Session Information
Title: Systemic Sclerosis, Fibrosing Syndromes and Raynaud’s – Pathogenesis, Animal Models and Genetics
Session Type: Abstract Submissions (ACR)
Background/Purpose:
Systemic sclerosis (SSc) is an autoimmune rare connective tissue disorder of unknown aetiology, heterogeneous clinical manifestations and an often progressive course which includes skin changes which are partly mediated by keratinocytes. It is proposed that immunoglobulin from patients with SSc causes activation of toll like receptors (TLR) 2 and 3.
Methods:
Initially, patient IgG samples which had previously been shown to up-regulate interleukins in HaCat immortalised keratinocytes were studied. More patient samples of IgG were then purified using a protein A column and TLR2 and TLR3 activation was measured using the HEK cell line which was co-transfected with either the hTLR2 or hTLR3 gene, and a secreted embryonic alkaline phosphatase (SEAP) gene. Concentrations of IgG used were 1000, 100, 10, 1 and 0.1 μg/mL.
Results:
Initial assessment of signalling downstream of TLRs gave variable results but some SSc samples induced nuclear translocation of NFκB (RelA). .
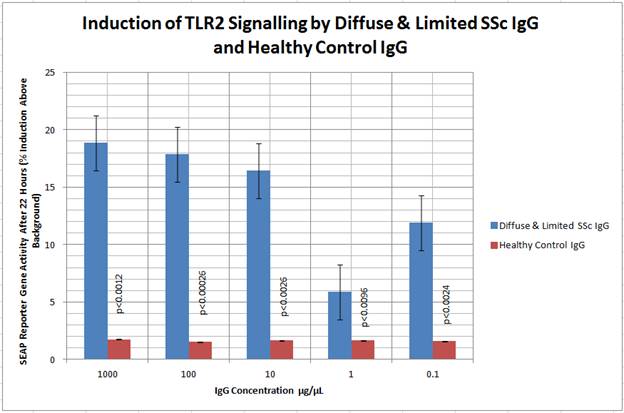
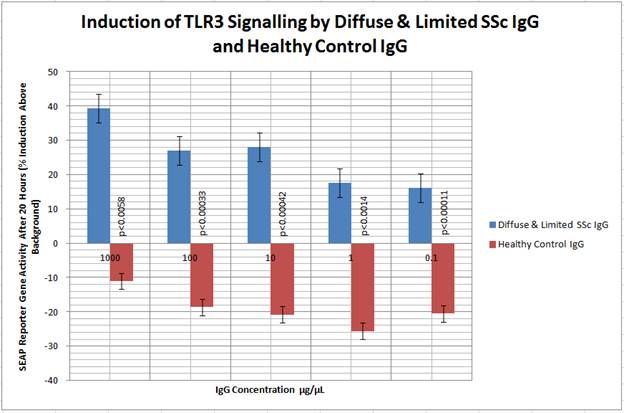
A total of 21 diffuse and limited SSc samples with 5 control samples were used. 13 SSc samples showed an increase in TLR2 signalling, whilst 3 SSC samples showed an increase in TLR3 signalling. No healthy control samples showed an increase in expression of TLR 2 or 3. On statistical analysis the data was grouped by disease type. At all concentrations studied p values were statistically significant showing an increase in TLR activity compared to healthy samples except for one, see figure 1 and 2.
Conclusion:
In conclusion SSc IgG induces TLR2 and TLR3 far more than healthy control IgG which may dampen the TLR2 and TLR3 response somewhat. The autoantibody component in SSc IgG that causes this is unknown. Further work will attempt to confirm the mechanism of TLR 2 and 3 activation.
Figure 1 Induction of TLR2 Signalling by Diffuse & Limited SSc IgG and Healthy Control IgG
HEK2 cells were exposed to Diffuse & Limited SSc (n = 21 patient samples) and control IgG (n = 5 control samples) at various concentrations for 24 hours. Treatment with Diffuse & Limited SSc IgG lead to induction of SEAP greater than healthy control IgG. Student’s t-test p values for Diffuse & Limited SSc vs control values shown.
Figure 2 Induction of TLR3 Signalling by Diffuse & Limited SSc IgG and Healthy Control IgG
HEK3 cells were exposed to Diffuse & Limited SSc (n = 21 patient samples) and control IgG (n = 5 control samples) at various concentrations for 20 hours. Treatment with Diffuse & Limited SSc IgG lead to induction of SEAP greater than healthy control IgG. Student’s t-test p values for Diffuse & Limited SSc vs control values shown.
Disclosure:
J. M. Watson,
None;
J. Nikitorowicz Buniak,
None;
X. Shiwen,
None;
D. J. Abraham,
None;
C. P. Denton,
None;
R. J. Stratton,
None.
« Back to 2012 ACR/ARHP Annual Meeting
ACR Meeting Abstracts - https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/role-of-endosomal-and-cell-membrane-toll-like-receptors-in-keratinocyte-activation-by-systemic-sclerosis-autoantibodies/