Session Information
Date: Tuesday, November 9, 2021
Title: RA – Treatments Poster III: RA Treatments & Their Safety (1674–1710)
Session Type: Poster Session D
Session Time: 8:30AM-10:30AM
Background/Purpose: In patients who experience intolerance or fail to respond to methotrexate, IL-6 receptor inhibitors (e.g. sarilumab) are one of the recommended options. The aim of this analysis was to assess the long-term safety and efficacy of sarilumab in patients with RA using data from two open-label studies: EXTEND (NCT01146652) and MONARCH (NCT02332590) open label extension (OLE).
Methods: EXTEND included patients from five trials which evaluated patients who were either inadequate responders to conventional synthetic DMARDs or biologic DMARDs. Patients enrolled in EXTEND received sarilumab 150 mg or 200 mg q2w (once every two weeks) based on their initial treatment for ≥264 weeks. MONARCH OLE included patients who completed the 24-week double blind (DB) period of the MONARCH study and opted to receive open label sarilumab 200 mg q2w for 276 weeks. Safety endpoints included treatment emergent adverse events (TEAEs), serious adverse events (SAEs), adverse events of special interest (AESI), and anti-drug antibody (ADA) positivity. Key efficacy endpoints were ACR 20/50/70 responses, mean change from baseline in DAS28-CRP, and clinical disease activity index for RA (CDAI). Safety and efficacy analyses in both open-label studies were descriptive.
Results: Total duration of sarilumab (N=111) and sarilumab+DMARD (N=1910) exposure was 453.8 patient years (PY) and 8552.7 PY in EXTEND and the cumulative duration of exposure to sarilumab (N=320) in MONARCH OLE was 1131.9 PY. Both studies had more females with a mean age of approximately 50 years. At least one TEAE was reported in 92.1% and 88.3% of patients in EXTEND and 86.9% of patients in MONARCH OLE; infections and infestations were the most common TEAEs in both studies. At least one SAE was reported in 32.3% and 24.3% of patients in EXTEND and 17.5% of patients in MONARCH OLE. In both studies, approximately 2.0% of patients died due to TEAEs. The number of patients who discontinued the treatment due to TEAEs were 26.0% and 13.5% in EXTEND and 13.1% in MONARCH OLE. Herpes Zoster was the most frequently reported opportunistic AESI in EXTEND (44/74 opportunistic infections) and MONARCH OLE (7/10 opportunistic infections). A detailed summary of adverse events reported in both studies is presented in Table. ADA positivity was low in both EXTEND and MONARCH OLE and was not associated with hypersensitivity reactions or discontinuations due to lack of efficacy. Clinical efficacy, measured as ACR 20/50/70 responses, mean changes from baseline in DAS28-CRP, and CDAI was maintained throughout the duration of both studies (Figure 1 and Figure 2).
Conclusion: Treatment of RA patients with sarilumab in EXTEND and MONARCH OLE revealed no new safety findings. Treatment with sarilumab demonstrated maintenance of efficacy, achieved during the DB period, over the entire open label treatment.
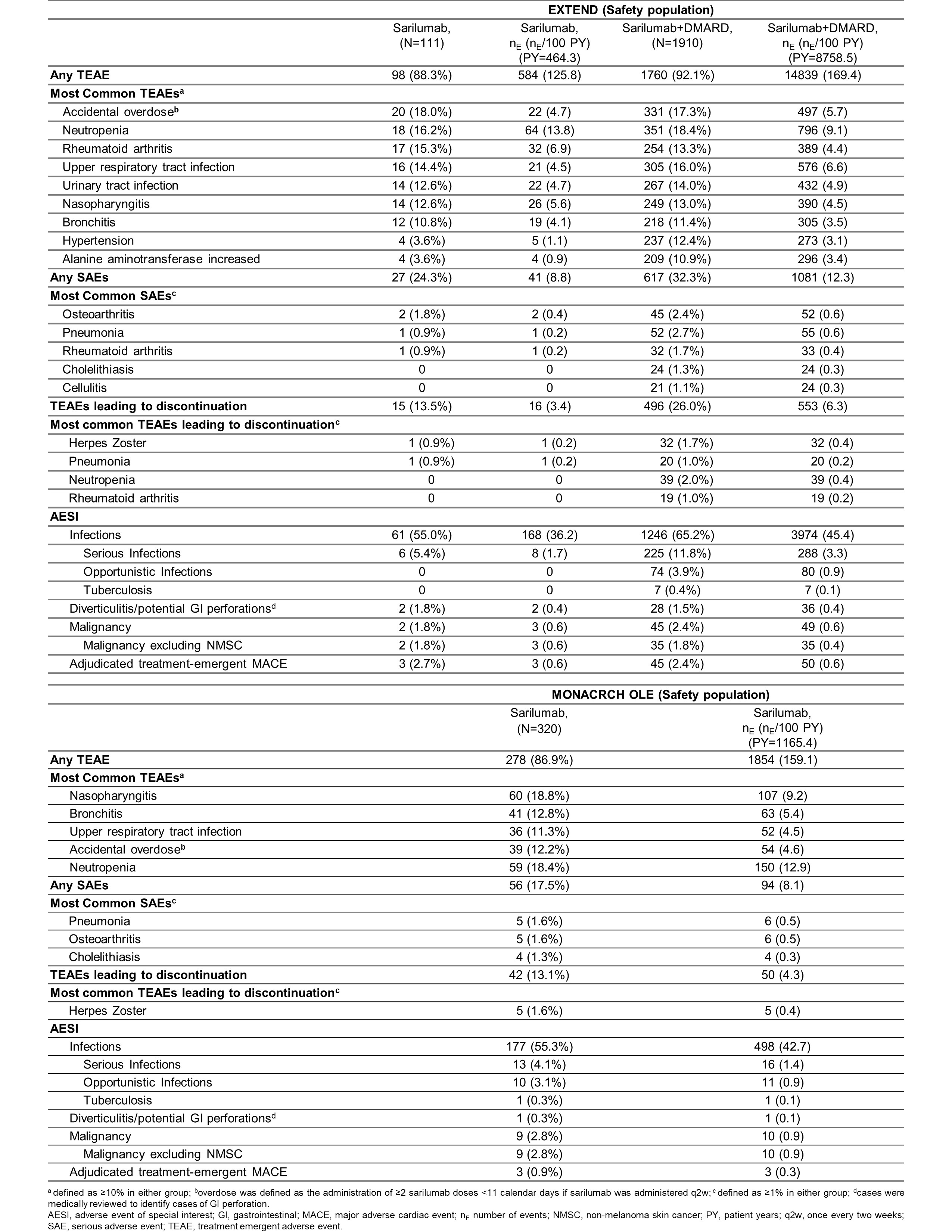 Table: Summary of AESI and most common TEAEs, SAEs, and TEAEs leading to discontinuation in EXTEND and MONARCH OLE
Table: Summary of AESI and most common TEAEs, SAEs, and TEAEs leading to discontinuation in EXTEND and MONARCH OLE
 Figure 1: Summary of Efficacy Outcomes in EXTEND (Safety Population)
Figure 1: Summary of Efficacy Outcomes in EXTEND (Safety Population)
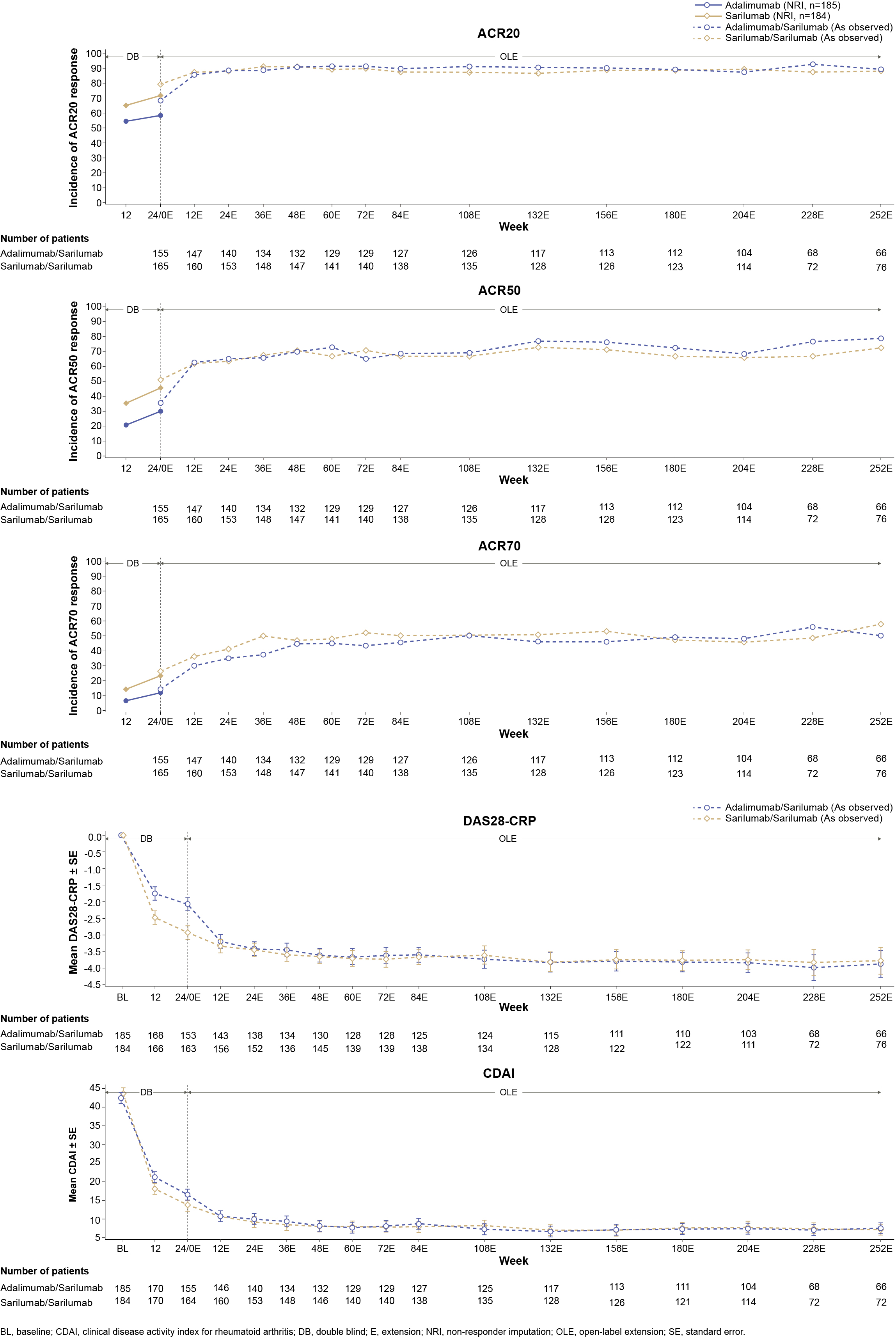 Figure 2: Summary of Efficacy Outcomes in MONARCH OLE (Full Intention to Treat Population)
Figure 2: Summary of Efficacy Outcomes in MONARCH OLE (Full Intention to Treat Population)
To cite this abstract in AMA style:
Burmester G, Strand V, Kivitz A, Hu C, Wang S, van Hoogstraten H, Tao R, Fleischmann R. Safety and Efficacy of Long-term Sarilumab Treatment in Patients with Active Rheumatoid Arthritis: EXTEND and MONARCH Open Label Extension Studies [abstract]. Arthritis Rheumatol. 2021; 73 (suppl 9). https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/safety-and-efficacy-of-long-term-sarilumab-treatment-in-patients-with-active-rheumatoid-arthritis-extend-and-monarch-open-label-extension-studies/. Accessed .« Back to ACR Convergence 2021
ACR Meeting Abstracts - https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/safety-and-efficacy-of-long-term-sarilumab-treatment-in-patients-with-active-rheumatoid-arthritis-extend-and-monarch-open-label-extension-studies/
