Session Information
Session Type: Abstract Submissions (ACR)
Risk of Ischemic Stroke in Patients with Systemic Sclerosis: A Systematic Review and Meta-analysis
Background/Purpose: Several chronic inflammatory disorders, such as rheumatoid arthritis and systemic lupus erythematosus, have been shown to increase risk of ischemic stroke secondary to accelerated atherosclerosis. However, the data on systemic sclerosis (SSc), another chronic inflammatory disease, remain unclear due to conflicting epidemiological studies. Thus, to further investigate this possible association, we conducted a systematic review and meta-analysis of observational studies that compared the risk of ischemic stroke in patients with SSc versus participants without it.
Methods : Two investigators (P.U. and P.C.) independently searched published studies indexed in MEDLINE, EMBASE and the Cochrane database from inception to March 2014 using the terms “systemic sclerosis” and “scleroderma” combined with the terms for cerebrovascular disease. A manual search of references of retrieved articles was also performed. The inclusion criteria were as follows: (1) observational studies published as original studies to evaluate the association between SSc and ischemic stroke and (2) odds ratios (OR’s), relative risk (RR’s) or hazard ratio (HR’s) or standardized incidence ratio (SIR’s) with 95% confidence intervals (CI’s) were provided. Study eligibility was independently determined by the two investigators noted above. Differing decisions were resolved by consensus with the senior investigator. The quality of each study was, again, independently assessed by the two investigators using Newcastle-Ottawa scale.
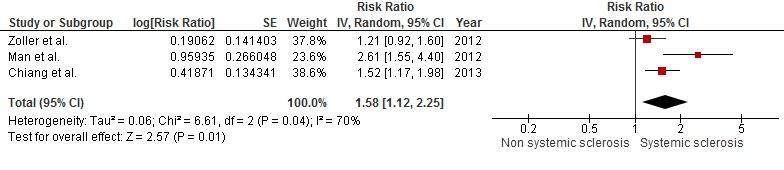
RevMan 5.2 software was used for the data analysis. Point estimates and standard errors were extracted from individual studies and were combined by the generic inverse variance method of DerSimonian and Laird. Given the high likelihood of between study variance, we used a random-effect model rather than a fixed-effect model. Statistical heterogeneity was assessed using the Cochran’s Q test.
Results : Out of 370 potentially relevant articles, three studies (all were retrospective cohort studies) with 3,861 cases of SSc were identified and included in our data analysis. The pooled risk ratio of ischemic in patients with SSc was 1.58 (95% CI, 1.12 to 2.25). The statistical heterogeneity of this meta-analysis was moderate with an I2 of 70%.
Conclusion : Our study demonstrated a statistically significant increased ischemic stroke risk among patients with SSc.
Disclosure:
P. Ungprasert,
None;
P. Ratanasrimetha,
None;
C. Thongprayoon,
None;
W. Cheungpasitporn,
None;
P. Suksaranjit,
None.
« Back to 2014 ACR/ARHP Annual Meeting
ACR Meeting Abstracts - https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/risk-of-ischemic-stroke-in-patients-with-systemic-sclerosis-a-systematic-review-and-meta-analysis/