Session Information
Date: Tuesday, November 9, 2021
Title: RA – Treatments Poster III: RA Treatments & Their Safety (1674–1710)
Session Type: Poster Session D
Session Time: 8:30AM-10:30AM
Background/Purpose: Baricitinib (bari) is an oral selective Janus kinase (JAK)1/JAK 2 inhibitor approved for the treatment of adult patients with moderately to severely active rheumatoid arthritis (RA). The objective of this analysis was to report bari’s safety profile with data up to 9.3 years of treatment.
Methods: Pooled data from 9 randomized (5 Phase 3, 3 Phase 2, 1 Phase 1b) and 1 long-term extension (LTE) study were assessed. Incidence rates (IR) per 100 patient-years at risk (PYR) were calculated for all patients treated with ≥1 dose of bari (All-bari-RA). Adverse events (AEs) of interest were assessed over time in 48-month intervals. Major adverse cardiovascular events (MACE) were adjudicated in 5 Phase 3 studies and the LTE. Incidence rates for MACE were also evaluated in subgroups of patients age ≥50 years and presenting with ≥1 cardiovascular risk factor (current smoker, hypertension, high-density lipoprotein cholesterol < 40 mg/dL, diabetes, or arteriosclerotic cardiovascular disease). To account for aging of the cohort, a standardized incidence ratio (SIR) for malignancy (excluding non-melanoma skin cancer [NMSC]) was estimated using the Surveillance, Epidemiology, and End Results 17 (SEER17), 2013-2017 US population cancer rates, and a standardized mortality ratio (SMR) was estimated using 2019 US population mortality calculated as compared to the general US population with the same age distribution. Exposure adjusted IRs (EAIRs) for deep vein thrombosis (DVT), pulmonary embolism (PE), and DVT and/or PE (DVT/PE) were also calculated for groups of patients while receiving bari 2-mg or bari 4-mg within All-bari-RA.
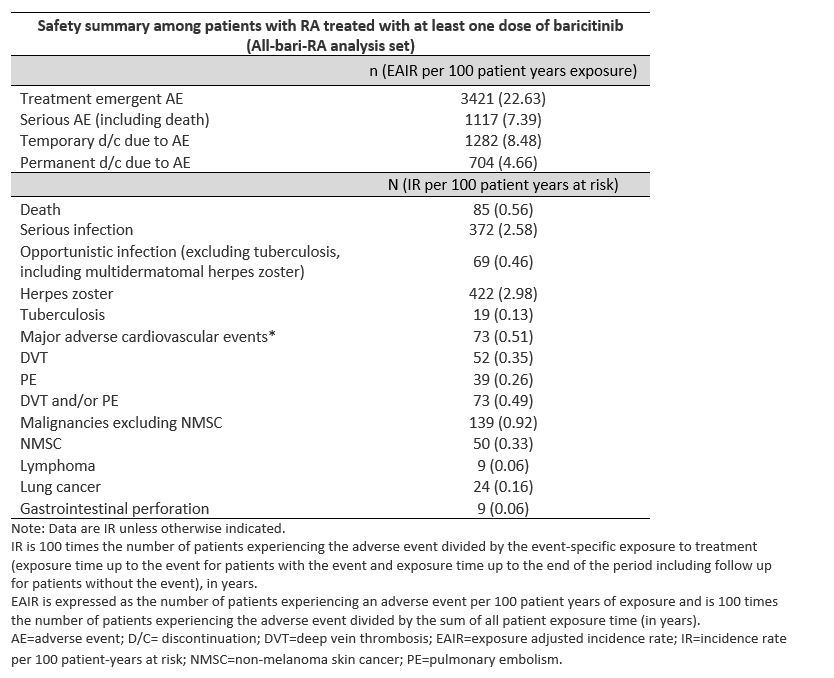
Results: A total of 3770 patients received bari for 14,744.4 PYE with a median exposure of 4.6 years and a maximum exposure of 9.3 years; 80.5% of PYE were bari 4-mg and 18.1% of PYE were bari 2-mg. Overall, EAIRs per 100 PYE for any treatment-emergent AE and serious AE (including death) were 22.6 and 7.4, respectively (Table). Overall IRs per 100 PYR were 2.58 for serious infections; 0.35 for DVT, 0.26 for PE, 0.49 for DVT/PE, 0.51 for MACE, and 0.92 for malignancy; IRs remained stable over time (Figure). The IR (95% CI) of MACE for patients age ≥50 years was 0.68 (0.52, 0.88). In patients age ≥50 with ≥1 of the cardiovascular risk factors, IR (95% CI) of MACE was 0.77 (0.56, 1.04). The SIR (95% CI) for malignancies excluding NMSC based on the SEER17 standard was 1.07 (0.90, 1.26); the SMR (95% CI) was 0.74 (0.59, 0.92) showing that the incidence of malignancy and death in patients treated with bari appear similar to the general US population. EAIRs (95% CI) for patients while receiving bari 2-mg (PYE=2678) and bari 4-g (PYE=11,872) were DVT 2-mg 0.41 (0.21, 0.73) and 4-mg 0.35 (0.25, 0.48); PE 2-mg 0.26 (0.11, 0.54) and 4-mg 0.27 (0.18, 0.38); and DVT/PE 2-mg 0.49 (0.26, 0.83) and 4-mg 0.51 (0.39, 0.66).
Conclusion: In this report with 14,774 PYE, bari maintained a safety profile similar to that previously reported1-3 with no increase of IRs across safety events through exposures up to 9.3 years.
References:
1Smolen JS et al. J Rheumatol. 2019;46(1):7-18
2Genovese MC et al. Ann Rheum Dis. 2019;78(supp. 2):A308
3Genovese MC et al Ann Rheumatic Dis 2020;79:642-643
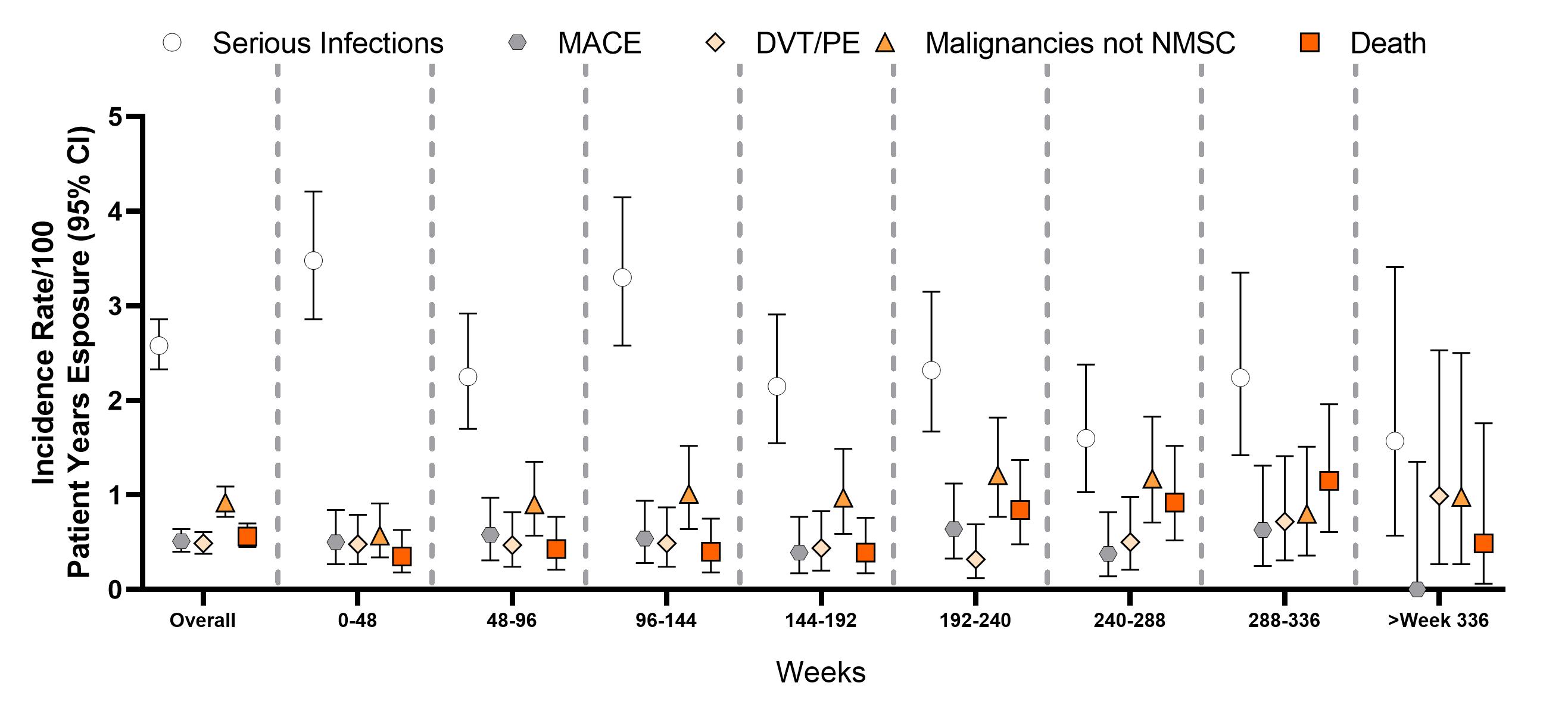 Figure: Incidence rates by 48-week exposure intervals.
Figure: Incidence rates by 48-week exposure intervals.
To cite this abstract in AMA style:
Taylor P, Takeuchi T, Burmester G, DUREZ P, Smolen J, Deberdt W, Zhong J, Terres J, Bello N, Winthrop K. Safety Profile of Baricitinib for the Treatment of Rheumatoid Arthritis up to 9.3 Years: An Updated Integrated Safety Analysis [abstract]. Arthritis Rheumatol. 2021; 73 (suppl 9). https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/safety-profile-of-baricitinib-for-the-treatment-of-rheumatoid-arthritis-up-to-9-3-years-an-updated-integrated-safety-analysis/. Accessed .« Back to ACR Convergence 2021
ACR Meeting Abstracts - https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/safety-profile-of-baricitinib-for-the-treatment-of-rheumatoid-arthritis-up-to-9-3-years-an-updated-integrated-safety-analysis/