Session Information
Session Type: Abstract Session
Session Time: 3:00PM-4:30PM
Background/Purpose: CD19-targeted chimeric antigen receptor (CAR) T cell therapy is FDA-approved to treat lymphoma. A recent prospective case series of CD19 CAR T cell therapy suggested impressive efficacy for refractory autoimmune diseases; however, it had limited follow-up, small sample size, and no comparator group. Therefore, we identified patients with and without pre-existing autoimmune disease within a cohort of patients receiving CAR T cell therapy for lymphoma to investigate safety, cancer progression, and autoimmune disease activity.
Methods: We analyzed all patients receiving CD19 CAR T cell therapy for lymphoma through clinical care at a large cancer center and tertiary healthcare system (2017-2023). We identified patients in this cohort with pre-existing autoimmune disease through medical record review and collected data on disease type, immunomodulator use, and flares. We collected baseline characteristics at CAR T cell infusion and post-infusion outcomes including cytokine release syndrome (CRS), immune effector cell-associated neurotoxicity syndrome (ICANS), lymphoma progression, and total mortality. We investigated whether pre-existing autoimmune disease was associated with presence and/or severity of CRS and ICANS using multivariable logistic regression. We analyzed whether pre-existing autoimmune disease was associated with lymphoma progression-free survival and total mortality using Cox regression. Finally, among only those with pre-existing autoimmune disease, we compared immunosuppression use and flare the year before vs. after CAR T cell therapy using paired McNemar’s tests.
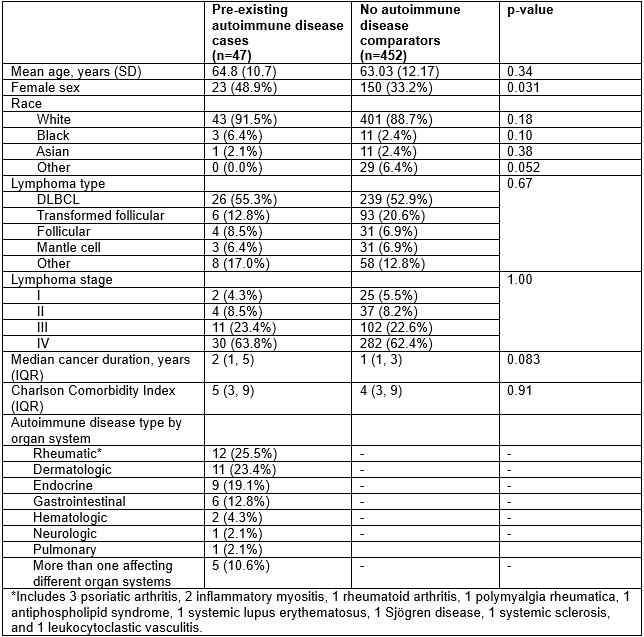
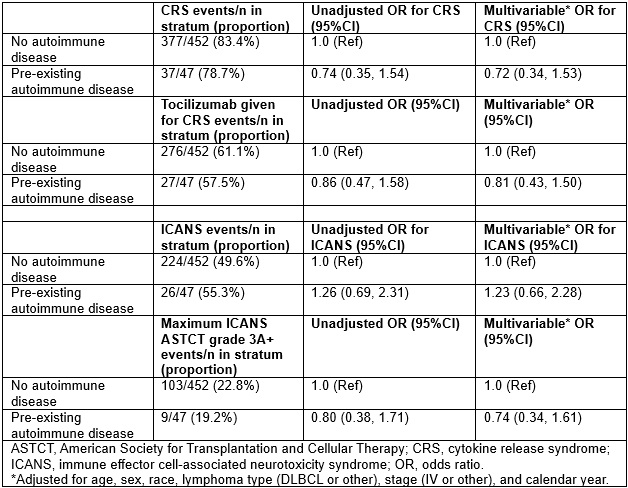
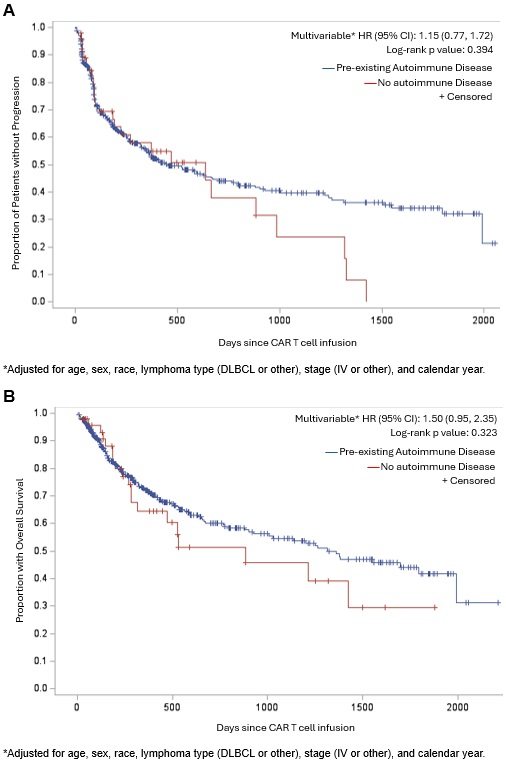
Results: Among 499 patients with lymphoma who received CD19 CAR T cell therapy, 47 patients had pre-existing autoimmune disease. The most common pre-existing autoimmune disease was psoriasis (n=10); n=12 had a systemic rheumatic disease (Table 1). CRS occurred in 78.7% of those with vs. 83.4% without pre-existing autoimmune disease (multivariable OR 0.72, 95%CI 0.34-1.53, Table 2). ICANS occurred in 55.3% of those with vs. 49.6% without pre-existing autoimmune disease (OR 1.23, 95%CI 0.66-2.28). There was no difference in the use of tocilizumab for CRS nor any difference in severe (grade 3+) ICANS. During median follow-up of 9.4 months, there were 208 progression events and 164 deaths. There were no associations of pre-existing autoimmune disease with lymphoma progression (HR 1.15, 95%CI 0.77-1.72, Figure 1) or total mortality (HR 1.50, 95%CI 0.95-2.35). Among patients with autoimmune disease, there was less immunomodulator use (25% vs. 13%, p=0.008) and flare (15% vs. 5%, p=0.058) in the year after CAR T cell therapy compared to the year before.
Conclusion: In this first comparative CAR T cell therapy study, patients with pre-existing autoimmune disease had similar safety and lymphoma outcomes compared to those without. Treatment and flares of autoimmune disease were improved. These findings are reassuring for safety of CD19 CAR T cell therapy for lymphoma among patients with autoimmune diseases and inform ongoing prospective studies of CAR T cell therapy to treat autoimmune diseases.
B. Overall survival of patients with pre-existing autoimmune disease compared to those with no history of autoimmune disease.
To cite this abstract in AMA style:
Vanni K, McCarter K, Wang X, Duffy C, Dela Cruz J, Wobma H, Nikiforow S, Massarotti E, Costenbader K, Little J, Gravallese E, McDermott G, Jacobson C, Sparks J. Safety, Cancer Progression, and Autoimmune Disease Activity in Patients with Pre-Existing Autoimmune Disease Undergoing CD19 CAR T Cell Therapy for Lymphoma: A Retrospective Comparative Cohort Study [abstract]. Arthritis Rheumatol. 2024; 76 (suppl 9). https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/safety-cancer-progression-and-autoimmune-disease-activity-in-patients-with-pre-existing-autoimmune-disease-undergoing-cd19-car-t-cell-therapy-for-lymphoma-a-retrospective-comparative-cohort-study/. Accessed .« Back to ACR Convergence 2024
ACR Meeting Abstracts - https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/safety-cancer-progression-and-autoimmune-disease-activity-in-patients-with-pre-existing-autoimmune-disease-undergoing-cd19-car-t-cell-therapy-for-lymphoma-a-retrospective-comparative-cohort-study/