Session Information
Session Type: Abstract Submissions (ACR)
Background/Purpose:
The number of biologic therapies approved for use in treating rheumatoid arthritis (RA) has grown steadily over the past 15 years. While many patients are treated with anti-TNF therapies, 30-40% of these patients fail to respond adequately as their disease progressively worsens. Tools to guide disease management and identify a priori which patients are likely to be non-responsive to anti-TNF therapies would allow these patients to seek alternative therapies to achieve faster relief from symptoms, avoid unnecessary treatment side effects, and avoid further disease progression.
Methods:
Four published gene expression data sets containing a total of 91 patients were used to train a classifier to identify anti-TNF non-responders. Gene expression measurements, collected prior to patient treatment with the anti-TNF infliximab, were grouped into disease-relevant biological signaling mechanisms to provide a stable, quantitative representation of biological state. Regularized logistic regression was used to train a classifier to identify non-responders, and a classifier score threshold was selected to optimize for detection of non-responders with high specificity.
Results:
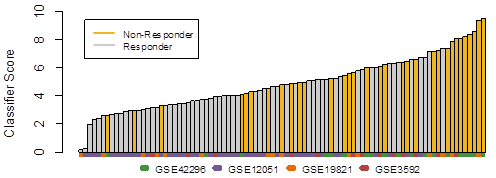
Repeated 10-fold cross-validation resulted in highly-specific prediction of non-response (specificity = 92%; likelihood ratio = 5.53; area under the receiver operator characteristic curve (AUROC) = 78%, p-value<0.00001; Figure 1), while still correctly identifying a significant fraction of non-responders (sensitivity = 45%). Prediction of non-response on independent infliximab treated cohorts, consisting of an independent 27 patient cohort as well as each of the four training when left out in turn from training, resulted in AUROCs between 63% and 80% and associated p-values between 0.029 and 0.15. Specificity of the classifier for infliximab and its therapeutic target TNF was supported by a lack of association with responses in small rituximab (anti-CD20) and tocilizumab (anti-IL6R) treated cohorts.
Figure 1. A representative patient stratification from 10-fold cross validation, matching the mean AUROC of 78% across all cross validation repeats, shows the classifier score for each patient. Patients were sorted by classifier score and colored by their clinical response calls.
Conclusion:
The classifier developed in this study identifies RA patients who are unlikely to respond to infliximab, and thus are good candidates for alternative biologic therapies. The test robustly predicts non-response across multiple patient cohorts. Future iterations of the test could include additional training cohorts and expansion to include complementary prediction of response to other RA therapies.
Disclosure:
T. Thomson,
Selventa,
1,
Selventa,
3;
R. Lescarbeau,
Selventa,
1,
Selventa,
3;
D. Drubin,
Selventa,
1,
Selventa,
3;
D. Fryburg,
Selventa,
1,
Selventa,
3;
D. de Graaf,
Selventa,
1,
Selventa,
3;
R. Deehan,
Selventa,
1,
Selventa,
3;
D. Laifenfeld,
Selventa,
1,
Selventa,
3;
A. Van Hooser,
Selventa,
1,
Selventa,
3.
« Back to 2014 ACR/ARHP Annual Meeting
ACR Meeting Abstracts - https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/robust-identification-of-anti-tnf-non-responders-in-ra-from-blood/