Session Information
Session Type: Poster Session (Tuesday)
Session Time: 9:00AM-11:00AM
Background/Purpose: Repository corticotropin injection (RCI) is a naturally sourced complex mixture of adrenocorticotropic hormone (ACTH1-39) analogues and other pituitary peptides that stimulates endogenous corticosteroid (CS) production and is an agonist for all 5 melanocortin receptors. RCI is approved by the US FDA for the treatment of acute exacerbations or as maintenance therapy in patients with systemic lupus erythematosus (SLE). In a pilot study,1 RCI improved disease activity (vs placebo) and was well tolerated in patients with SLE. In a separate study, RCI increased endogenous cortisol levels to a similar extent as < 10 mg ofexogenous prednisone (Figure 1; data on file). The current trial was designed to assess the efficacy and safety of RCI in patients with persistently active SLE despite use of moderate-dose CSs (ClinicalTrials.gov ID: NCT02953821). This abstract describes the safety data from 50% of the expected enrolled subjects from the blinded and ongoing trial.
Methods: Patients enrolled in this multicenter, double-blind, randomized, placebo-controlled, 24-week trial are required to have SLE (≥4 of 11 ACR 1997 criteria) and active disease (moderate to severe rash and/or arthritis) despite stable doses of CSs ≥4 weeks before screening. Treatments are 1 mL RCI (80 U) or placebo subcutaneously every other day for 4 weeks, followed by twice per week for 20 weeks. Randomization is stratified by study site location (US or outside of US) and prednisone or equivalent dose (≤20, >20 mg/d). Patients remain on stable doses of CSs through week 16, with tapering encouraged between weeks 16 and 24. The primary efficacy end point is the proportion of SLE Responder Index-4 (SRI-4) responders at week 16. Secondary and exploratory end points include measures of disease activity, prednisone dose, and serum biomarkers (ie, complements, autoantibodies, and inflammatory and bone turnover markers). Target enrollment is 270 patients; 162 are expected to be randomly assigned at ~60 global sites. Safety assessments include treatment-emergent AEs (TEAEs), physical examination, and vital signs and are summarized with descriptive statistics only.
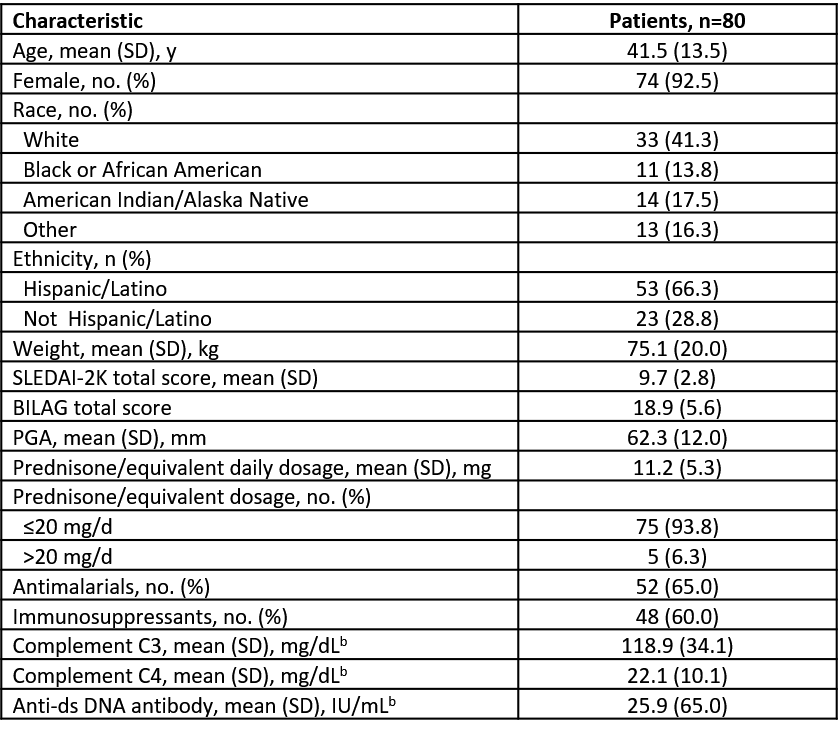
Results: The 80 patients in this evaluation represent ~50% of the patients expected to be randomly assigned in the study. Data from these patients were blinded. Demographics and baseline characteristics show a racially diverse population (Table 1). A total 53 (66.3%) patients reported a TEAE, with the most common being headache (8.8%) and insomnia (6.3%). TEAEs of special interest are shown in Table 2. The reported serious AEs (pneumonia, hypertension) were deemed related to treatment and expected. No Suspected Unexpected Serious Adverse Reactions or deaths were reported.
Conclusion: In a study of RCI in patients with active SLE despite moderate‑dose CS, blinded 50% enrollment data show disease characteristics consistent with those expected for patients with moderate/severe SLE. The safety profile suggests that RCI is well tolerated, consistent with a modest increase in cortisol production. The complete dataset will provide valuable information on the role of RCI in refractory SLE.
1 Furie R, et al. Lupus Sci Med. 2016;3(1):e000180.
Abbreviation: RCI, repository corticotropin injection.
b n=79.
Abbreviations: anti-ds, anti–double stranded; BILAG, British Isles Lupus Assessment Group; mITT, modified intent-to-treat; PGA, Physician’s Global Assessment; SD, standard deviation; SLEDAI-2K, Systemic Lupus Erythematosus Disease Activity Index-2000.
Abbreviation: TEAE, treatment-emergent adverse event.
To cite this abstract in AMA style:
Askanase A, Munirathinam D, Zhao E, Zhu J, Connolly-Strong E, Furie R. Safety Results of 50% Enrollment from a Multicenter, Randomized, Double‑blind, Placebo‑controlled Study to Assess the Efficacy and Safety of Repository Corticotropin Injection in Patients with Systemic Lupus Erythematosus Despite Moderate‑dose Corticosteroid Use [abstract]. Arthritis Rheumatol. 2019; 71 (suppl 10). https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/safety-results-of-50-enrollment-from-a-multicenter-randomized-double%e2%80%91blind-placebo%e2%80%91controlled-study-to-assess-the-efficacy-and-safety-of-repository-corticotropin-injection-in-patien/. Accessed .« Back to 2019 ACR/ARP Annual Meeting
ACR Meeting Abstracts - https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/safety-results-of-50-enrollment-from-a-multicenter-randomized-double%e2%80%91blind-placebo%e2%80%91controlled-study-to-assess-the-efficacy-and-safety-of-repository-corticotropin-injection-in-patien/