Session Information
Session Type: ACR Poster Session B
Session Time: 9:00AM-11:00AM
Background/Purpose: Rituximab (RTX) is a chimeric monoclonal antibody approved for the treatment rheumatoid arthritis (RA) patients who failed to respond to tumor necrosis factor inhibitors. Due to its effect on induction of B cell depletion, the administration of multiple cycles can lead to a decrease in immunoglobulins (Ig) which may increase the risk of infection. We aim to evaluate the long-term safety of RTX in RA patients.
Methods: Retrospective observational study was conducted including RA patients treated in a tertiary hospital between June 2006 and May 2017 who had received at least two RTX cycle. At RTX initiation we analyzed: comorbidities and Charlson score, presence of rheumatoid factor (RF) / anti-citrullinated protein antibodies (ACPA), previous biological DMARD (bDMARD); concomitant treatment (csDMARD / glucocorticoids (GC)) as well as demographic and clinical features. Serum Ig levels before every RTX cycle, the number of RTX cycles and adverse events (AE), including serious and opportunistic infections were also analyzed. Non-disseminated Herpes-Zoster (HZ) were not considered opportunistic infection.
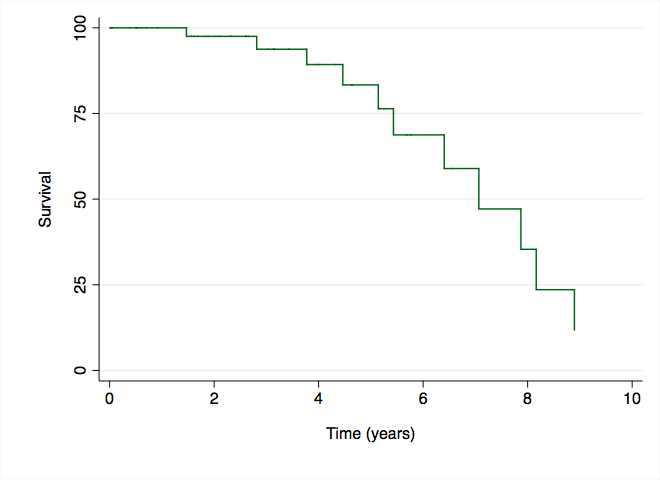
Results: 53 patients were included (86.8% women, mean age 55.5 ± 13.5 years), 58% had a Charlson score ≥ 3. Mean disease duration was 16 ± 9.1 years; 84.9% and 92.5% were RF and ACPA positive, respectively. Before starting RTX, 81% of patients had received other bDMARD (58.5% ≥ 2), 88% received concomitant csDMARD, (52% methotrexate and 32% leflunomide) and 81% were treated with GC (median dose 10 mg, P25-75 5-10 mg). The median number of RTX cycles received per patient was 5 (P25-75 2-6). 80 AE were reported: 12 infusion reactions, 8 cases of neutropenia, 51 infections (18 respiratory, 8 urinary, 4 skin and soft tissues, 8 gastrointestinal, 4 cases of non-disseminated HZ, 1 bacteremia, 2 septic shock and 6 other) of which 19 were serious. 5 malignancies (2 melanomas, 2 cervix, and 1 bladder) were also notified. The incidence rate of serious infections was 6.75 / 100 PY, and its appearance remained stable throughout the follow-up time (Figure.1). No opportunistic infections or HBV reactivations were reported.
Ig levels were obtained for 41 subjects: 7, 5 and 1 patients had low levels of IgG, IgM and IgA, respectively. Patients who developed infections received a greater number of RTX cycles (p<0.0002) and had more frequently low levels of serum IgG during follow-up (p><0.044) than those who did not have infections.><0.002) and had more frequently low levels of serum IgG during follow-up (p<0.044) than those who did not have infections.
Conclusion: Long-term exposure to RTX showed a good safety profile with a low incidence of serious infectious and no opportunistic infections. Only number of cycles received and low serum levels of IgG at any point during follow-up were associated with the development of infections.
Figure 1. Evolution of Serious Infections Occurrence During Follow-up
To cite this abstract in AMA style:
Castellanos-Moreira R Sr., Rodriguez-Garcia SC, Hernández MV, Ruiz-Esquide V, Camacho O Sr., Cuervo A, Ramírez J, Cañete J, Gomez Puerta J, Sanmarti R. Rituximab Safety in Patients with Rheumatoid Arthritis. an Eleven-Year Follow-up Observational Study [abstract]. Arthritis Rheumatol. 2018; 70 (suppl 9). https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/rituximab-safety-in-patients-with-rheumatoid-arthritis-an-eleven-year-follow-up-observational-study/. Accessed .« Back to 2018 ACR/ARHP Annual Meeting
ACR Meeting Abstracts - https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/rituximab-safety-in-patients-with-rheumatoid-arthritis-an-eleven-year-follow-up-observational-study/
