Session Information
Session Type: Poster Session (Sunday)
Session Time: 9:00AM-11:00AM
Background/Purpose: In the SELECT-COMPARE study in rheumatoid arthritis (RA) patients (pts) with inadequate response to methotrexate (MTX), upadacitinib (UPA), a JAK1- selective inhibitor, was superior to placebo (PBO) or adalimumab (ADA), for treatment of signs & symptoms and for inhibition of radiographic progression vs PBO up to 26 weeks (wks). All pts were on stable background MTX. 1
We report safety and efficacy of UPA plus stable background MTX up to 48 wks in this phase 3 study.
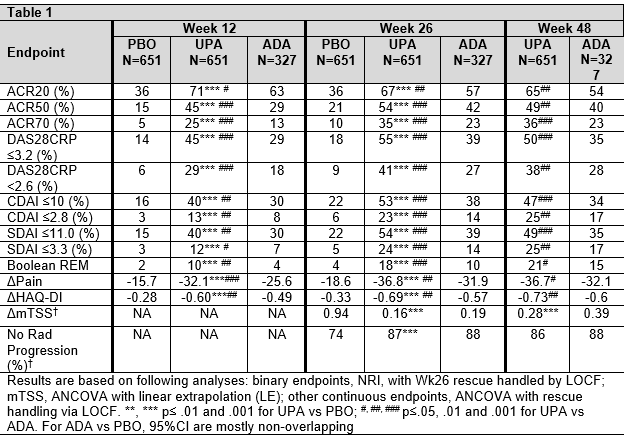
Methods: Pts were randomized to once-daily (QD) UPA 15mg, PBO, or ADA 40mg every other wk, with all patients continuing background MTX. The study was double-blind for 48 wks. Between Wks14-26, pts were rescued (from PBO to UPA, UPA to ADA, or ADA to UPA) if there was < 20% improvement in tender/swollen joint count (Wks 14/18/22) or if Clinical Disease Activity Index (CDAI) was >10 (Wk26); all PBO pts who were not rescued were switched to UPA at Wk 26. Efficacy was analyzed by randomized group. Non-responder imputation (NRI) was used for binary endpoints for rescue prior to Wk26. Last observation carried forward (LOCF) was used for continuous endpoints and binary endpoints after Wk26. Treatment-emergent adverse events (AE) per 100 pt yrs (PY) were summarized up to July 6 2018 for pts with any exposure to ADA or UPA.
Results: In SELECT-COMPARE, 1629 pts were randomized at BL. Among 651 pts randomized to UPA, 38.7% were rescued between Wks 14-26; of those who remained on UPA, 86% completed Wk 48, while 5.8% and 0.3% discontinued study drug between BL and Wk 48 due to AE and lack of efficacy (LoE), respectively. Among 327 pts randomized to ADA, 48.6% were rescued between Wks 14-26; of those who remained on ADA, 76% completed Wk48, while 13.1% and 0 discontinued study drug between BL and Wk48 due to AE and LoE, respectively. The cumulative exposures were 1243.3 and 467.8 PYs for UPA and ADA, respectively. At Wk26, and Wk48, significantly more pts in the UPA vs ADA group achieved ACR20/50/70, low disease activity and remission (Table); this was also true for visits between Wks 26 and 48. Similarly, improvements in pain and function were significantly greater in the UPA vs ADA group through Wk48. At Wk26, there was significantly less radiographic progression for UPA vs PBO, which was maintained through Wk48 (based on linear extrapolation).
Adverse events are reported in the table (in events per 100 PY). The rate of AE leading to discontinuation was higher with “any ADA” vs “any UPA”, while the rate of Herpes zoster was higher with “any UPA” exposure.
Conclusion: UPA continued to demonstrate superior clinical and functional responses vs ADA through Wk48. Inhibition of structural joint damage with UPA was also maintained through 48 wks vs PBO. Safety was consistent with observations in the first 26 wks.1
1. Fleischmann R, et al. Arthritis Rheumatol. 2018;70 -supp10-:
To cite this abstract in AMA style:
Fleischmann R, Enejosa J, Song I, Mysler E, Bessette L, Peterfy C, Durez P, Östör A, Zhou Y, Genovese M. Safety and Effectiveness of Upadacitinib or Adalimumab in Patients with Rheumatoid Arthritis: Results at 48 Weeks [abstract]. Arthritis Rheumatol. 2019; 71 (suppl 10). https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/safety-and-effectiveness-of-upadacitinib-or-adalimumab-in-patients-with-rheumatoid-arthritis-results-at-48-weeks/. Accessed .« Back to 2019 ACR/ARP Annual Meeting
ACR Meeting Abstracts - https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/safety-and-effectiveness-of-upadacitinib-or-adalimumab-in-patients-with-rheumatoid-arthritis-results-at-48-weeks/