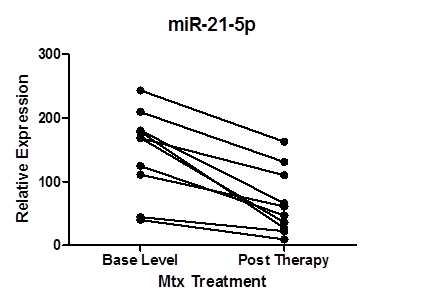Session Information
Date: Sunday, November 5, 2017
Title: Spondyloarthropathies and Psoriatic Arthritis – Pathogenesis, Etiology Poster I
Session Type: ACR Poster Session A
Session Time: 9:00AM-11:00AM
Background/Purpose: Psoriatic arthritis (PsA) is an inflammatory arthritis occurring in patients with psoriasis. miRNA’s are small non coding RNAs whose main function, at a post transcriptional level, is to modulate the expression of target genes via translation inhibition or mRNA degradation. A recent study identified miR-215p to be upregulated in early PsA and early rheumatoid arthritis (RA) and found down regulation post 12 weeks of methotrexate (MTX) treatment. Mir-21-5p was also found to be upregulated in several inflammatory and autoimmune diseases such as systemic sclerosis, systemic lupus erythematous, RA, type 1diabetes, and psoriasis. We aimed to determine the role of miR-21-5p as a biomarker for PsA and response to methotrexate.
Methods: Whole blood RNA samples collected in Tempus tubes from 40 patients with early PsA (<2 years disease duration and not receiving biologic therapy), 40 patients with PsC who have been confirmed by rheumatologist not to have PsA (>10 years psoriasis duration, not receiving biologic therapy, and matched to PsA patients on age, sex, psoriasis duration, and age of psoriasis onset), and 42 HC (matched to patients based on age, sex). RNA was extracted using the Tempus Spin RNA Isolation Kit with a genomic DNA removal step. miR-21-5p was validated using droplet digital PCR (ddPCR), a novel and sensitive technology for miRNA quantification. miR-21-5p expression was also measured in 10 PsA patients before and after 24 weeks of MTX treatment.
Results: The clinical, laboratory and miRNA expression data are presented in Table 1. Significant up regulation of miR-21-5p was seen in both early PsA and in PsC in comparison to HC (p<0.001). There was more upregulation in early PsA compared with PsC (p< 0.001), miR-21-5p was significantly down regulated 24 weeks post treatment in 10 patients (p< 0.008) (figure 1).
Conclusion: We have determined the role of miR21-5p as a biomarker for early PsA and response to methotrexate. Our results support previous work suggesting the potential role of miR21-5P in response to treatment biomarker in early PsA and as in inflammatory disorder marker.
Fig 1: miR 21-5p expression in PsA patients at baseline and after 24 weeks of therapy (p <0.008).
|
Table 1: Demographic, clinical and relative expression data |
||||
|
Variable |
PsA (N=40) |
PsC (N=40) |
CTL (N=42) |
P Value |
|
miR-21-5p* |
122.7 (93.1) |
58.5 (36.0) |
11.5 (9.6) |
<0.001 |
|
Gender – Male Gender – Female |
16 (40%) 24 (60%) |
15 (38%) 25 (63%) |
15 (38%) 25 (63%) |
0.97 |
|
Age* |
40.7 (11.0) |
41.9 (11.0) |
43.8 (12.0) |
0.002 |
|
PASI* |
7.1 (10.8) |
6.2 (4.4) |
N/A |
0.61 |
|
Actively inflamed joints* |
6.4 (7.0) |
NA |
N/A |
NA |
|
CRP (positive), n (%) |
6 (15%) |
1 (3%) |
N/A |
0.048 |
|
*mean±SD; PASI-psoriasis area severity index, actively inflamed joints tender and/or swollen joints; CRP- C reactive protein. |
||||
To cite this abstract in AMA style:
Machhar R, Ye J, Chandran V, Gladman DD. Role of Mir-21-5p As a Potential Biomarker of Psoriatic Arthritis and Response to Treatment [abstract]. Arthritis Rheumatol. 2017; 69 (suppl 10). https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/role-of-mir-21-5p-as-a-potential-biomarker-of-psoriatic-arthritis-and-response-to-treatment/. Accessed .« Back to 2017 ACR/ARHP Annual Meeting
ACR Meeting Abstracts - https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/role-of-mir-21-5p-as-a-potential-biomarker-of-psoriatic-arthritis-and-response-to-treatment/