Session Information
Date: Monday, November 18, 2024
Title: RA – Treatment Poster III
Session Type: Poster Session C
Session Time: 10:30AM-12:30PM
Background/Purpose: Rheumatoid Arthritis (RA) is a progressive inflammatory autoimmune disease affecting 1% of the global population for which there is currently no cure. Recent research has focused on prevention strategies in individuals at increased risk of RA with the aim of reducing this risk. One such strategy involves dietary interventions. In a secondary analysis of a large prospective clinical trial (VITAL), vitamin-D and Omega-3 fatty acid supplementation have shown promise in reducing incident RA. In a collagen induced arthritis murine model of RA, we showed that a diet supplemented with Curcumin, Omega-3 and Vitamin-D (COD) reduced arthritis severity and incidence when given during the induction phase (PMID 33494792). Biologically, COD each have unique and potentially synergistic anti-inflammatory/immunomodulatory effects. Based on these considerations, we are planning a prospective RA prevention trial using COD in anti-citrullinated protein antibody (ACPA) positive individuals. However, there are no clinical trials which have evaluated the combined use of COD in humans. Thus, we conducted PASCOD (Pilot Assessment and Safety of COD) to evaluate the safety and tolerability of COD in healthy human volunteers.
Methods: Healthy volunteers aged 18-49 years with no history of RA or other autoimmune diseases were recruited (n=50) for a 4-week open-label pre-post design. Baseline visits included overall health and medications survey, anthropometric measures, functional status (RAPID3), a joint symptom questionnaire and a clinical assessment of 44 joints, all of which were repeated at the final visit. Blood specimens were collected for routine hematology and biochemistry. Weekly surveys were sent to participants to report side effects. The study was powered to detect the rate of common side effects ( >5% frequency), which was the primary outcome.
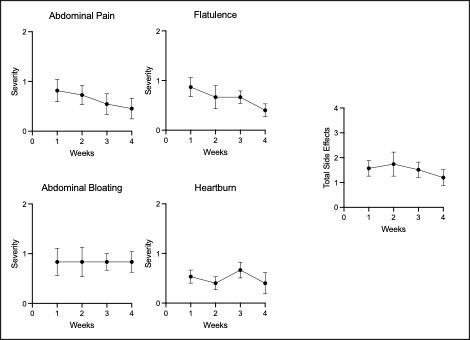
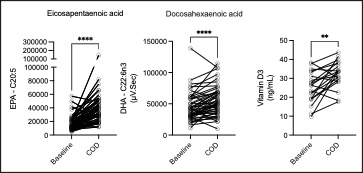
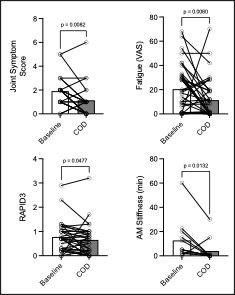
Results: Most reported side effects were mild (81.8%), with the most common being heartburn (32%), fishy taste (30%), and abdominal bloating (24%), which mostly improved over time (Fig1). No laboratory abnormalities attributable to the study protocol were detected. Mean adherence was 97% for all 3 supplements. Reflective of this, we observed increases in eicosapentaenoic acid (EPA, p< 0.0001), docosahexaenoic acid (DHA, p< 0.0001) levels measured in plasma by gas chromatography, and Vitamin D levels by ELISA (Fig2, p=0.01). Despite the absence of inflammatory arthritis, RAPID3 scores significantly decreased over the trial (p=0.048), driven by a reduction in self-reported joint pain visual analogue scale (VAS, p=0.002). Self-reported joint pain score (p=0.008), fatigue VAS (p=0.008) and minutes of AM stiffness (Fig3, p=0.01) all reduced after COD treatment.
Conclusion: Overall, four weeks of COD was well-tolerated, with high adherence and mild side effects which mostly improved over time. We observed improvements in self-reported symptoms relevant to individuals at-risk for future RA development. These data suggest that COD supplementation is a feasible strategy for consideration in an RA prevention trial.
To cite this abstract in AMA style:
Cochrane H, Mcfadyen C, Mayor K, Silva R, James K, Meng X, Mackay D, El-Gabalawy H, O'Neil L. Safety and Tolerability of a Combination of Curcumin, Omega-3 and Vitamin-D: Results from the PASCOD Study, an RA Prevention Protocol [abstract]. Arthritis Rheumatol. 2024; 76 (suppl 9). https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/safety-and-tolerability-of-a-combination-of-curcumin-omega-3-and-vitamin-d-results-from-the-pascod-study-an-ra-prevention-protocol/. Accessed .« Back to ACR Convergence 2024
ACR Meeting Abstracts - https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/safety-and-tolerability-of-a-combination-of-curcumin-omega-3-and-vitamin-d-results-from-the-pascod-study-an-ra-prevention-protocol/