Session Information
Session Type: Poster Session D
Session Time: 8:30AM-10:30AM
Background/Purpose: Immunogenicity is related to loss of efficacy and safety to TNFα inhibitors and is frequently observed early in the treatment course. The highest rate of anti-drug antibody (ADAb) formation has been reported for infliximab (IFX). Knowledge about risk factors for immunogenicity might contribute to better handling of this problem in clinical practice. The aim of this sub study of the NOR-DRUM A trial (main results recently published in JAMA1) was to identify risk factors for ADAb formation during the early phase of infliximab (IFX) treatment.
Methods: 411 patients with immune-mediated inflammatory diseases (84 rheumatoid arthritis (RA), 119 spondyloarthritis (SpA), 45 psoriatic arthritis, 83 ulcerative colitis, 58 Crohn’s disease and 22 psoriasis) initiating IFX treatment were included in the 38-week NOR-DRUM A trial and randomised 1:1 to therapeutic drug monitoring or standard IFX therapy.1 The primary endpoint was clinical remission at week 30. Serum (s) IFX levels and ADAb were measured at each infusion by in-house assays; time-resolved fluorometric assay for sIFX and inhibition assay for ADAb.1 Possible risk factors for ADAb formation including demographic variables, diagnosis, comedication, disease activity, IFX dose, sIFX and drug holidays, were assessed using logistic regression. Variables with a p-value < 0.25 in univariate analyses were further examined in multivariate analyses adjusting for potential confounders (diagnosis, disease activity, age and gender).
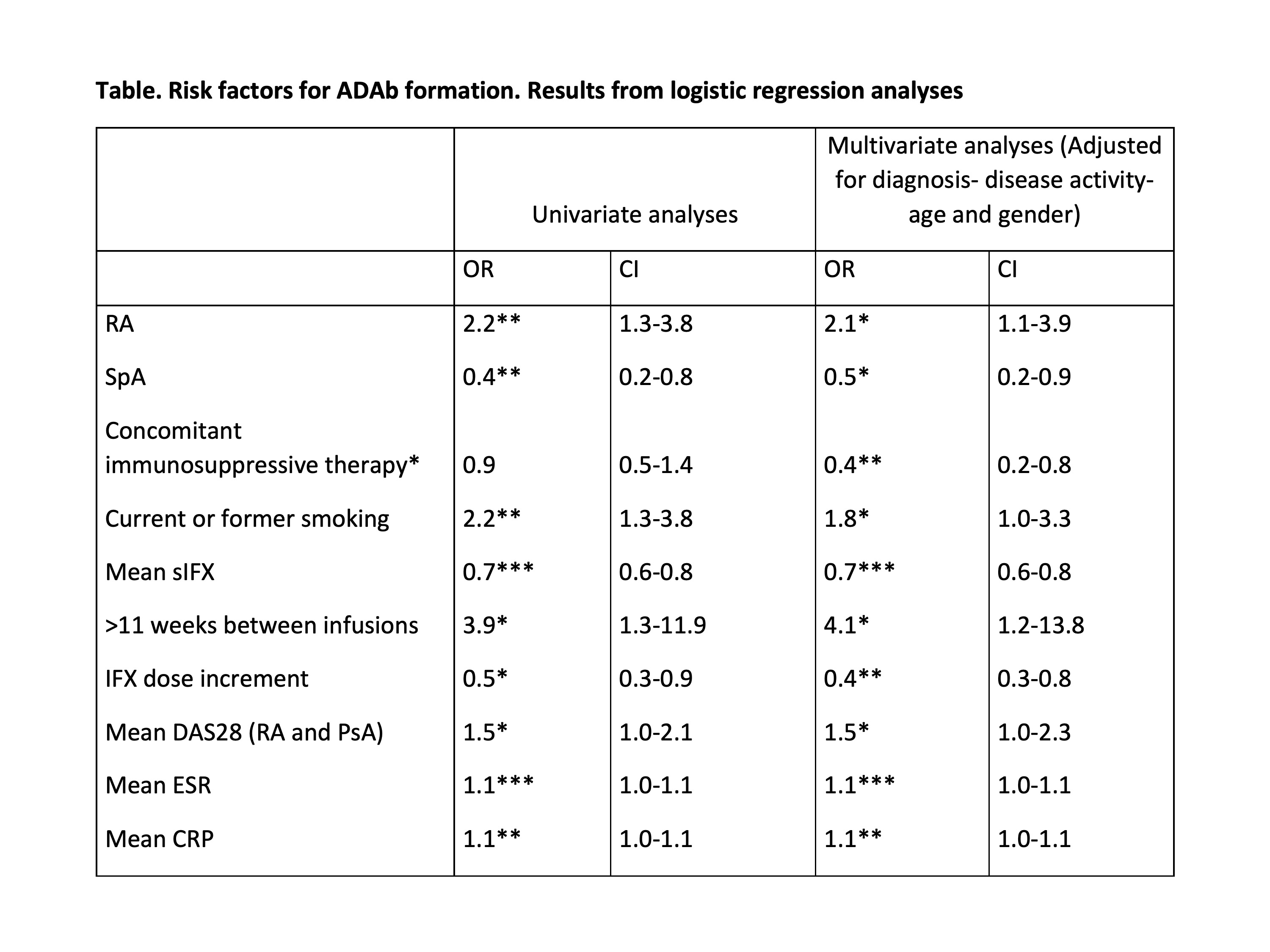
Results: 410 patients with at least one available sIFX measurement were included in the present analyses. 76% were biologic-naive, and 45% (18% of RA patients) used IFX as monotherapy. Patients received a mean IFX dose of 3.2-5.9 mg/kg (RA 3.2 mg/kg). ADAb were detected in 78 (19%) patients. The Table shows variables with a significant association to ADAb formation. Analyses revealed an increased risk of ADAb development in patients with RA (Odds ratio (OR) 2.1, 95% confidence interval (CI) 1.1-3.9) ADAb formation, while SpA had a lower risk (OR 0.5, CI 0.2-0.9) compared to the other diagnoses. These findings were consistent in both univariate- and multivariate analyses. Figure 1 shows the cumulative hazard for ADAb formation according to diagnosis. Other risk factors for ADAb formation (Table) were smoking (OR 1.8, CI 1.0-3.3) and drug holidays of more than 11 weeks (OR 4.1, CI 1.2-13.8). Additionally, the risk of ADAb increased with higher disease activity (OR 1.5, CI 1.0-2.3) and lower sIFX levels (OR 0.7, CI 0.6-0.8). Patients using concomitant immunosuppressive medication (OR 0.4, CI 0.2-0.8), or having one or more IFX dose increments (OR 0.4, CI 0.3-0.8), had a reduced risk of immunogenicity.
Conclusion: This study identified smoking, drug holidays, high disease activity, IFX monotherapy and low sIFX levels as risk factors for ADAb development. Of particular interest, we found that RA patients had an increased risk of ADAb compared to the other immune-mediated inflammatory diseases. Whether this novel finding reflects different underlying disease mechanisms or the fact that RA patients receive a lower IFX dose, is not known and needs to be further explored.
1 Syversen SW et al. JAMA. 2021;325(17):1744–1754.
All variables with a P-value < 0.25 in univariate analyses were examined in multivariate analyses adjusting for potential confounders. Only variables with a p-value < 0.05 are shown. Non-significant variables include other demographic variables and IFX dose. *Included in table despite an unadjusted P-value>0.25 because this variable vas significant in adjusted analysis.
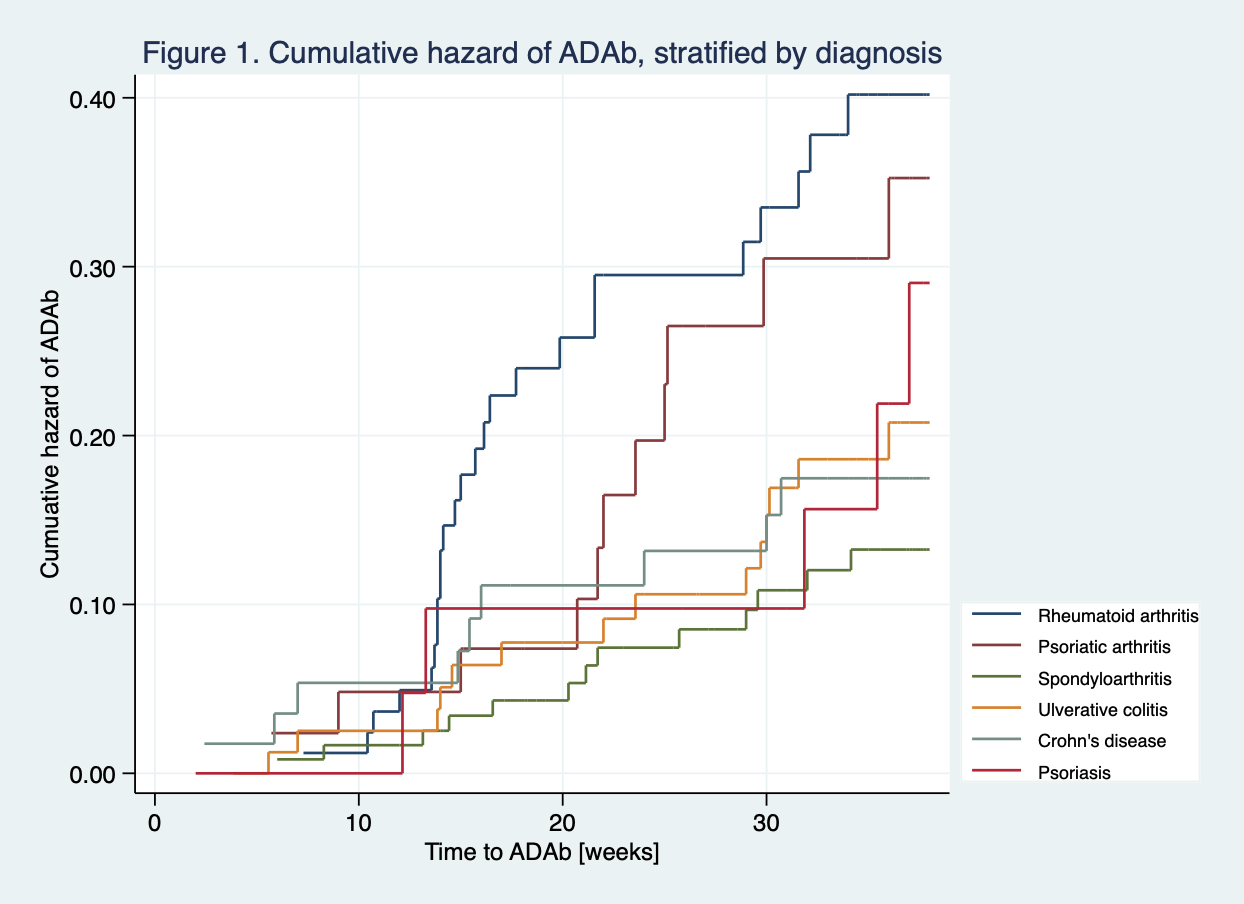 Nelson-Aalen plot showing the cumulative hazard of ADAb for each diagnosis. Each step indicates a new event (ADAb). The slope of the curve indicates the hazard rate.
Nelson-Aalen plot showing the cumulative hazard of ADAb for each diagnosis. Each step indicates a new event (ADAb). The slope of the curve indicates the hazard rate.
To cite this abstract in AMA style:
Brun M, Goll G, Jørgensen K, Sexton J, Gehin J, Sandanger , Olsen I, Klaasen R, Warren D, Mørk C, Kvien T, Jahnsen J, Bolstad N, Haavardsholm E, Syversen S. Risk Factors for Anti-infliximab Antibody Formation: Results from a Randomized Controlled Trial [abstract]. Arthritis Rheumatol. 2021; 73 (suppl 9). https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/risk-factors-for-anti-infliximab-antibody-formation-results-from-a-randomized-controlled-trial/. Accessed .« Back to ACR Convergence 2021
ACR Meeting Abstracts - https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/risk-factors-for-anti-infliximab-antibody-formation-results-from-a-randomized-controlled-trial/