distillation of the overall results was limited by study heterogeneity, a similar number of studies reported increased risk or equal risk for RMD patients with few reporting decreased risk.
To cite this abstract in AMA style:
Conway R, Grimshaw A, Konig M, Putman M, Duarte-Garcia A, Low C, Jin S, Cabrera D, Chock Y, Degirmenci B, Duff E, Egeli B, Graef E, Gupta A, Harkins P, Hoyer B, Jayatilleke A, Kasia C, Khilnani A, Kilian A, Kim A, Lin C, Proulx L, Sattui S, Singh N, Sparks J, Tam H, Tseng L, Ugarte-Gil M, Ung N, Wise L, Yang Z, Young K, Liew J, Grainger R, Wallace Z, Hsieh E. SARS-CoV-2 Infection and COVID-19 Outcomes in Rheumatic Disease: A Systematic Literature Review [abstract]. Arthritis Rheumatol. 2021; 73 (suppl 9). https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/sars-cov-2-infection-and-covid-19-outcomes-in-rheumatic-disease-a-systematic-literature-review/. Accessed .« Back to ACR Convergence 2021
ACR Meeting Abstracts - https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/sars-cov-2-infection-and-covid-19-outcomes-in-rheumatic-disease-a-systematic-literature-review/