Session Information
Session Type: ACR Poster Session C
Session Time: 9:00AM-11:00AM
Background/Purpose: The MONARCH study (NCT02332590) evaluated monotherapy with sarilumab 200 mg subcutaneous (SC) + placebo every 2 weeks (Q2W) versus adalimumab 40 mg SC + placebo Q2W in RA patients who were either intolerant of, inadequate responders to, or considered inappropriate candidates for continued treatment with methotrexate. The dose regimen could be changed to once weekly (qw) administration of adalimumab or matching placebo in the sarilumab group. This analysis examined 24-week per-patient drug costs (2017 US, wholesale acquisition) associated with effective treatment, based on outcomes from MONARCH.
Methods: The endpoint of effective treatment at 24 weeks was defined on three outcomes: ACR20, ACR50, and EULAR Moderate/Good (DAS28-ESR 0.6+ improvement). Cost per responder for each outcome was calculated in addition to incremental cost per effectively treated patient (difference in 24-week drug cost multiplied by the number needed to treat [NNT]) for sarilumab compared with adalimumab, with adalimumab costs based on the Q2W 40mg dose. One-way sensitivity analyses were conducted by varying the odds ratio of response rates for sarilumab on the three outcomes to the upper and lower bounds of their 95% confidence intervals, by increasing and decreasing sarilumab costs by 10%, and by varying the adalimumab cost based on a weighted average of patient proportions with dosing adjustments.
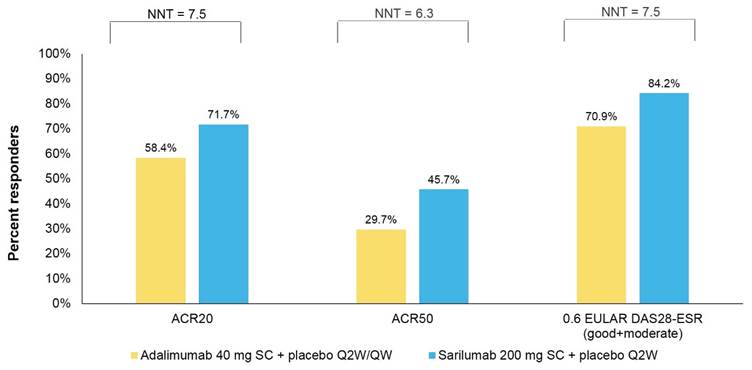
Results: The ITT population included 184 and 185 patients in the sarilumab and adalimumab arms, respectively. Estimated NNTs for sarilumab on ACR20, ACR50 and EULAR DAS28-ESR were 7.5, 6.3 and 7.5, respectively. Based on 24-week drug costs of $18,000 for sarilumab 200mg SC Q2W and $26,647 for adalimumab 40 mg SC Q2W, costs per responder for sarilumab versus adalimumab, respectively, were $25,105 versus $45,629 on ACR20; $39,387 versus $89,722 on ACR50; and $21,378 versus $37,584 on EULAR DAS28-ESR. Sarilumab was consistently the more effective and cost-saving treatment on all outcomes of incremental cost per effectively treated patient.
Conclusion: Sarilumab versus adalimumab was the economically dominant treatment with respect to incremental cost per effectively treated patient. Given the higher levels of responses on ACR20, ACR50 and 0.6 EULAR DAS25-ESR, coupled with the lower 24-week drug costs, sarilumab across all analyses was the favourable treatment in terms of cost per responder. These results were maintained within the sensitivity analyses.
Figure 1: Percentage of patients achieving response and number needed to treat (NNT)
To cite this abstract in AMA style:
Fournier M, Chen CI, Kuznik A, Proudfoot C, Mallya U, Michaud K. Sarilumab for the Treatment of Active, Moderate-to-Severe Rheumatoid Arthritis (RA): An Analysis of Cost per Effectively Treated Patient [abstract]. Arthritis Rheumatol. 2017; 69 (suppl 10). https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/sarilumab-for-the-treatment-of-active-moderate-to-severe-rheumatoid-arthritis-ra-an-analysis-of-cost-per-effectively-treated-patient/. Accessed .« Back to 2017 ACR/ARHP Annual Meeting
ACR Meeting Abstracts - https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/sarilumab-for-the-treatment-of-active-moderate-to-severe-rheumatoid-arthritis-ra-an-analysis-of-cost-per-effectively-treated-patient/