Session Information
Session Type: Abstract Submissions (ACR)
Patients with rheumatoid arthritis (RA) and carotid artery plaques (CP) have increased risk of acute coronary syndromes. Statin treatment with low density lipoprotein cholesterol (LDL-c) goal ≤ 1.8 mmol/L is recommended for patients with CP in the general population. In the ROsuvastatin in Rheumatoid Arthritis, Ankylosing Spondylitis and other inflammatory joint diseases (RORA-AS) study, the aim was to evaluate the effect of 18 months intensive rosuvastatin treatment on change in CP height.
Methods
Eighty-six patients (60.5% female) with CP and IJD [RA (n=55), ankylosing spondylitis (n=21) and psoriatic arthritis (n=10)] were treated with rosuvastatin to obtain LDL-c goal. CP height was evaluated by B–mode ultrasound.
Results
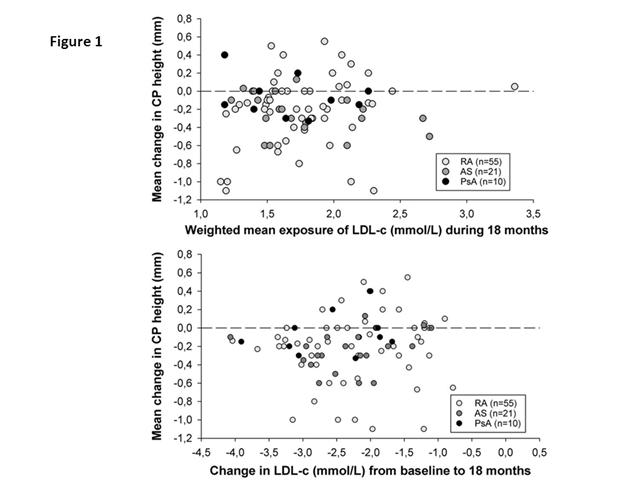
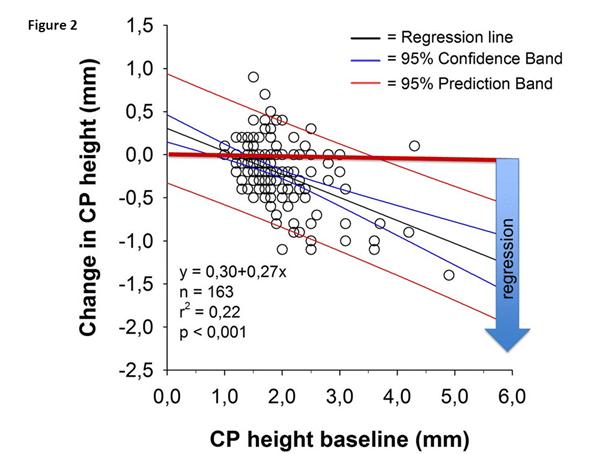
Age was 60.8±8.5 years (mean±SD). At baseline, median number and height of CP was 1.0 (range 1-6) and 1.80 mm (IQR 1.60, 2.10), respectively. Change in CP height after 18 months rosuvastatin treatment was -0.19±0.35 mm (p<0.001). Baseline and change in LDL-c was 4.0±0.9 mmol/L and -2.3±0.8 mmol/L (p<0.001). Mean LDL-c level during 18 months rosuvastatin treatment was 1.7±0.4 mmol/L (area under the curve). The degree of CP height reduction was independent of the LDL-c level exposure during the study period (p=0.36) (adjusted for age/gender/blood pressure)(Fig. 1a). Attainment of LDL-c ≤ 1.8 mmol/L or the change in LDL-c did not influence the degree of CP height reduction (p=0.44 and p=0.46, respectively) (Figure 1b). The higher the CP at baseline – the larger height reduction after 18 months with rosuvastatin treatment (p< 0.001)(Fig. 2). Disease activity during the study period measured by DAS28 (area under the curve) was inversely associated with change in CP height (p=0.02), so that patients with the highest disease activity had the smallest change in CP height and vice versa.
Conclusion
This is the first clinical study showing that intensive lipid lowering with statin induced regression of atherosclerosis in patients with IJD. Our results indicate that disease activity may influence the effect of anti-atherosclerotic treatment.
Disclosure:
S. Rollefstad,
None;
E. Ikdahl,
None;
J. Hisdal,
None;
I. C. Olsen,
None;
I. Holme,
None;
H. B. Hammer,
None;
K. T. Smerud,
None;
G. Kitas,
None;
T. R. Pedersen,
None;
T. K. Kvien,
None;
A. G. Semb,
None.
« Back to 2014 ACR/ARHP Annual Meeting
ACR Meeting Abstracts - https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/rosuvastatin-induced-carotid-plaque-regression-in-patients-with-inflammatory-joint-diseases/