Session Information
Session Type: Abstract Session
Session Time: 11:00AM-11:15AM
Background/Purpose: The global COVID-19 pandemic is starting to be controlled by massive vaccination. Some immunosuppressed patients have already paid a high price to the pandemic with increased risk of death in cancer patients and in autoimmune diseases patients treated with rituximab (hazard ratio of death: 4,04 (2,32-7,03). Despite the tremendous efficacy of novel mRNA vaccines, some immunocompromised patients seem not to respond at the same level compared to healthy controls to these vaccines when anti-spike antibodies are considered.
Objectives: To compare autoimmune diseases patients treated with either rituximab (RTX) or other immunosuppressants (other IS) and controls regarding response to mRNA vaccines.
Methods: Patients and healthy controls (HC) were vaccinated with BNT162b2 at days 0 and 28 and sampled at days 28 and 56. Patients with detectable levels of anti-nucleocapsid at any time points were excluded. Patients were divided into 2 groups: “RTX group” if they had received RTX ≤1 year, or “other IS group” if they were treated with other immunosuppressants. Serological assessment of vaccine response (ECLIA Cobas, Roche) and neutralization (iFlash-2019-nCoV Nab assay, Ylho) was performed. According to preliminary data, a threshold ≥ 50 of anti-Spike IgG was defined as a response to vaccine (since it is the value were patients had detectable neutralizing antibodies in the neutralization test). T-cell response against spike peptides using intra-cellular staining of TNF, IFNg, IL6, granzyme and perforine on activated CD4 and CD8 T cells will also be analyzed in all patients and will be presented at the time of the ACR meeting.
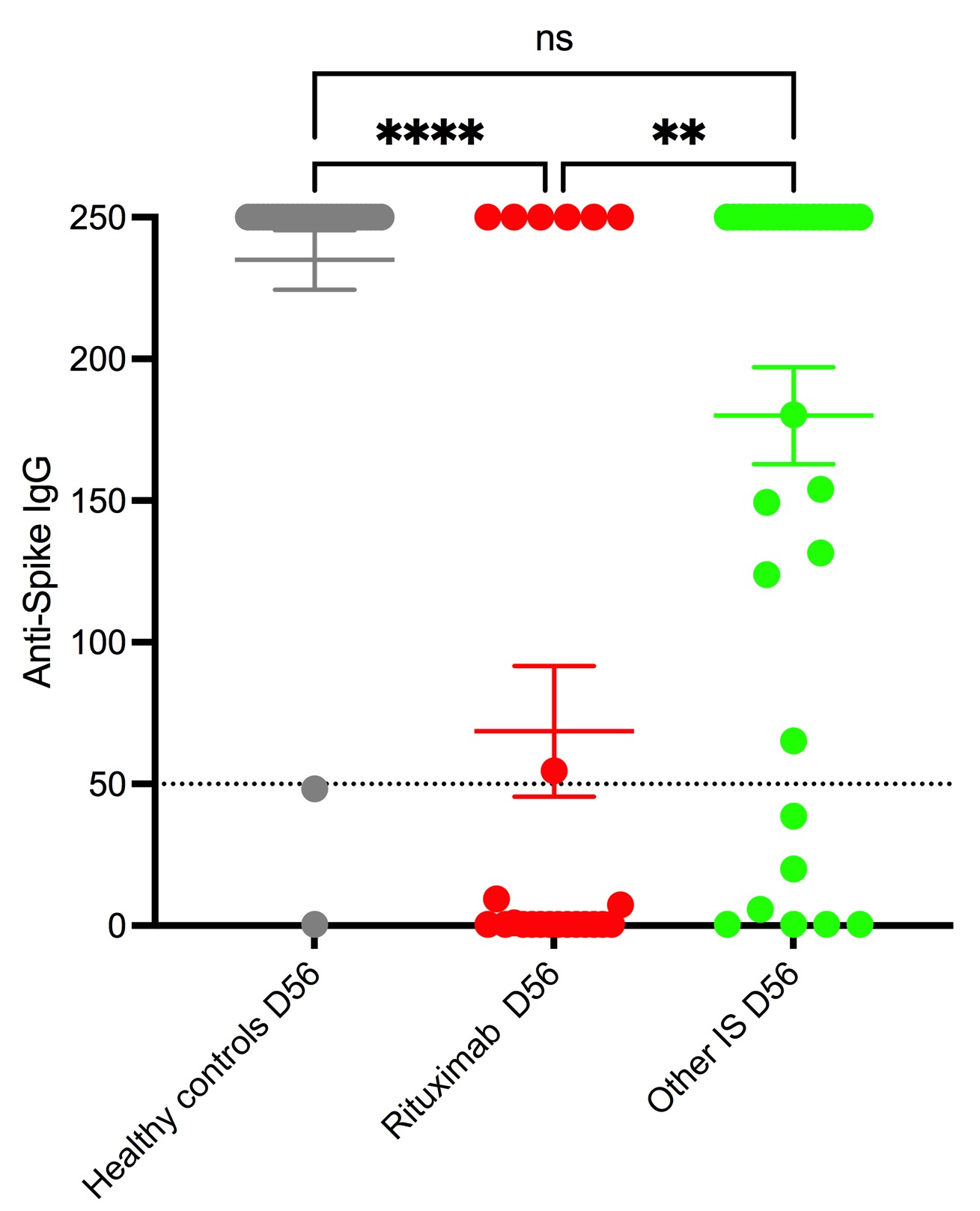
Results: 28 HC and 57 patients with autoimmune diseases were included: 24 patients in rituximab group and 33 in other IS group. On day 28, HC had significantly higher median levels of anti-Spike IgG (46.7 IQR 146) compared to RTX and other Is : 0.4 IQR 3.8 and 4.5 IQR 20.5 respectively. At day 56, compared to both control (250 IQR 0) and other IS groups (250 IQR 141), the RTX (0.4 IQR 250) group had significantly lower median levels of anti-spike IgG (see figure). The RTX group also had a lower response rate : 29,2% in RTX group vs.79.4% in other IS group and 92,2% in HC There was no difference in anti-Spike IgG levels or percentage of response between the HC and other IS group. Within the RTX group, the median time to last RTX infusion was significantly lower in the non-responders (81 days IQR 147) compared to responders (231 days IQR 89). None of the patients having received RTX in the previous 6 months responded to the vaccine.
Conclusion: In patients with autoimmune disorders treated with immunosuppressors, responses after 1 dose of mRNA COVID vaccine were lower to that of HC. However, assessed one month after the second dose responses remained significantly impaired only in RTX treated patients (lower response rate and IgG anti-spike levels), but not in patients with patients treated with other IS. In RTX treated patients, the main factor associated with lack of response was time since last infusion. Given the low frequency of patients on RTX having a humoral response, it will be key to assess if these patients will have or not a cellular response. Data will be presented at the congress.
To cite this abstract in AMA style:
Bitoun S, Henry J, Vauloup Fellous C, Seror R, Mouna L, Joly C, Desjardins D, Bitu M, Le Grand R, Roque Afonso A, Mariette X. Rituximab Treatment Dramatically Reduces Neutralizing Humoral Response to mRNA SARS-COV-2 Vaccines in Patients with Autoimmune Diseases [abstract]. Arthritis Rheumatol. 2021; 73 (suppl 9). https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/rituximab-treatment-dramatically-reduces-neutralizing-humoral-response-to-mrna-sars-cov-2-vaccines-in-patients-with-autoimmune-diseases/. Accessed .« Back to ACR Convergence 2021
ACR Meeting Abstracts - https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/rituximab-treatment-dramatically-reduces-neutralizing-humoral-response-to-mrna-sars-cov-2-vaccines-in-patients-with-autoimmune-diseases/