Session Information
Date: Monday, October 27, 2025
Title: (1467–1516) Systemic Lupus Erythematosus – Diagnosis, Manifestations, & Outcomes Poster II
Session Type: Poster Session B
Session Time: 10:30AM-12:30PM
Background/Purpose: Lupus nephritis (LN) affects over half of patients with systemic lupus erythematosus (SLE) and is associated with an increased risk for adverse kidney outcomes. We sought to identify risk factors for chronic kidney disease (CKD) and end-stage kidney disease (ESKD) in patients with newly diagnosed LN.
Methods: We identified an inception cohort of patients with biopsy-proven LN in the Mass General Brigham health system. We included patients with an index kidney biopsy between 2001-2024, excluding those with prior kidney transplant, and with available laboratory signs of LN prior to the index kidney biopsy. These included a spot or timed urine protein estimating ≥500mg/24 hr or microalbumin ≥300mg/24 hr, urinalysis with ≥2+ protein, or RBC casts. We assessed the effect of time between the first abnormal LN laboratory sign and kidney biopsy (>90 days versus ≤90 days), chronicity index score on kidney biopsy ( >3 compared to ≤3), as well as the use of hydroxychloroquine (HCQ) and an ACEi or ARB in the 12 months prior to kidney biopsy, on subsequent kidney outcomes. Primary outcomes included new-onset CKD stage ≥3 and ESKD through 5 years following the first kidney biopsy. We used Cox proportional hazards regression, adjusting for age, sex, race and ethnicity, diagnoses of diabetes and hypertension, and prior SLE immunosuppressant use (including oral and biologic immunosuppressants but not glucocorticoids). We also performed subgroup analyses among patients with membranoproliferative LN (class III or IV +/- class II or V) as well as those with membranoproliferative LN who had not received treatment with an immunosuppressant prior to the kidney biopsy.
Results: There were 387 patients with newly diagnosed, biopsy-proven LN with a mean age of 38.9 years (SD 16.1); 83% were female, 43% were White, and 26% were Black (Table 1). Two-thirds of patients had membranoproliferative LN and one-third had previously received treatment with an immunosuppressive agent. Among those with membranoproliferative LN, a chronicity index score >3 on the first kidney biopsy was associated with an increased risk of new-onset CKD stage ≥3 and ESKD (adjusted HR [aHR] 2.94 [95% CI 1.44-5.99] and 12.27 [95% CI 2.16-69.67], respectively (Table 2). The risk increased further among those with membranoproliferative LN without prior immunosuppressant use (aHR 3.79 [95% CI 1.47-9.81] and 70.43 [95% CI 2.68-1852.16], respectively. The rates of CKD and ESKD were numerically higher with a longer time to kidney biopsy from the first LN laboratory sign. Treatment with HCQ at baseline was protective against new-onset ESKD in unadjusted HRs, but did not reach statistical significance in the adjusted models.
Conclusion: In this cohort of patients with newly diagnosed LN on kidney biopsy, a higher chronicity index score was associated with a substantially increased risk of new-onset CKD stage ≥3 and ESKD. A duration of more than 90 days to kidney biopsy from the first LN laboratory sign may also portend an increased risk of these adverse kidney outcomes though did not reach statistical significance. HCQ use may be protective. Our data is limited by a small sample size. These findings highlight risk factors associated with a worse prognosis among newly diagnosed patients with LN.
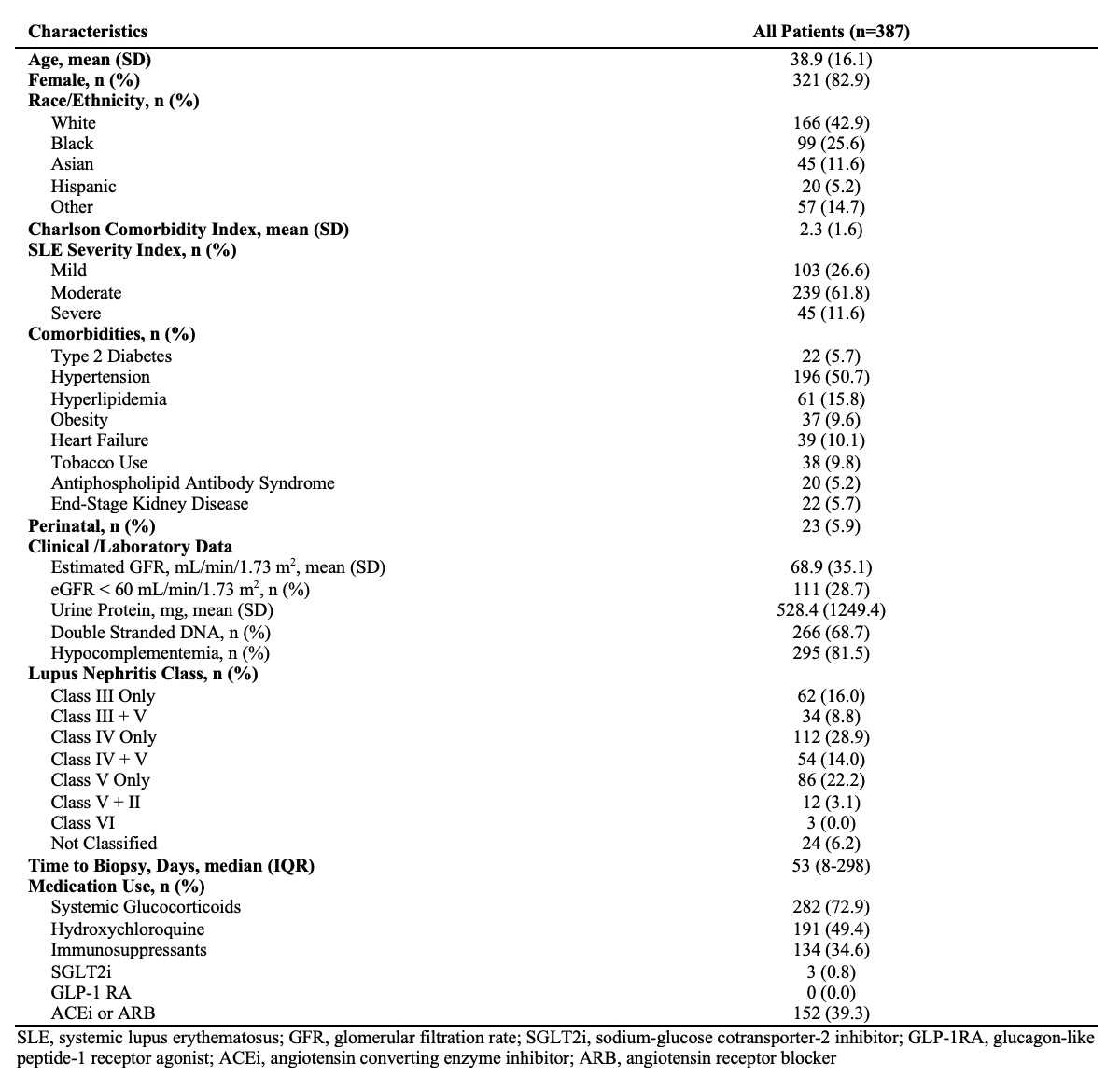 Table 1: Baseline Characteristics of Patients with Newly Diagnosed, Biopsy-Proven Lupus Nephritis
Table 1: Baseline Characteristics of Patients with Newly Diagnosed, Biopsy-Proven Lupus Nephritis
.jpg) Table 2: Risks of Chronic Kidney Disease Stage ≥3 and End-Stage Kidney Disease at 5 Years Among Patients with Newly Diagnosed, Biopsy-Proven Lupus Nephritis
Table 2: Risks of Chronic Kidney Disease Stage ≥3 and End-Stage Kidney Disease at 5 Years Among Patients with Newly Diagnosed, Biopsy-Proven Lupus Nephritis
Disclosures: A. Patel: None; L. Zhang: None; H. Choi: Ani, 2, LG, 2, Shanton, 2, Sobi, 2; A. Jorge: Bristol-Myers Squibb(BMS), 5.
To cite this abstract in AMA style:
Patel A, Zhang L, Choi H, Jorge A. Risk Factors Associated with Chronic Kidney Disease and End-Stage Kidney Disease in Patients with Newly Diagnosed Lupus Nephritis [abstract]. Arthritis Rheumatol. 2025; 77 (suppl 9). https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/risk-factors-associated-with-chronic-kidney-disease-and-end-stage-kidney-disease-in-patients-with-newly-diagnosed-lupus-nephritis/. Accessed .« Back to ACR Convergence 2025
ACR Meeting Abstracts - https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/risk-factors-associated-with-chronic-kidney-disease-and-end-stage-kidney-disease-in-patients-with-newly-diagnosed-lupus-nephritis/
