Session Information
Date: Monday, October 27, 2025
Title: (1517–1552) Systemic Lupus Erythematosus – Treatment Poster II
Session Type: Poster Session B
Session Time: 10:30AM-12:30PM
Background/Purpose: Plasmacytoid dendritic cells (pDCs) are known to be the main source of type 1 interferon (IFN), which is the cause of various autoimmune diseases. The increased accumulation of pDCs in tissues is associated with inflammation and damage in Lupus. KK4277 is a monoclonal antibody targeting pDCs with its unique dual mode of action that directly depletes pDCs by enhanced Antibody-Dependent-Cellular-Cytotoxicity activity and independently inhibits type 1 IFN production from pDCs.
Methods: This was a first-in-human study that consisted of a randomized, placebo-controlled, double-blind, single-dose ascending study in Japanese and non-Asian healthy men (Part 1) and a multicenter, randomized, placebo-controlled, double-blind, multiple-dose ascending study in SLE or Cutaneous Lupus Erythematosus (CLE) Asian patients with active skin lesions (Part 2) (NCT05411016). In Part 1, healthy adult men were enrolled in eight cohorts for intravenous (IV) administration, 0.005 to 150 mg/body and four cohorts for subcutaneous (SC) administration, 100 to 300 mg/body (n=8 for each cohort). In Part 2, SLE or CLE patients who had active skin lesions without any disease severity requirements were enrolled in 5 mg/body cohort. The patients with CLE Disease Area and Severity Index Activity (CLASI-A) score of ≥8 were enrolled in 100 mg/body cohort. Participants received KK4277 or placebo intravenously with their standard of care every 2 weeks for 6 doses, followed by safety observation until Week 24. pDC and myxovirus resistance protein A (MxA) in skin were measured in addition to pDC and type 1 IFN signature in blood. CLASI-A score was assessed by investigators through the study. Another cohort of SC multiple administrations was undergoing at the time of data cut-off, and the data is not included.
Results: In Part 1, 97 subjects were enrolled. No serious or severe adverse event (AE) occurred. The tolerability of up to 150 mg/body IV and 300 mg/body SC was confirmed. More than a 90% reduction in blood pDCs was observed at 5 mg/body or higher doses, and the duration of the reduction increased in a dose-dependent manner. In part 2, 21 subjects were enrolled and received the study treatment. In 100 mg/body IV (KK4277: 8, Placebo: 4), more than a 90% reduction in blood pDCs was observed in the KK4277 group after the first administration and maintained until Week 14 (Figure 1). The median change in type 1 IFN signature was -69% in the KK4277 group and -2% in the placebo group at Week 12 (Figure 2). Three and two skin samples were provided in the KK4277 and placebo group, respectively, and a great reduction of pDC and MxA was obtained in all KK4277-treated individuals. Whereas the median change of CLASI-A score at Week 12 was not clearly different between the groups (KK4277: -62%, placebo: -56%), numerically huge improvements were observed in several subjects in the KK4277 group, including severe patients. No serious or severe AE was observed. The proportion of AE incidences was similar between the groups (KK4277: 63%, placebo: 75%).
Conclusion: Multiple doses of 100 mg/body IV were tolerable. KK4277 greatly depleted pDC in blood and skin and reduced type I IFN. A proof of pharmacological action was obtained. An additional study is expected for further evaluation in Lupus.
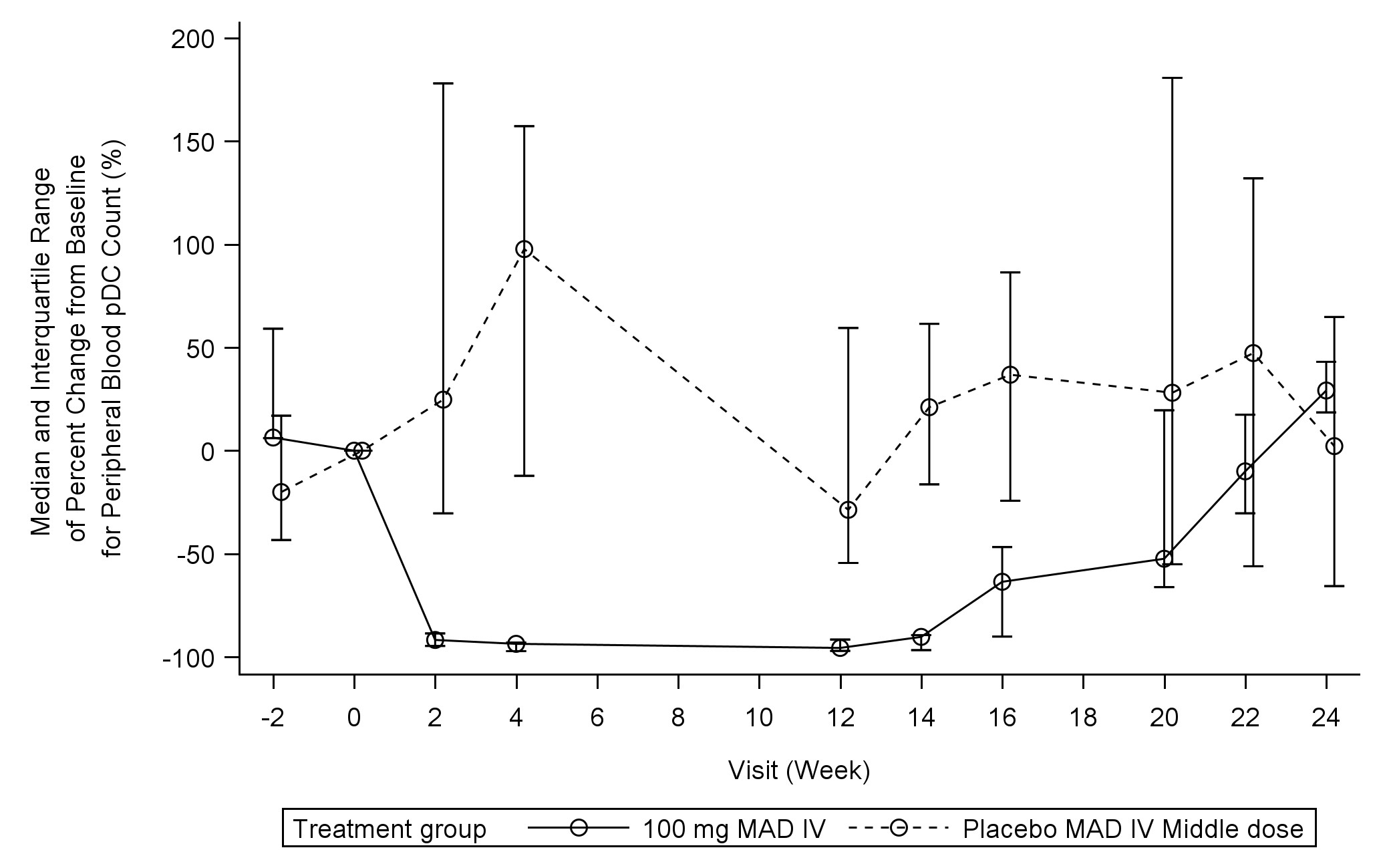 Figure 1: Median and interquartile range of percent change from baseline for peripheral blood pDC count (%) in 100 mg/body IV
Figure 1: Median and interquartile range of percent change from baseline for peripheral blood pDC count (%) in 100 mg/body IV
.jpg) Figure 2: Median and interquartile range of percent change from baseline for Type 1 IFN signature (%) in 100 mg/body IV
Figure 2: Median and interquartile range of percent change from baseline for Type 1 IFN signature (%) in 100 mg/body IV
To cite this abstract in AMA style:
Hasegawa M, Kinoshita J, Otsubo S, Yamada K, Esfandiari E. Safety, Pharmacodynamics, and Efficacy of a Novel Plasmacytoid Dendritic Cells Targeting Antibody in Healthy Adults and Patients with SLE or Cutaneous Lupus Erythematosus with Active Skin Lesions: A First-In-Human Study of KK4277 [abstract]. Arthritis Rheumatol. 2025; 77 (suppl 9). https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/safety-pharmacodynamics-and-efficacy-of-a-novel-plasmacytoid-dendritic-cells-targeting-antibody-in-healthy-adults-and-patients-with-sle-or-cutaneous-lupus-erythematosus-with-active-skin-lesions-a-f/. Accessed .« Back to ACR Convergence 2025
ACR Meeting Abstracts - https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/safety-pharmacodynamics-and-efficacy-of-a-novel-plasmacytoid-dendritic-cells-targeting-antibody-in-healthy-adults-and-patients-with-sle-or-cutaneous-lupus-erythematosus-with-active-skin-lesions-a-f/
