Session Information
Session Type: Poster Session A
Session Time: 9:00AM-11:00AM
Background/Purpose: RA increases a patient’s systemic inflammatory burden, which has been associated with development of chronic kidney disease (CKD), especially in patients with comorbid hypertension, diabetes, or cardiovascular events1,2. Propensity-matched real-world cohorts show that treatment of RA with biologic therapies lowers the risk of glomerular filtration rate decline1. In the ICHIBAN study, tocilizumab (TCZ) was effective and well tolerated in clinical practice in Germany over up to 2 years3. Here, we present a post-hoc analysis of ICHIBAN patients with baseline renal insufficiency (RI; assessed as comorbidity by the study physician).
Methods: ICHIBAN was a prospective, multi-center, non-interventional study (NCT01194401; ML22928) that included adults with active, moderate-to-severe RA who received TCZ according to the local label in Germany. Safety was analysed in all patients who received one dose of TCZ (SAF). Effectiveness outcomes (SAF patients with no prior TCZ analyzed) included DAS28-ESR, CDAI, HAQ, and patient-reported outcomes (PROs) assessed via visual analogue scales (VAS; 0=best; 100=worst).
Results: Of the 3164 patients in the SAF, 90 (2.84 %) had RI at baseline. These patients were on average 12.8 years older; had a higher frequency of additional comorbidities, such as diabetes, hypertension and coronary heart disease (Table 1); and generally worse baseline physical functioning and PROs (especially sleep disturbances) (Table 2) than those without RI.
The mean treatment duration was similar patients with and without RI. At baseline, patients with RI less frequently received csDMARDS (Table 1), and slightly more frequently glucocorticoids (GCs; 85.4 vs 81.4%) than patients without RI. At last visit however, both groups showed identical proportions of GC therapy (74.4 vs 74.4%).
Importantly, TCZ treatment led to similar improvements in DAS28-ESR, CDAI, HAQ and PROs regardless of RI (Table 2; Figure 1).
The rates of adverse events (AEs) and serious AEs per 100 patient years were higher in patients with RI than in those without (169.3 vs 106.8, and 53.6 vs 23.1, respectively). The rate of infections was similar in both groups (23.3 vs 21.1) while the rate of serious infections was higher in patients with RI (11.3 vs 3.7). The rate of gastrointestinal perforations per 100 patient years was 1.9 in patients with RI and 0.2 in those without. The rate of treatment discontinuations due to AE was similar in both groups (9.4 vs 9.2).
Conclusion: In the non-interventional ICHIBAN study, despite worse baseline disease in affected patients, the effectiveness of TCZ was similar in patients with and without RI. GC sparing was even more pronounced in patients with CKD compared with those without. As expected, higher rates of baseline comorbid risk factors, such as diabetes and hypertension, and age-dependent serious infections were observed in patients with RI. However, TCZ discontinuation due to an AE was not increased. Overall, this analysis supports the effectiveness and tolerability of TCZ in patients with RA and RI in real-world clinical practice.
1Sumida et al. Kidney Int 2018(93):1207–1216
2Kochi et al. J Cardiol 2018(71):277–283
3Specker et al. Clin Exp Rheumatol (in press)
 Figure 1: HAQ and patient-reported outcomes (PRO) at baseline and last visit in patient with and without renal insuffciency. A) Mean HAQ score and B) PROs accoring to the visual analogue scale, median mm. Error is presented in standard deviation for HAQ score and interquartile range for PROs. In case of discontinuation of tocilizumab treatment, the last available value was taken and carried forward (last observation carried forward, LOCF). Only patients with data at baseline and last visit under tocilizumab (or LOCF). 9 patients with missing renal status were not analyzed.
Figure 1: HAQ and patient-reported outcomes (PRO) at baseline and last visit in patient with and without renal insuffciency. A) Mean HAQ score and B) PROs accoring to the visual analogue scale, median mm. Error is presented in standard deviation for HAQ score and interquartile range for PROs. In case of discontinuation of tocilizumab treatment, the last available value was taken and carried forward (last observation carried forward, LOCF). Only patients with data at baseline and last visit under tocilizumab (or LOCF). 9 patients with missing renal status were not analyzed.
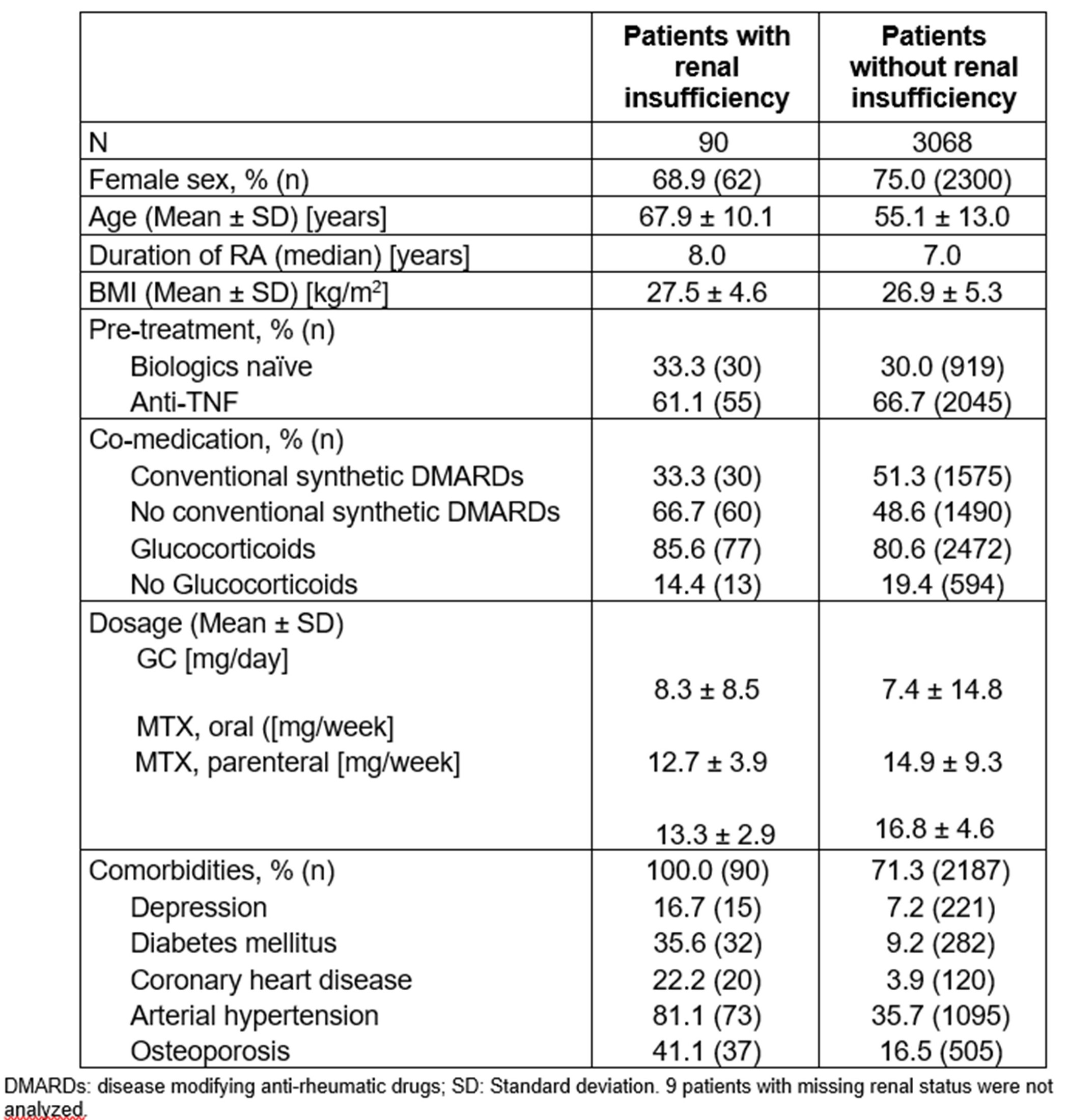 Table 1: Baseline characteristics of patient with and without renal insufficiency
Table 1: Baseline characteristics of patient with and without renal insufficiency
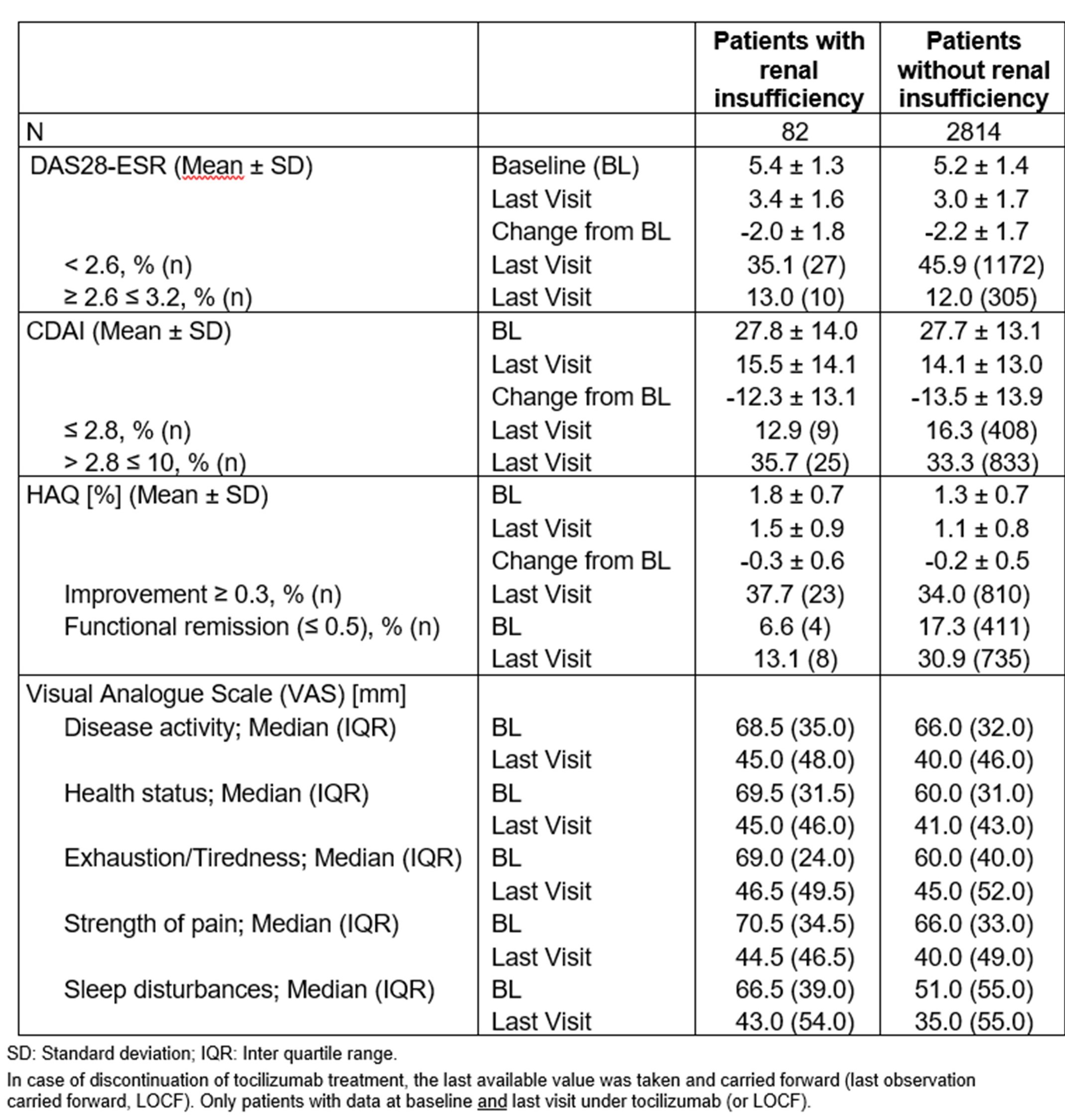 Table 2: Effectiveness after two years of observation
Table 2: Effectiveness after two years of observation
To cite this abstract in AMA style:
Specker C, Aringer M, Burmester G, Gerlach J, Hofmann M, Kellner H, Moosig F, Tony H, Fliedner G. Safety and Effectiveness of Tocilizumab in Patients with Renal Insufficiency in the Non-interventional Study ICHIBAN [abstract]. Arthritis Rheumatol. 2020; 72 (suppl 10). https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/safety-and-effectiveness-of-tocilizumab-in-patients-with-renal-insufficiency-in-the-non-interventional-study-ichiban/. Accessed .« Back to ACR Convergence 2020
ACR Meeting Abstracts - https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/safety-and-effectiveness-of-tocilizumab-in-patients-with-renal-insufficiency-in-the-non-interventional-study-ichiban/
