Session Information
Date: Sunday, November 17, 2024
Title: Abstracts: Muscle Biology, Myositis & Myopathies – Basic & Clinical Science I
Session Type: Abstract Session
Session Time: 3:00PM-4:30PM
Background/Purpose: CD19 targeting chimeric antigen receptor (CAR) T cells have demonstrated durable drug-free responses and remission in patients with idiopathic inflammatory myopathies (IIM) and systemic lupus erythematosus (SLE) reported from a compassionate use program. As a fully human, autologous 4-1BB anti-CD19-CAR T cell therapy, CABA-201 is being investigated for the treatment of multiple B cell-mediated autoimmune diseases. RESET-Myositis (NCT06154252) and RESET-SLE (NCT06121297) are ongoing phase I/II clinical trials evaluating the safety and efficacy of CABA-201 in 4 independent myositis cohorts of immune-mediated necrotizing myopathy (IMNM), antisynthetase syndrome (ASyS), dermatomyositis, and juvenile IIM as well as 2 independent SLE cohorts of non-renal SLE and lupus nephritis (LN), respectively. We report on the initial results of the first IMNM and first non-renal SLE patients treated with CABA-201.
Methods: For the RESET-Myositis trial, eligible patients are ≥18 and ≤75 years or pediatric patients with a clinical diagnosis of IIM, the presence of serum myositis-specific or myositis-associated antibodies, and evidence of active disease despite standard therapy. For the RESET-SLE study, eligible patients are ≥18 to ≤65 years with an SLE diagnosis, ANA+ or anti-dsDNA+, and SLEDAI 2K ≥8 despite standard therapy (non-renal cohort) or active, biopsy-confirmed LN class III or IV ± V (renal cohort). For both trials, a single infusion of 1×106 CAR T cells/kg is administered following a preconditioning regimen of cyclophosphamide and fludarabine. Per protocol, participants are inpatient for a minimum of 4 days post infusion.
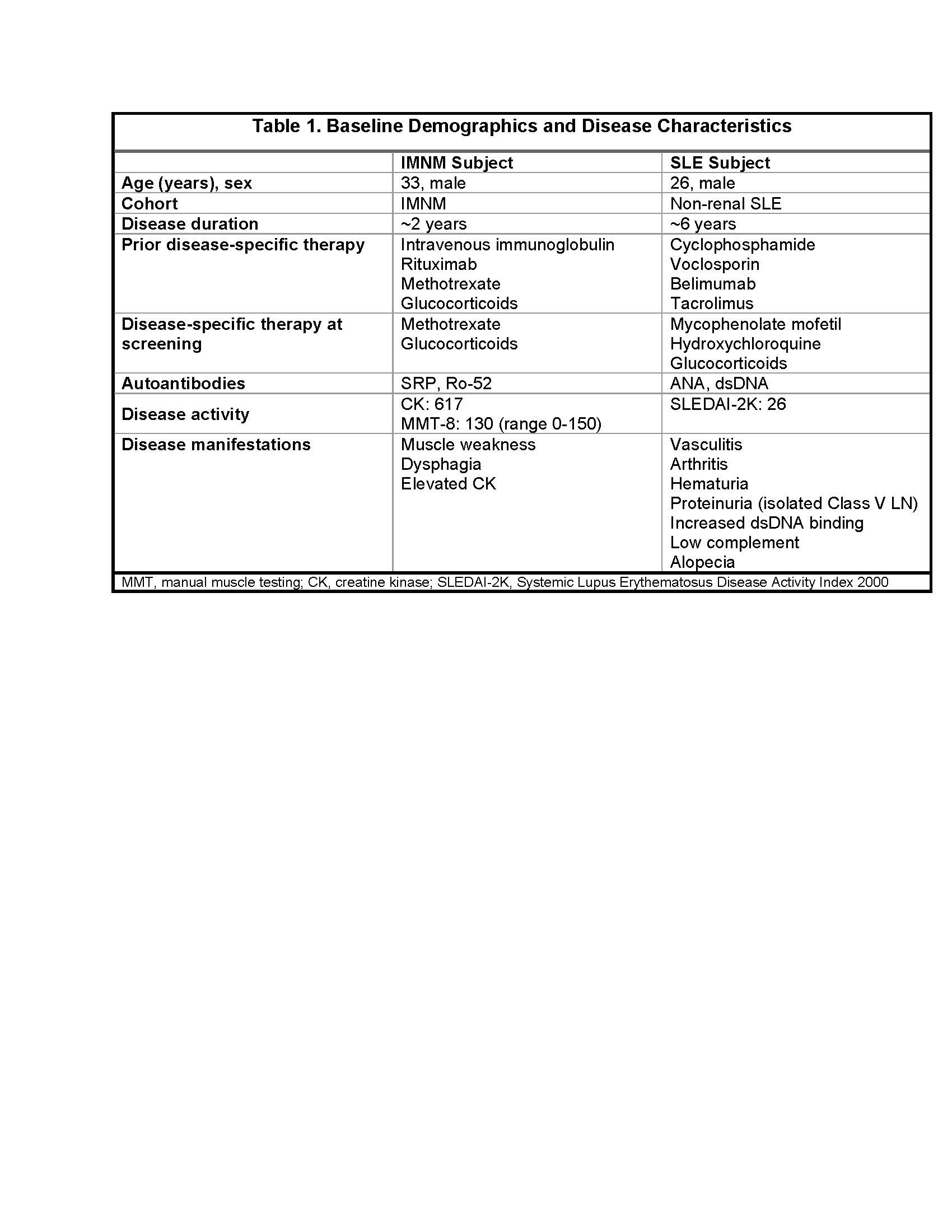
Results: Baseline data on the 2 treated subjects are in Table 1.
In both subjects, CABA-201 expansion peaked at day 15 and peripheral B cells were rapidly reduced, achieving complete B cell depletion by day 15. At 3 months post infusion, the IMNM subject achieved a meaningful response in the total improvement score, associated with improvements in the CK to 308 and MMT-8 to 134, as well as reduction in anti-SRP and anti-Ro52 levels, while off methotrexate and glucocorticoids. At 1 month post infusion, the SLE subject achieved a SLEDAI-2K improvement of 16 points with resolution of vasculitis, arthritis, and hematuria and reduction in the anti-dsDNA titer, while off mycophenolate and hydroxychloroquine and on a prednisone taper.
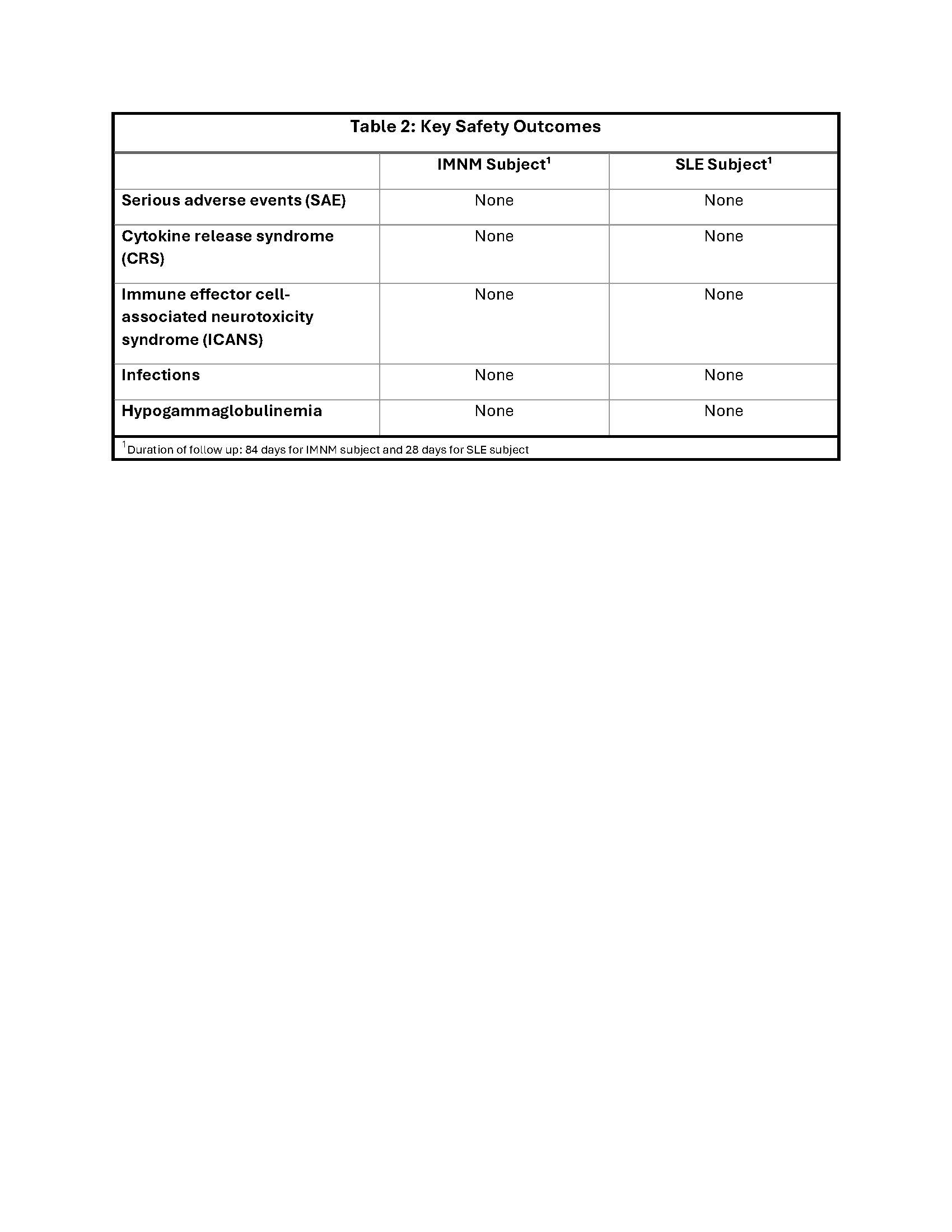
Safety outcomes are in Table 2.
Conclusion: Both subjects tolerated CABA-201 treatment with no SAE, CRS, or ICANS. The administered dose of CABA-201 resulted in CAR T cell expansion, peripheral B cell depletion, and biomarker and clinical improvements consistent with the data observed in a previous report in ASyS and SLE/LN patients. These findings support the safety and the potential for favorable outcomes of CABA-201 in patients with SRP+ IMNM and non-renal SLE. Evaluation of the selected CABA-201 dose continues in the ongoing RESET-Myositis and RESET-SLE clinical trials.
Reference: Müller F, et al. NEJM 2024; 390:687
To cite this abstract in AMA style:
Sheikh S, Mozaffar T, Derebail V, Grover N, Hogan J, Little C, White Y, Miller C, Estremera R, Volkov J, Nunez D, Stadanlick J, Werner M, Vorndran Z, Ellis A, Williams J, Cicarelli J, Lam Q, Furmanak t, Schmitt C, Nezhad F, Thompson D, Basu S, Chang D. Safety and Efficacy of CABA-201, a Fully Human, Autologous 4-1BB Anti-CD19 CAR T Cell Therapy in Patients with Immune-Mediated Necrotizing Myopathy and Systemic Lupus Erythematosus from the RESET-MyositisTM and RESET-SLETM Clinical Trials [abstract]. Arthritis Rheumatol. 2024; 76 (suppl 9). https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/safety-and-efficacy-of-caba-201-a-fully-human-autologous-4-1bb-anti-cd19-car-t-cell-therapy-in-patients-with-immune-mediated-necrotizing-myopathy-and-systemic-lupus-erythematosus-from-the-reset-myos/. Accessed .« Back to ACR Convergence 2024
ACR Meeting Abstracts - https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/safety-and-efficacy-of-caba-201-a-fully-human-autologous-4-1bb-anti-cd19-car-t-cell-therapy-in-patients-with-immune-mediated-necrotizing-myopathy-and-systemic-lupus-erythematosus-from-the-reset-myos/