Session Information
Date: Monday, November 13, 2023
Title: (1052–1081) Immunological Complications of Medical Therapy Poster
Session Type: Poster Session B
Session Time: 9:00AM-11:00AM
Background/Purpose: Rituximab (RTX) is a murine/human chimeric monoclonal antibody directed against the CD20 receptor expressed on pre-B and mature B cells. Rituximab is used effectively in the treatment of different rheumatic diseases, but it can induce hypogammaglobulinemia as a side effect. The purpose of our study was to analyze the prevalence of hypogammaglobulinemia and its association with infections in patients with rheumatic diseases treated with RTX.
Methods: Multicenter, retrospective, observational study. Patients with rheumatic diseases treated with RTX in 4 centers in Madrid, in which serum immunoglobulin counts were available were included. Demographic and clinical variables of the sample were analyzed, changes in immunoglobulin G concentrations during treatment from baseline were assessed. The chi-square test was used to examine the relationship between variables, considering a p value < 0.05 as statistically significant. Logistic regression models were used to analyze the association between hypogammaglobulinemia and sample characteristics.
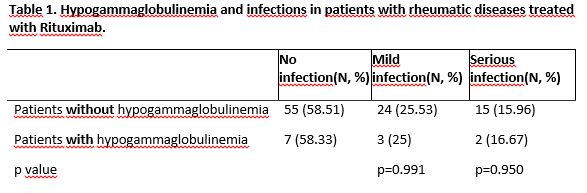
Results: One hundred and seven patients were included: 18 men (16.8%) and 89 women (83.2%), with a mean age of 55.9 (±13.9) years, a mean disease duration of 13.1 (±0.8) years, and a mean age of 51 (±14.4) years at the start of treatment. The most prevalent diagnoses were rheumatoid arthritis (RA) (50.5%), primary Sjogren’s syndrome (pSS) (10.3%), and systemic lupus erythematosus (SLE) (10.3%). Fourteen (13%) patients were treated with RTX monotherapy. The rest of the patients received concomitant treatment with other immunomodulators such as corticosteroids (64.5%), methotrexate (29%), hydroxychloroquine (27%), leflunomide (9.3%), sulfasalazine (1.9%), or mycophenolate mofetil (2.8%). Twelve (11.21%) patients developed hypogammaglobulinemia (IgG< 600 mg/dl): 6 (50%) had RA, 1 (8.3%) SLE, 1 (8.3%) ANCA vasculitis, 1 (8.3%) leukocytoclastic vasculitis, 1 (8.3%) IgG4-related disease, 1 (8.3%) dermatomyositis, and 1 (8.3%) pSS. Patients with hypogammaglobulinemia had significantly lower mean serum IgG concentrations at the start of treatment (876.3 vs 1249.4 mg/dl; p=0.05). In the multivariate analysis no variable related to hypogammaglobulinemia was found. Fifty-three (49.5%) patients presented infection, of which 17 (15.9%) were serious infections (those that required admission). The distribution of infection by groups (patients with and without hypogammaglobulinemia) is shown in Table 1. No significant differences were found in the development of infections or serious infections between patients with and without hypogammaglobulinemia. Only corticosteroid doses equivalent to ≥7.5 mg/day of prednisone were found as a risk factor for the development of infections (OR 3.48, 95% CI: 1.20-0.11; p=0.02).
Conclusion: Patients with hypogammaglobulinemia had significantly lower mean IgG concentrations at the start of treatment with RTX than those who did not develop it. No greater frequency or severity of infections was observed between patients with and without hypogammaglobulinemia. Prednisone equivalent daily dose ≥7.5 mg/day was a risk factor for occurrence of infections. Larger sample size studies are needed to confirm these findings.
To cite this abstract in AMA style:
Rusinovich O, Calvo-Aranda E, Gomez C, Cardoso Peñafiel P, Navarro Alonso P, Cantalejo Moreira M, Diaz y Oca A, Navarro P, Machattou M, Alonso M, Navarro C, Merino C, Godoy H, Barbadillo Mateos M, Isasi C, Perez Ferro M, Polo J, Garcia V, Andreu-Sánchez J, Campos J, Sanz J. Rituximab-Associated Hypogammaglobulinemia in Patients with Rheumatic Diseases: A Multicenter Retrospective Observational Study [abstract]. Arthritis Rheumatol. 2023; 75 (suppl 9). https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/rituximab-associated-hypogammaglobulinemia-in-patients-with-rheumatic-diseases-a-multicenter-retrospective-observational-study/. Accessed .« Back to ACR Convergence 2023
ACR Meeting Abstracts - https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/rituximab-associated-hypogammaglobulinemia-in-patients-with-rheumatic-diseases-a-multicenter-retrospective-observational-study/