Session Information
Date: Sunday, November 8, 2020
Session Type: Poster Session C
Session Time: 9:00AM-11:00AM
Background/Purpose: The presence of interstitial lung disease (ILD) in patients with autoimmune diseases (AD)s influences significantly on their morbidity and mortality [1]. Different treatment strategies have been proposed, including lung transplantation as the last alternative [2]. Corticosteroids, cyclophosphamide and mycophenolate mofetil are the most widely used conventional immunosuppressive drugs [3]. Rituximab (RTX), a chimeric (human/ murine) monoclonal antibody against the surface antigen CD20 expressed on pre-B and B lymphocytes, has shown efficacy in the treatment of patients with ILD associated with AD (AD-ILD), even as a rescue alternative in severe and refractory cases [4]. In the present study, we aimed to report our experience with RTX in the treatment of patients with AD-ILD.
Methods: We performed a retrospective study of patients assessed from May 2016 until March 2020 in a referral clinic of ILD and lung transplantation (Hospital Universitario Marqués de Valdecilla, Santander, Spain). Patients with a diagnosis of AD-ILD who received RTX were assessed. The main indications for RTX administration were the presence of a significant ILD in the setting of AD or the identification of an AD in the course of an established ILD. Clinical characteristics, radiological findings and pulmonary function tests (PFTs) were evaluated. PFTs were collected at baseline (RTX onset), at 6 months and annually until 2 years with RTX therapy.
Results: A total of 26 patients were included, with a mean age of 58.3 ± 11.1 years at ILD diagnosis. The most frequent ADs related to ILD were systemic sclerosis, idiopathic inflammatory myositis (including anti-synthetase syndrome) and rheumatoid arthritis. Non-specific interstitial pneumonia and usual interstitial pneumonia were the predominant radiological patterns. Demographic and clinical characteristics of the AD-ILD patients are shown in Table 1. A sustained improvement of PFTs was observed from the initiation of RTX, with a statistically significant increase of DLCO from basal to one year after RTX (mean + 4.2%, p = 0.024). Overall, no differences were found comparing PFT’s outcomes according to the radiological pattern (Figure 1) or the specific type of AD.
Conclusion: RTX constitutes a good therapeutic option to preserve lung function in patients with AD-ILD, regardless of the radiological pattern or the underlying AD.
 Table 1. Demographic and clinical characteristics of 26 AD-ILD patients included in this study.
Table 1. Demographic and clinical characteristics of 26 AD-ILD patients included in this study.
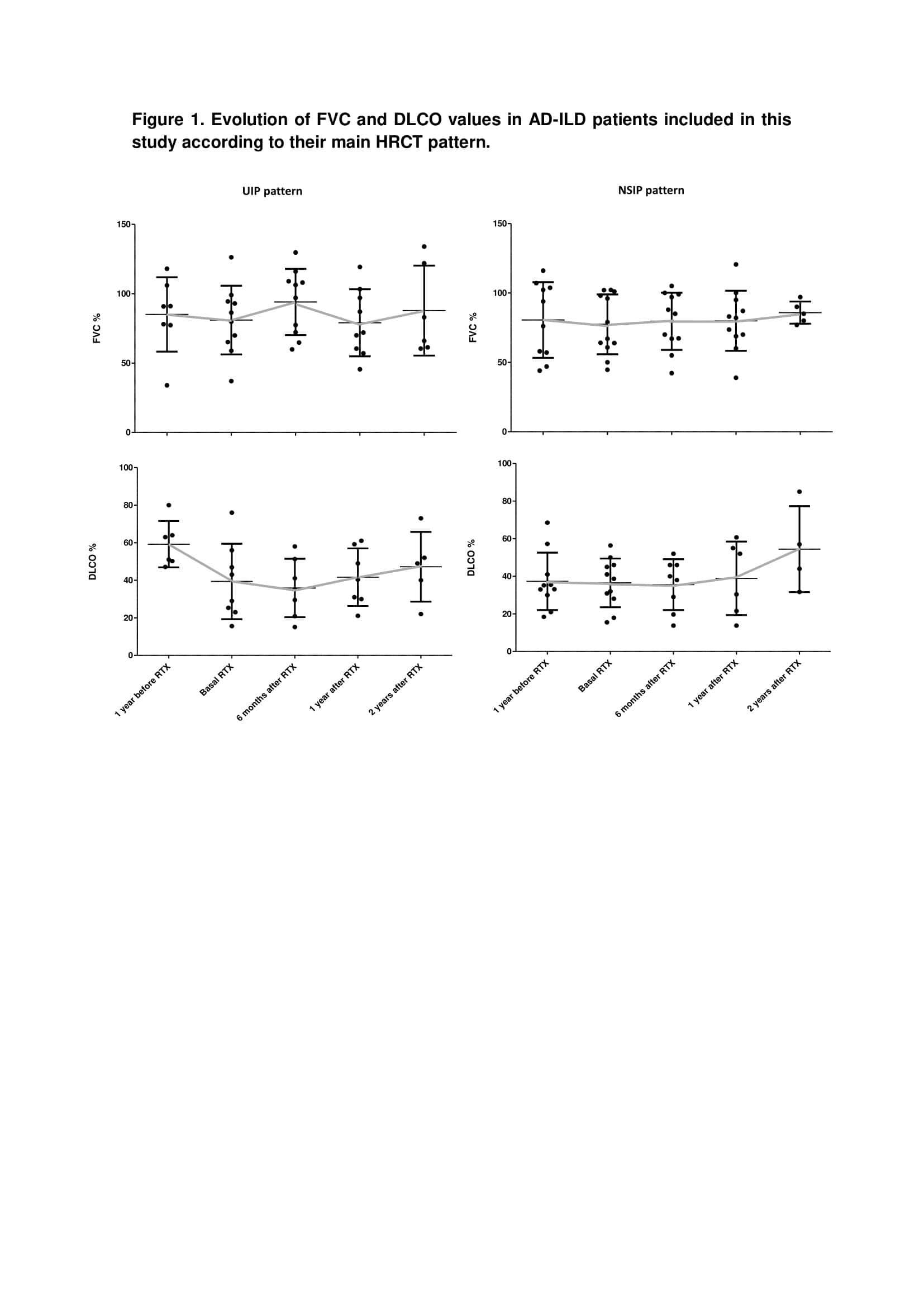 Figure 1. Evolution of FVC and DLCO values in AD-ILD patients included in this study according to their main HRCT pattern.
Figure 1. Evolution of FVC and DLCO values in AD-ILD patients included in this study according to their main HRCT pattern.
To cite this abstract in AMA style:
Atienza-Mateo B, Remuzgo-Martínez S, Prieto-Peña D, Mora Cuesta V, Iturbe-Fernández D, Fernández Rozas S, Corrales A, Cifrián J, González-Gay M. Rituximab in the Treatment of Interstitial Lung Disease Associated with Autoimmune Diseases: Experience from a Single Referral Center [abstract]. Arthritis Rheumatol. 2020; 72 (suppl 10). https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/rituximab-in-the-treatment-of-interstitial-lung-disease-associated-with-autoimmune-diseases-experience-from-a-single-referral-center/. Accessed .« Back to ACR Convergence 2020
ACR Meeting Abstracts - https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/rituximab-in-the-treatment-of-interstitial-lung-disease-associated-with-autoimmune-diseases-experience-from-a-single-referral-center/
